This question is about sodium and compounds of sodium.
(a) (i) Describe the bonding in a metallic element such as sodium.
You may include a diagram as part of your answer.
(ii) Describe how solid sodium conducts electricity.
(b) Some properties of sodium chloride are shown:
- melting point of 801°C
- non-conductor of electricity when solid
- conductor of electricity when molten
- soluble in water.
(i) Name the type of bonding in sodium chloride.
(ii) Explain why sodium chloride conducts electricity when molten.
(c) A student determines the concentration of a solution of dilute sulfuric acid, H2SO4, by titration with aqueous sodium hydroxide, NaOH.
step 1 – 25.0cm3 of 0.200mol/dm3 NaOH is transferred into a conical flask.
step 2 – Three drops of methyl orange indicator are added to the conical flask.
step 3 – A burette is filled with H2SO4.
step 4 – The acid in the burette is added to the conical flask until the indicator changes colour. The volume of acid is recorded. This process is known as titration.
step 5 – The titration is repeated several times until a suitable number of results is obtained.
(i) Name the piece of apparatus used to measure exactly 25.0cm3 of 0.200mol/dm3 NaOH in step 1.
(ii) State the colour change of the methyl orange indicator in step 4.
(iii) State how the student decides that a suitable number of results have been obtained.
(iv) 20.0cm3 of H2SO4 reacts with 25.0cm3 of 0.200mol/dm3 NaOH.
The equation for the reaction is shown.
H2SO4 + 2NaOH → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
Calculate the concentration of H2SO4 using the following steps.
- Calculate the number of moles in 25.0cm3 of 0.200mol/dm3 NaOH.
- Determine the number of moles of H2SO4 that react with the NaOH.
- Calculate the concentration of H2SO4.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) (i)
Metallic bonding in sodium consists of a lattice of positive sodium ions (Na+) surrounded by a “sea” of delocalized electrons. These electrons are free to move, which gives metals their characteristic properties like conductivity and malleability. The electrostatic attraction between the positive ions and the delocalized electrons holds the structure together.
(a) (ii)
Solid sodium conducts electricity due to the movement of its delocalized electrons, which can carry charge through the metal lattice.
(b) (i)
Sodium chloride has ionic bonding, formed by the transfer of electrons from sodium to chlorine, resulting in Na+ and Cl– ions.
(b) (ii)
Molten sodium chloride conducts electricity because the ions (Na+ and Cl–) are free to move and carry charge, unlike in the solid state where ions are fixed in position.
(c) (i)
A pipette is used to measure exactly 25.0 cm3 of NaOH solution.
(c) (ii)
Methyl orange changes from yellow to orange at the endpoint of the titration.
(c) (iii)
The student decides a suitable number of results have been obtained when at least two titrations give volumes within 0.2 cm3 of each other (concordant results).
(c) (iv)
Step 1: Moles of NaOH = (25.0/1000) × 0.200 = 0.005 mol
Step 2: From the equation, 2 moles of NaOH react with 1 mole of H2SO4. Thus, moles of H2SO4 = 0.005/2 = 0.0025 mol.
Step 3: Concentration of H2SO4 = (0.0025)/(20.0/1000) = 0.125 mol/dm3.
(a) Propanol is a solvent.
Sugar is soluble in propanol. Salt (sodium chloride) is insoluble in propanol.
A student wants to separate a mixture of solid salt and solid sugar.
(i) Describe how she could separate the salt from the sugar.
You may draw a labelled diagram to help you answer this question.
(ii) Describe how the student could obtain solid sodium chloride from a solution of sodium chloride in water.
(b) The diagram shows the structure of sodium chloride.
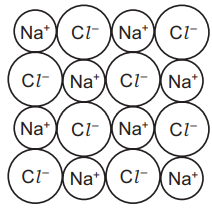
(i) Deduce the simplest formula for sodium chloride.
(ii) What type of bonding is present in sodium chloride?
Put a ring around the correct answer.
covalent ionic metallic weak
(c) The diagram shows the apparatus used to electrolyze a concentrated aqueous solution of sodium chloride.

(i) Which letter on the diagram, A, B, C or D, represents the electrolyte?
(ii) Name the product formed at
the positive electrode,
the negative electrode.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) (i) Ans: Filter sugar solution from salt
1. Dissolve the mixture in propanol (sugar dissolves, salt remains).
2. Filter the mixture—salt stays on the filter paper.
3. Evaporate propanol from the filtrate to recover sugar.
(ii) Ans: Evaporate the water
Heat the solution to evaporate water, leaving solid NaCl behind.
(b) (i) Ans: NaCl
Sodium chloride has a 1:1 ratio of Na+ and Cl− ions.
(ii) Ans: Ionic
NaCl forms an ionic lattice due to the transfer of electrons from Na to Cl.
(c) (i) Ans: D
The electrolyte is the aqueous NaCl solution (D), which conducts electricity.
(ii) Ans: Chlorine (Cl2) at the anode, Hydrogen (H2) at the cathode
Chloride ions (Cl−) are oxidized to Cl2 at the anode (+).
Water is reduced, producing H2 at the cathode (−).
