Question
(a) State the name of the reflection of a sound wave or ultrasound wave
(b) Fig. 5.1 shows an ultrasound wave being used to scan an internal organ of a human body.
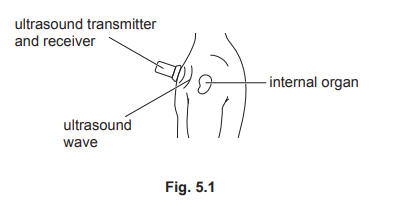
The ultrasound wave has a frequency of 2.0 MHz and passes through human tissue at a speed of 1500 m / s.
Calculate the wavelength of the ultrasound wave in human tissue.
wavelength =
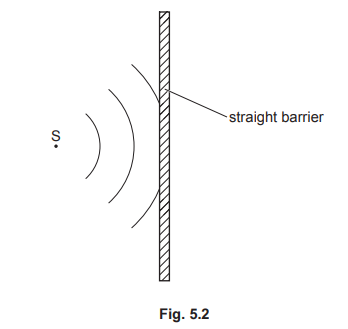
(c) Fig. 5.2 shows crests of a wave from a point source S approaching a straight barrier.
![]()
(i) On Fig. 5.2, indicate and label one wavelength.
(ii) On Fig. 5.2, draw three crests of the wave reflected from the barrier.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) echo (b) (λ=) 7.5 × \(10^{-4}\) m
(λ=) v / f OR v = fλ in any form
(λ=) 1.5 × \(10^3\) / 2 × \(10^6\)
(c)(i),(ii) labelled wavelength of incident wave
3 part circles to the left of the barrier and centred to right of the barrier
wavelengths of reflected and incident waves same
Question
(a) A periscope is an optical instrument containing two mirrors in a long tube.
Fig. 6.1 shows the path of a ray of light through a periscope, without the tube.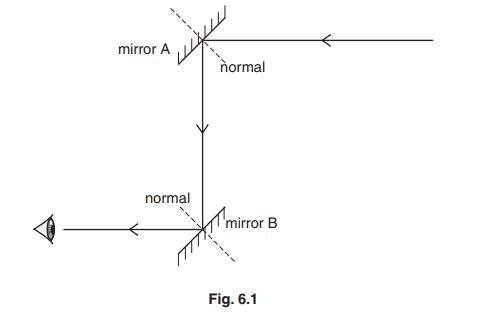
(i) On Fig. 6.1,
- use the letter i to indicate clearly the angle of incidence of the ray striking mirror A,
- use the letter r to indicate clearly the angle of reflection of the ray leaving mirror A.
(ii) Write down the equation that links i and r.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(iii) Suggest a use for the periscope.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(iv) State what happens if mirror B is rotated through a small angle.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
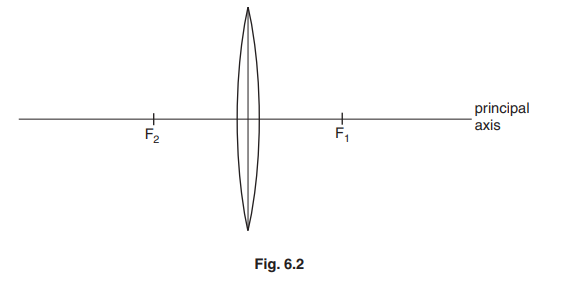
(b) Fig. 6.2 shows a converging lens. The lens has one principal focus at \(F_1\) and the other principal focus at \(F_2\).
Use your ruler to help you answer this question.
(i) On Fig. 6.2, clearly mark two distances that are each the focal length of the lens.
(ii) On Fig. 6.2, draw a ray on the left side of the lens, which strikes the lens, above and parallel to the principal axis. Label this ray: ray 1.
Continue this ray to show its path through the lens and at least 6 cm to the right of the lens.
(iii) On Fig. 6.2, draw a ray that emerges from the lens, below and parallel to the principal axis. Label this ray: ray 2.
Show clearly the path of this ray before it reached the lens.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) i and r both clearly correct
(ii) i = r
(iii) seeing over/around an obstacle
(iv) image/ray moves/misses eye OR viewer can no longer see image/ray /anything OR viewer sees inside of tube OR angle of incidence/reflection changes
(b) (i) 2 focal lengths indicated
(ii) ray parallel to axis AND emergent ray goes through F1
refraction shown at centre line OR at each surface
(iii) incident ray through principal focus AND emergent ray parallel to axis
