
The diagram shows the positions of three points A, B and C in a field.
(a) Show that BC is 118.1m, correct to 1 decimal place.
(b) Calculate angle ABC.
(c) The bearing of C from A is 147°.
Find the bearing of
(i) A from B,
(ii) B from C.
(d) Mitchell takes 35 seconds to run from A to C.
Calculate his average running speed in kilometres per hour.
(e) Calculate the shortest distance from point B to AC.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) Ans: BC = 118.1 m
Using the cosine rule: \( BC^2 = 80^2 + 115^2 – 2 \times 80 \times 115 \cos 72^\circ \).
Calculate: \( BC^2 = 6400 + 13225 – 18400 \times 0.3090 \).
Simplify: \( BC = \sqrt{13938.4} \approx 118.1 \, \text{m} \).
(b) Ans: Angle ABC = 67.8°
Using the sine rule: \( \frac{\sin ABC}{115} = \frac{\sin 72^\circ}{118.1} \).
Calculate: \( \sin ABC = \frac{115 \sin 72^\circ}{118.1} \approx 0.926 \).
Thus: \( ABC \approx \sin^{-1}(0.926) \approx 67.8^\circ \).
(c)(i) Ans: Bearing of A from B = 255°
Given bearing of C from A is 147°, the angle between AB and north is 180° – 147° = 33°.
Thus, bearing of A from B is \( 180° + 33° + 42° = 255° \).
(c)(ii) Ans: Bearing of B from C = 007.2°
Using angle BCA: \( 180° – 72° – 67.8° \approx 40.2° \).
Bearing of B from C is \( 180° – 40.2° – (90° – 42°) \approx 7.2° \).
(d) Ans: Average speed = 11.8 km/h
First, find AC using cosine rule: \( AC^2 = 80^2 + 115^2 – 2 \times 80 \times 115 \cos 42^\circ \).
Calculate: \( AC \approx 115.0 \, \text{m} \).
Speed: \( \frac{115.0 \, \text{m}}{35 \, \text{s}} \times \frac{3600}{1000} \approx 11.8 \, \text{km/h} \).
(e) Ans: Shortest distance = 76.1 m
Using area formula: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times 80 \times 115 \sin 42^\circ \approx 3079.5 \, \text{m}^2 \).
Shortest distance: \( \frac{2 \times 3079.5}{115.0} \approx 76.1 \, \text{m} \).
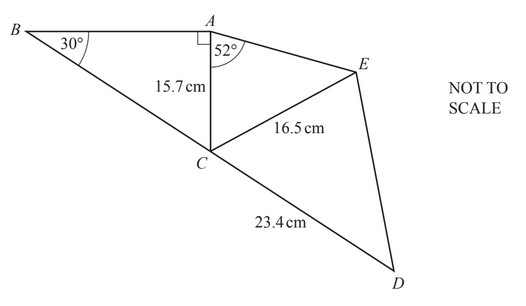
In the diagram, BCD is a straight line and ABDE is a quadrilateral.
Angle BAC = 90°, angle ABC = 30° and angle CAE = 52°.
AC = 15.7 cm, CE = 16.5 cm and CD = 23.4 cm.
(a) Calculate BC.
(b) Use the sine rule to calculate angle AEC.
Show that it rounds to 48.57°, correct to 2 decimal places.
(c) (i) Show that angle ECD = 40.6°, correct to 1 decimal place.
(ii) Calculate DE.
(d) Calculate the area of the quadrilateral ABDE.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) Ans: 31.4 cm
In right-angled triangle ABC, \(\cos 30° = \frac{AC}{BC}\).
Thus, \(BC = \frac{AC}{\cos 30°} = \frac{15.7}{0.866} \approx 31.4 \, \text{cm}\).
(b) Ans: 48.57°
Using the sine rule in triangle ACE:
\(\frac{AC}{\sin E} = \frac{CE}{\sin 52°}\).
\(\sin E = \frac{15.7 \times \sin 52°}{16.5} \approx 0.7509 \Rightarrow E \approx 48.57°\).
(c)(i) Ans: 40.6°
Angle ACE = \(180° – 52° – 48.57° = 79.43°\).
Since BCD is a straight line, angle ECD = \(180° – 79.43° – 60° = 40.57° \approx 40.6°\).
(c)(ii) Ans: 15.3 cm
Using the sine rule in triangle CDE:
\(\frac{DE}{\sin 40.57°} = \frac{CD}{\sin E}\).
\(DE = \frac{23.4 \times \sin 40.57°}{\sin (180° – 40.57° – 60°)} \approx 15.3 \, \text{cm}\).
(d) Ans: 466 cm²
Area of quadrilateral ABDE = Area of ABC + Area of ACE – Area of CDE.
Calculate each area using \(\frac{1}{2}ab \sin C\) and sum appropriately to get \(\approx 466 \, \text{cm}^2\).
