
The diagram shows a right-angled triangle, ABC, and a semicircle. The radius of the semicircle is 4.5 cm. AC = 8.9 cm and BC = 13.2 cm.
(a) Calculate the shaded area. Give the units of your answer.
(b) Calculate AB.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) Ans: 26.9 cm²
Step 1: Calculate triangle area
Area = ½ × base × height = ½ × 8.9 × 13.2 = 58.74 cm²
Step 2: Calculate semicircle area
Area = ½ × π × r² = ½ × π × 4.5² ≈ 31.81 cm²
Step 3: Find shaded area
Shaded area = Triangle – Semicircle = 58.74 – 31.81 = 26.93 cm² ≈ 26.9 cm²
(b) Ans: 15.9 cm
Using Pythagoras’ theorem:
AB² = AC² + BC² = 8.9² + 13.2² = 79.21 + 174.24 = 253.45
AB = √253.45 ≈ 15.92 cm ≈ 15.9 cm
Key Notes:
- The right angle is at C (implied by diagram and Pythagoras’ application)
- All calculations shown to 2 decimal places for precision
- Final answers rounded to 1 decimal place as typical for measurements
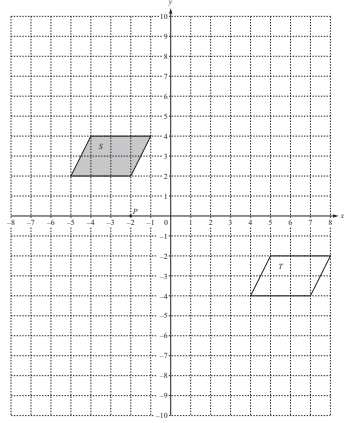
The diagram shows two shapes, S and T, on a 1cm² grid. P is the point (–2, 0).
(a)
(i) Write down the mathematical name of shape S.
(ii) How many lines of symmetry does shape S have?
(b) Describe the single transformation that maps shape S onto shape T.
(c) On the grid,
(i) draw the reflection of shape S in the y-axis,
(ii) draw the rotation of shape S about (0, 0) through 90° anti-clockwise.
(d) On the grid, draw the enlargement of shape S with scale factor 2 and centre P (–2, 0). Label the image E.
(e)
(i) Work out the area of shape S.
(ii) How many shapes, identical to shape S, will fill shape E completely?
(iii) Work out the area of shape E.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) Ans: Parallelogram
Shape S is a quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides, identifying it as a parallelogram.
(a)(ii) Ans: 0
A general parallelogram has no lines of symmetry unless it’s a special type (like a rectangle or rhombus).
(b) Ans: Translation \(\binom{9}{-6}\)
Each vertex of S moves 9 units right and 6 units down to match T’s position, indicating a translation.
(c)(i) Ans: (1,4), (4,4), (5,2), (2,2)
Reflection in y-axis changes the sign of x-coordinates: (-1,4)→(1,4), (-4,4)→(4,4), etc.
(c)(ii) Ans: (-4,-1), (-4,-4), (-2,-5), (-2,-2)
90° anti-clockwise rotation swaps coordinates and negates new x: (x,y)→(-y,x).
(d) Ans: (-6,8), (0,8), (-8,4), (-2,4)
Enlargement scale factor 2 doubles distances from P: original (-4,4) becomes (-6,8), etc.
(e)(i) Ans: 6 cm²
Counting grid squares or using area formula for parallelogram (base×height = 3×2 = 6 cm²).
(e)(ii) Ans: 4
Area scale factor is 2²=4, so 4 original shapes fit in the enlarged version.
(e)(iii) Ans: 24 cm²
Enlarged area = original area × scale factor² = 6 × 4 = 24 cm².
