Ethanoic acid is manufactured by the reaction of methanol with carbon monoxide.
An equilibrium mixture is produced.
\(CH_{3}OH\left ( g \right )+CO\left ( g \right )\rightleftharpoons CH_{3}COOH\left ( g \right )\)
(a) State two characteristics of an equilibrium.
(b) The purpose of the industrial process is to produce a high yield of ethanoic acid at a high rate of reaction.
The manufacture is carried out at a temperature of 300°C.
The forward reaction is exothermic.
Use this information to state why the manufacture is not carried out at temperatures:
- below 300°C
- above 300°C.
(c) Complete the table using only the words increases, decreases or no change.

(d) Suggest which of the following metals is a suitable catalyst for the reaction. Give a reason for your answer.
aluminium calcium cobalt magnesium potassium
(e) Ethanoic acid is a member of the homologous series of carboxylic acids.
State the general formula of this homologous series.
(f) Draw the structure of the carboxylic acid containing three carbon atoms. Show all of the atoms and all of the bonds.
(g) When carboxylic acids react with alcohols, esters are produced.
The formula of ester X is CH3CH2CH2COOCH3.
(i) Name ester X.
(ii) Give the name of the carboxylic acid and the alcohol that react together to produce ester X.
(h) Ester Y has the following composition by mass:
C, 48.65%; H, 8.11%; O, 43.24%.
Calculate the empirical formula of ester Y.
(i) Ester Z has the empirical formula C2H4O and a relative molecular mass of 88.
Determine the molecular formula of ester Z.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) Two characteristics of equilibrium:
1. Rate of forward reaction equals the rate of reverse reaction (dynamic equilibrium).
2. Concentrations of reactants and products remain constant (macroscopic properties are stable).
(b) Temperature rationale:
– Below 300°C: Rate of reaction is too slow (kinetic energy insufficient).
– Above 300°C: Yield decreases (Le Chatelier’s principle favors the endothermic reverse reaction).
(c) Table completion:
– Rate of reaction: Increases (higher temperature = more collisions).
– Yield of ethanoic acid: Decreases (forward reaction is exothermic).
– Time to reach equilibrium: Decreases (faster reaction).
(d) Suitable catalyst: Cobalt.
Reason: Transition metals (like cobalt) are effective catalysts due to their variable oxidation states.
(e) General formula: CnH2n+1COOH.
(f) Structure of propanoic acid:
(Must show all bonds: COOH group and CH3-CH2-COOH).
(g)(i) Ester X: Methyl butanoate.
(ii) Carboxylic acid: Butanoic acid; Alcohol: Methanol.
(h) Empirical formula calculation:
1. Divide % by atomic masses: C (48.65/12 = 4.05), H (8.11/1 = 8.11), O (43.24/16 = 2.70).
2. Divide by smallest (2.70): C (1.5), H (3), O (1).
3. Multiply by 2: C3H6O2.
(i) Molecular formula:
Empirical formula mass = 44 (C2H4O).
Multiplier = 88/44 = 2 → C4H8O2.
Dinitrogen tetroxide, \(N_2O_4\), decomposes into nitrogen dioxide, \(NO_2\). The reaction is reversible.
A gas syringe containing a mixture of dinitrogen tetroxide and nitrogen dioxide gases was sealed and heated. After reaching equilibrium the mixture was a pale brown colour.

(a) State what is meant by the term equilibrium.
(b) The plunger of the gas syringe is pushed in. The temperature does not change. The mixture initially turns darker brown. After a few seconds the mixture turns lighter brown because the equilibrium shifts to the left.
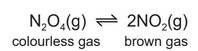
(i) Explain why the mixture initially turns darker brown.
(ii) Explain why the position of equilibrium shifts to the left.
(c) The forward reaction is endothermic.
(i) State what happens to the position of equilibrium when the temperature of the mixture is increased.
(ii) State what happens to the rate of the forward reaction and the rate of the backward reaction when the temperature of the mixture is increased.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) Equilibrium is a dynamic state where:
1. The forward and reverse reaction rates are equal.
2. The concentrations of reactants and products remain constant.
(b) (i) The mixture turns darker brown initially because:
– Pushing the plunger increases pressure, forcing \(NO_2\) molecules closer together (as shown in the gas syringe image).
– This increases the visible concentration of brown \(NO_2\) gas temporarily.
(ii) Equilibrium shifts left (toward colorless \(N_2O_4\)) because:
– The left side has fewer gas molecules (1 mole vs. 2 moles of \(NO_2\), as per the equation image).
– The system reduces pressure by favoring the side with lower gas moles (Le Chatelier’s Principle).
(c) (i) For an endothermic forward reaction (as indicated in the question):
Increasing temperature shifts equilibrium right (toward brown \(NO_2\)) to absorb heat.
(ii) Rate changes with temperature increase:
– Forward rate: Increases (more energy for bond breaking in \(N_2O_4\)).
– Backward rate: Also increases (higher collision frequency), but less than the forward rate initially.
