Question
Fig. 7.1 shows a transverse wave.
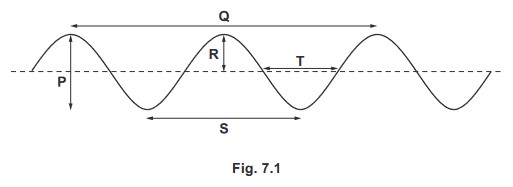
(a) Give the label letter P, Q, R, S or T for the arrow which represents:
1. the amplitude of the wave .
2. the wavelength of the wave.
(b) A student stands next to a pond and observes water waves on its surface. She counts 12
complete waves passing a point in the pond in a time of 8.0 s.
Calculate the frequency of the water waves.
frequency = ……………………………………………. Hz
(c) Fig. 7.1 shows a transverse wave. Describe the difference between transverse and
longitudinal waves.
You may draw a labelled diagram.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) 1 (amplitude of wave = arrow) R
2 ( wavelength of wave = arrow) S
(b) (frequency =) number of (complete) waves per second
(frequency =) 12 ÷ 8
1.5 (Hz)
(c) vibration(s) OR oscillation(s)
in transverse waves is / are perpendicular / at right angles to the direction of energy transfer / wave travel
in longitudinal waves is / are in same direction OR parallel to the direction of energy transfer / wave travel
Quesiton
Fig. 8.1 represents a travelling wave at an instant in time.
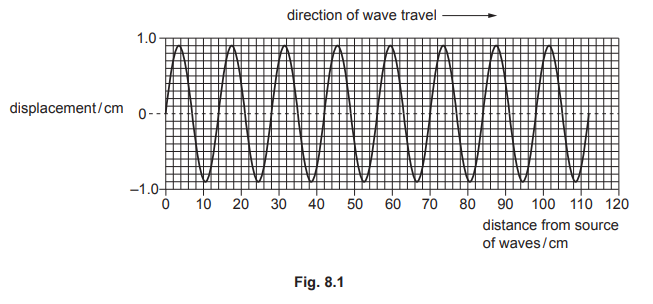
(a) (i) Determine the amplitude of the wave.
amplitude = ………………………………………….. cm
(ii) Determine the wavelength of the wave.
wavelength = ………………………………………….. cm
(iii) It takes 2.0 s for a source to emit the wave shown in Fig. 8.1.
Calculate the frequency of the wave.
frequency = …………………………………………… Hz
(b) Fig. 8.2 shows the main regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
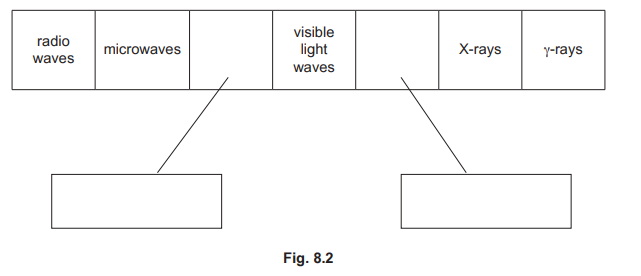
(i) Two of the regions are not labelled.
Add the correct label to each of the unlabelled regions by writing in each box.
(ii) Describe one use of γ-rays.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a)
(i) (amplitude =) 0.9 (cm)
(ii) (wavelength =) 112 ÷ 8
(wavelength =) 14 (cm)
(iii) (frequency =) 8 ÷ 2
(frequency =) (Hz)
(b)
(i) bottom left box labelled infrared
bottom right box labelled ultraviolet
(ii) treating cancer / identifying cancer / gamma ray photography / sterilise medical equipment
