$(\mathbf{a})$
$C=\frac{1}{4}xy^2$
$(\mathbf{i})$ Find $C$ when $x=5$ and $y=8.$
$(\mathbf{ii})$ Find the positive value of $y$ when $C=15$ and $x=2.4.$
$(\mathbf{b})$ Write as a single fraction in its simplest form.
$\frac{4}{x-1}-\frac{3}{2x+5}$
$(\mathbf{c})$ Expand and simplify
$(2x+3)(4-x)^2$
$(\mathbf{d})$ Simplify $\left(\frac{y^8}{16x^{16}}\right)^{-\frac{3}{4}}$
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) Ans: 80
Substitute \( x = 5 \) and \( y = 8 \) into \( C = \frac{1}{4}xy^2 \):
\( C = \frac{1}{4} \times 5 \times 64 = 80 \).
(a)(ii) Ans: 5
Substitute \( C = 15 \) and \( x = 2.4 \) into \( C = \frac{1}{4}xy^2 \):
\( 15 = \frac{1}{4} \times 2.4 \times y^2 \implies y^2 = 25 \implies y = 5 \).
(b) Ans: \(\frac{5x + 23}{(x-1)(2x+5)}\)
Combine the fractions using a common denominator:
\(\frac{4(2x+5) – 3(x-1)}{(x-1)(2x+5)} = \frac{5x + 23}{(x-1)(2x+5)}\).
(c) Ans: \(2x^3 – 13x^2 + 8x + 48\)
First expand \((4-x)^2 = 16 – 8x + x^2\), then multiply by \((2x+3)\):
\(2x^3 – 16x^2 + 32x + 3x^2 – 24x + 48 = 2x^3 – 13x^2 + 8x + 48\).
(d) Ans: \(\frac{8x^{12}}{y^6}\)
Apply exponent rules:
\(\left(\frac{y^8}{16x^{16}}\right)^{-\frac{3}{4}} = \frac{8x^{12}}{y^6}\).
(a) Solve the following equations.
(i) \(\frac{5}{w} = \frac{3}{w+1}\)
(ii) \((y+1)^2 = 4\)
(iii) \(\frac{x+1}{3} – \frac{x-2}{5} = 2\)
(b)(i) Factorise \(u^2 – 9u – 10\).
(ii) Solve the equation \(u^2 – 9u – 10 = 0\).
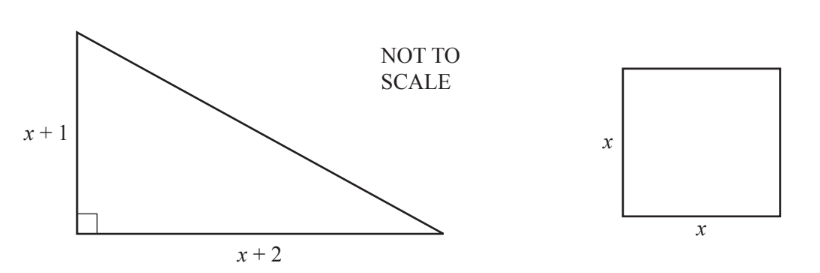
The area of the triangle is equal to the area of the square. All lengths are in centimetres.
(i) Show that \(x^2 – 3x – 2 = 0\).
(ii) Solve the equation \(x^2 – 3x – 2 = 0\), giving your answers correct to 2 decimal places. Show all your working.
(iii) Calculate the area of one of the shapes.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
(i) Ans: \(w = -2.5\)
Cross-multiply: \(5(w+1) = 3w \implies 5w + 5 = 3w \implies 2w = -5 \implies w = -2.5\).
(ii) Ans: \(y = -3\) or \(y = 1\)
Take square roots: \(y+1 = \pm 2 \implies y = -3\) or \(y = 1\).
(iii) Ans: \(x = 9.5\)
Multiply by 15 (LCM of 3 and 5): \(5(x+1) – 3(x-2) = 30 \implies 5x + 5 – 3x + 6 = 30 \implies 2x = 19 \implies x = 9.5\).
(b)
(i) Ans: \((u – 10)(u + 1)\)
Find two numbers that multiply to \(-10\) and add to \(-9\): \(-10\) and \(+1\).
(ii) Ans: \(u = -1\) or \(u = 10\)
Set each factor to zero: \(u – 10 = 0 \implies u = 10\) and \(u + 1 = 0 \implies u = -1\).
(c)
(i) Show \(x^2 – 3x – 2 = 0\)
Area of triangle = \(\frac{(x+1)(x+2)}{2}\), area of square = \(x^2\). Set equal: \(\frac{(x+1)(x+2)}{2} = x^2\). Expand and simplify to get \(x^2 – 3x – 2 = 0\).
(ii) Ans: \(x \approx -0.56\) or \(x \approx 3.56\)
Use quadratic formula: \(x = \frac{3 \pm \sqrt{9 + 8}}{2} = \frac{3 \pm \sqrt{17}}{2}\).
(iii) Ans: 12.7 cm²
Using \(x \approx 3.56\), area of square = \((3.56)^2 \approx 12.67\) cm².
