Question
(a) Equal volumes of steel, oil and hydrogen are heated from 20 °C to 60 °C. Their volumes increase by thermal expansion.
State which of these substances has the greatest increase in volume.
(b)Fig. 7.1 shows a liquid-in-glass thermometer.
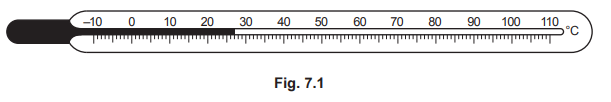
(i) State the temperature reading on the thermometer
(ii) State the temperature range of the thermometer.
(iii) State the values of the fixed points of the Celsius scale of temperature.
(c) The liquid-in-glass thermometer uses the thermal expansion of mercury.
State and explain one other application or consequence of thermal expansion.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) hydrogen (gas)
(b)
(i) 27 (°C)
(ii) –10 (°C) to 110 (°C)
(iii) 0 (°C) AND 100 (°C)
(c) use / consequence of thermal expansion identified
description of effect
explanation of effect
Question
Fig. 4.1 shows a balloon near a window on a warm sunny day.
Fig. 4.2 shows how the volume of the balloon changes throughout the day.
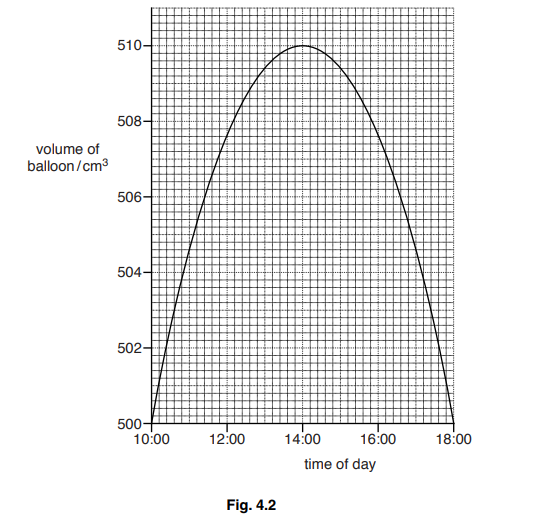
(a) Describe how the volume changes throughout the day.
(b )Explain, in terms of the gas molecules inside the balloon, why the volume changes in this way between 10:00 and 14:00.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) volume of balloon increases (until 14:00) then decreases again
(b) any three from:
• temperature (in room/ balloon) increases
• gas molecules move faster/ have more energy OR collisions more energetic when heated
• more frequent/ harder collisions
• collisions result in greater force on balloon (surface)/ gas pressure increases
