This question is about zinc and its compounds.
(a) Zinc is extracted from its ore which is mainly zinc sulfide, ZnS.
The steps for this extraction are shown.
step 1 – Zinc sulfide is converted into zinc oxide.
step 2 – The zinc oxide is then reduced to zinc in a furnace. The zinc formed becomes a gas.
step 3 – The zinc gas is cooled to form molten zinc.
(i) Name the ore of zinc, which is mainly zinc sulfide.
(ii) Describe how zinc sulfide is converted into zinc oxide in step 1.
(iii) Name the reducing agent used in step 2.
(iv) Explain why the zinc forms a gas in step 2 inside the furnace.
(v) State the name of the physical change occurring when zinc gas is converted into molten zinc.
(b) Zinc sulfate crystals, ZnSO4•7H2O, are hydrated.
Zinc sulfate crystals are made by reacting zinc carbonate with dilute sulfuric acid.
The equation for the overall process is shown.
ZnCO3 + H2SO4 + 6H2O → ZnSO4•7H2O + CO2
step 1 – Large pieces of solid zinc carbonate are added to dilute sulfuric acid until the zinc carbonate is in excess. This forms aqueous zinc sulfate.
step 2 – The excess zinc carbonate is separated from the aqueous zinc sulfate.
step 3 – The aqueous zinc sulfate is heated until a saturated solution is formed.
step 4 – The saturated solution is allowed to cool and crystallise.
step 5 – The crystals are removed and dried.
(i) In step 1, zinc carbonate is in excess when no more zinc carbonate dissolves. State one other observation that indicates the zinc carbonate is in excess in step 1.
(ii) Name a different substance, other than zinc carbonate, that can be added to dilute sulfuric acid to produce aqueous zinc sulfate in step 1.
(iii) Step 1 is repeated using powdered zinc carbonate instead of large pieces. All other conditions are kept the same. The rate of reaction increases. Give a reason why the rate of reaction increases. Explain your answer in terms of particles.
(iv) Suggest what is observed when the solution is saturated in step 3.
(v) The formula of zinc sulfate crystals is ZnSO4•7H2O. Give the formula of the solid formed if the crystals are heated to dryness in step 3.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) (i) The ore is zinc blende (common name for zinc sulfide ore).
(a) (ii) Zinc sulfide is converted to zinc oxide by roasting in air (heating with oxygen).
(a) (iii) The reducing agent is carbon (C) or carbon monoxide (CO).
(a) (iv) Zinc forms a gas because the furnace temperature (≈1200°C) exceeds zinc’s boiling point (907°C).
(a) (v) The physical change is condensation (gas → liquid).
(b) (i) Excess zinc carbonate is indicated by no more bubbles/effervescence (CO₂ stops forming).
(b) (ii) Alternative substances: zinc (Zn), zinc oxide (ZnO), or zinc hydroxide (Zn(OH)₂).
(b) (iii) Powdered zinc carbonate increases the rate because:
1. Larger surface area exposes more particles to react.
2. More frequent collisions between particles and acid molecules.
(b) (iv) Saturation is observed when crystals begin to form on a glass rod or the container.
(b) (v) Heating to dryness yields anhydrous ZnSO4 (water of crystallization is removed).
Zinc can be extracted from zinc sulfide ore in three steps.
(a) In the first step, zinc sulfide is heated in air to produce zinc oxide.
(i) Complete the symbol equation for this reaction.
2ZnS + __ O2 → 2ZnO + __ SO2
(ii) The product sulfur dioxide, SO2, is harmful to the environment.
Explain why it is harmful to the environment and state one effect it has on buildings.
(b) In the second step, zinc oxide reacts with sulfuric acid to form zinc sulfate.
zinc oxide + sulfuric acid → zinc sulfate + water
Zinc sulfate is soluble in water.
Some insoluble impurities in the zinc oxide do not react with the sulfuric acid.
Suggest how these insoluble impurities are removed from the zinc sulfate solution.
(c) In the third step, zinc is extracted from zinc sulfate by electrolysis using the cell shown below.
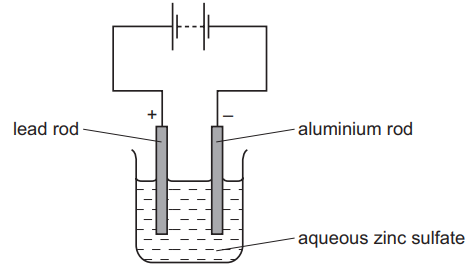
(i) Which word best describes the aluminum rod?
Put a ring around the correct answer.
anion anode cathode cation electrolyte product
(ii) Suggest which statement about this electrolysis is completely correct.
Tick one box.

▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) (i) The balanced equation is: 2ZnS + 3O2 → 2ZnO + 2SO2.
Explanation: For every 2 moles of ZnS, 3 moles of O2 are needed to produce 2 moles each of ZnO and SO2.
(a) (ii) SO2 is harmful because:
– It dissolves in rainwater to form acid rain (H2SO3), which damages ecosystems.
– It erodes limestone buildings (reacts with calcium carbonate) and corrodes metal structures.
(b) Insoluble impurities are removed by filtration.
Explanation: The zinc sulfate solution passes through a filter, leaving behind solid impurities.
(c) (i) The aluminum rod is the cathode (negative electrode where Zn2+ ions gain electrons to form zinc metal).
(c) (ii) Correct statement: “Zinc forms at the negative electrode and oxygen forms at the positive electrode.”
Explanation:
– At the cathode (negative electrode): Zn2+ + 2e− → Zn.
– At the anode (positive electrode): 2H2O → O2 + 4H+ + 4e−.
