Rose oil contains 2-phenylethanol.
The structure of 2-phenylethanol is shown below.
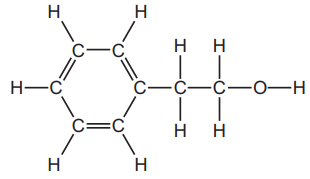
(a) On the structure above, draw a ring around the alcohol functional group.
(b) When heated with an alkali, 2-phenylethanol forms styrene.
Styrene is an unsaturated compound.
Describe a test for an unsaturated compound.
(c) Rose petals contain a variety of different coloured pigments.
(i) She grinds up rose petals with a solvent.
Explain why.
(ii) She then filters the solution through some glass wool.
Suggest why she does not use filter paper.
(d) The student uses the apparatus shown below to identify the different pigments in the mixture.
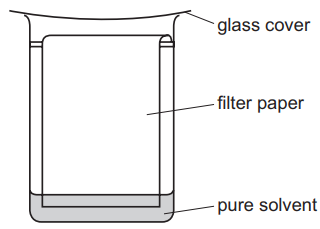
(i) State the name of this method of separating the pigments.
(ii) On the diagram above, draw a spot, ●, to show where the mixture of pigments is placed at the start of the experiment.
(iii) What is the purpose of the glass cover?
(iv) The student also puts four spots of pure pigments, A, B, C and D, onto the filter paper. The diagram below shows the results of her experiment.
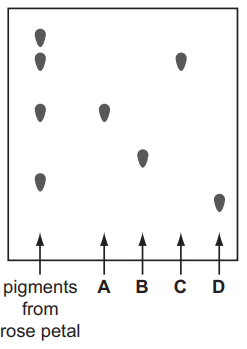
Which of the pigments, A, B, C and D, are present in the rose petals?
(e) The solvent used in the experiment is ethanol.
Draw the structure of a molecule of ethanol showing all atoms and bonds.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) The alcohol functional group is the \(\text{-OH}\) group. It should be ringed in the structure.
(b) Test for unsaturation:
Test: Add bromine water.
Result: Bromine water decolorizes (turns from orange to colorless) if the compound is unsaturated.
(c) (i) Grinding rose petals with a solvent helps break the cell walls and dissolve the pigments, extracting them from the petals.
(ii) Glass wool is used instead of filter paper because pigments may adsorb (stick) to filter paper, reducing yield.
(d) (i) The method is chromatography.
(ii) The spot (●) should be placed on the baseline (starting line) above the solvent level.
(iii) The glass cover prevents solvent evaporation, maintaining a saturated atmosphere.
(iv) Pigments A and C are present in the rose petals (they match the spots in the mixture).
(e) The structure of ethanol (\(\text{C}_2\text{H}_5\text{OH}\)) is:
(Shows \(\text{H}_3\text{C}-\text{CH}_2-\text{OH}\) with all bonds and atoms labeled.)
Titanium is extracted from an ore called rutile. Rutile is an impure form of titanium(IV) oxide, TiO2.
(a) Rutile is mixed with coke and heated in a furnace through which chlorine gas is passed. The product is gaseous titanium(IV) chloride, TiCl4.
TiO2(s) + 2C(s) + 2Cl2(g) → TiCl4(g) + 2CO(g)
The gaseous titanium(IV) chloride produced is condensed into the liquid state. The titanium(IV) chloride is then separated from liquid impurities.
(i) Suggest the name of the process by which liquid titanium(IV) chloride could be separated from the liquid impurities.
(ii) Carbon monoxide, CO(g), is also produced in the reaction.
Why should carbon monoxide not be released into the atmosphere?
(b) Calculate the volume of chlorine gas, Cl2(g), at room temperature and pressure, that reacts completely with 400g of TiO2(s) using the following steps.
TiO2(s) + 2Cl2(g) + 2C(s) → TiCl4(g) + 2CO(g)
- Calculate the relative formula mass, Mr, of TiO2.
Mr of TiO2 =
- Calculate the number of moles in 400g of TiO2.
mol
- Determine the number of moles of Cl2 that react with 400g of TiO2.
moles of Cl2 = mol
- Calculate the volume of Cl2 that reacts with 400g of TiO2.
volume of Cl2 = dm3
(c) Titanium(IV) chloride, TiCl4, is heated with an excess of magnesium, in an atmosphere of argon.
(i) Balance the chemical equation for the reaction.
TiCl4 + ….. Mg → Ti + ….. MgCl2
(ii) Titanium(IV) chloride can be reacted with sodium instead of magnesium.
The reaction between titanium(IV) chloride and sodium is similar to the reaction between titanium(IV) chloride and magnesium.
Write a chemical equation for the reaction between titanium(IV) chloride and sodium.
(iii) Suggest why the reaction between titanium(IV) chloride and magnesium is done in an atmosphere of argon and not in air.
(d) After titanium(IV) chloride is heated with magnesium, the unreacted magnesium is removed by adding an excess of dilute hydrochloric acid to the mixture.
The dilute hydrochloric acid also dissolves the magnesium chloride.
The dilute hydrochloric acid does not react with the titanium or dissolve it.
(i) Give two observations and write a chemical equation for the reaction that occurs when dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium.
(ii) Name the process that is used to separate the titanium from the mixture after all the magnesium has been removed.
(iii) Titanium does not react with the dilute hydrochloric acid or dissolve in it.
Suggest why titanium does not react with dilute hydrochloric acid.
(e) Magnesium cannot be produced by electrolysis of aqueous magnesium chloride using inert electrodes.
(i) Name the product formed at the negative electrode (cathode) during the electrolysis of aqueous magnesium chloride.
(ii) Suggest how magnesium can be produced from magnesium chloride by electrolysis.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) The process is fractional distillation, which separates liquids based on their boiling points.
(a)(ii) Carbon monoxide is toxic (binds irreversibly to hemoglobin, causing oxygen deprivation).
(b) Calculations:
- Mr of TiO2: 48 (Ti) + 2 × 16 (O) = 80.
- Moles of TiO2: 400g ÷ 80 g/mol = 5 mol.
- Moles of Cl2: 5 mol TiO2 × 2 = 10 mol (from stoichiometry).
- Volume of Cl2: 10 mol × 24 dm3/mol = 240 dm3 (at RTP).
(c)(i) Balanced equation: TiCl4 + 2Mg → Ti + 2MgCl2.
(c)(ii) With sodium: TiCl4 + 4Na → Ti + 4NaCl (sodium replaces magnesium 1:2).
(c)(iii) Argon is inert; magnesium would react with oxygen/nitrogen in air, forming oxides/nitrides.
(d)(i) Observations:
- Effervescence (hydrogen gas evolution).
- Magnesium dissolves (forms MgCl2 solution).
Equation: Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2.
(d)(ii) Separation method: Filtration (titanium is insoluble).
(d)(iii) Titanium is below hydrogen in the reactivity series (less reactive than H2).
(e)(i) Cathode product: Hydrogen (H2; water is reduced instead of Mg2+).
(e)(ii) Electrolyze molten MgCl2 (no water competes for reduction).
