Question

S is a point on PQ such that PS : SQ = 4 : 5.
Find \(\overrightarrow{OS}\), in terms of a and b, in its simplest form.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Solution
(5/9)a + (4/9)b
PS:SQ = 4:5 means S divides PQ in ratio 4:5
OS = OP + (4/9)PQ = a + (4/9)(b-a)
Simplify: a + (4/9)b – (4/9)a = (5/9)a + (4/9)b
Question
The diagram shows a trapezium OPQR.
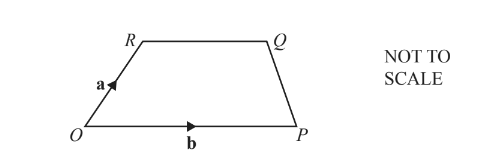
O is the origin, \(\overrightarrow{OR}=a\) and \(\overrightarrow{OP}=b\).
\(\left | \overrightarrow{RQ} \right |=\frac{3}{5}|\overrightarrow{OP}|\)
(a) Find \(\overrightarrow{PQ}\) in terms of a and b in its simplest form.
(b) When PQ and OR are extended, they intersect at W. Find the position vector of W.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) \(a – \frac{2}{5}b\) (or equivalent simplified form)
(b) \(\frac{5}{2}a\) (or equivalent)
Explanation:
Part (a):
- Given \(|\overrightarrow{RQ}| = \frac{3}{5}|\overrightarrow{OP}| = \frac{3}{5}|b|\)
- Since OPQR is a trapezium, RQ is parallel to OP, so \(\overrightarrow{RQ} = \frac{3}{5}b\)
- Using vector addition: \(\overrightarrow{PQ} = \overrightarrow{PR} + \overrightarrow{RQ} = (a – b) + \frac{3}{5}b = a – \frac{2}{5}b\)
Part (b):
- When extended, PW and OW are scalar multiples: \(\overrightarrow{OW} = k\overrightarrow{OR} = ka\)
- Also \(\overrightarrow{PW} = t\overrightarrow{PQ} = t(a – \frac{2}{5}b)\)
- Equating expressions: \(ka = b + t(a – \frac{2}{5}b)\)
- Solving gives \(t = \frac{5}{2}\), so position vector of W is \(\frac{5}{2}a\)
