Question
(a) The lamp of a car headlight is rated at 12 V, 50 W.
Calculate the current in the lamp when operating normally.
current =……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b) A car is driven at night.
In a journey, the total charge that passes through the 12 V battery is 270 kC.
(i) Calculate the electrical energy transferred.
energy = ………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(ii) The fuel used by the car provides 3.6 × \(10^4\) J / \(cm^3\).
Calculate the volume of fuel used to provide the energy calculated in (b)(i).
volume =…………………………………………………………………………………….
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) P = IV
OR (I =) 50 / 12
4.2
(b)(i) (E =) QV
(E =) 270 × \(10^3\) × 12
3.2 × \(10^6\) J / 3200 kJ
(ii) Volume of fuel used = 3.2 × \(10^6\) / 3.6 × \(10^4\)
89 \(cm^3\)
OR 90 \(cm^3\) if 3.24 × \(10^6\) used
Question
(a) Fig. 6.1 shows crests of a water wave moving from left to right in a harbour.
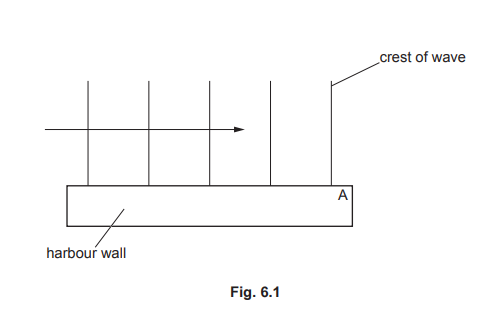
(i) On Fig. 6.1, draw three more crests to the right of point A.
(ii) State the name of the wave process that occurs as the wave passes point A.
(b) Fig. 6.2 shows the crests of another wave moving from left to right in a different part of the harbour. This wave moves from deep water to shallow water.
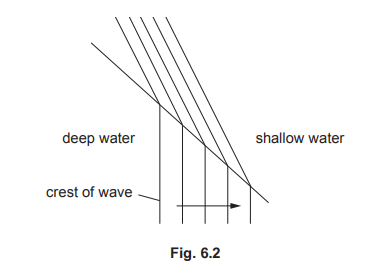
(i) On Fig. 6.2, draw an arrow to show the direction of movement of the wave after it haspassed into the shallow water.
(ii) State the name of the process that occurs as the wave passes into the shallow water.
(iii) Complete Table 6.1 to state whether each of the properties of the wave increases,decreases or stays the same as the wave passes into the shallow water. Table 6.1
property | effect |
wavelength | |
frequency | |
speed |
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) 3 straight crests, to the right of A parallel to incident crests AND same λ by eye
curving round correct way below A
(ii) diffraction
(b) (i) correct arrow perpendicular to wave fronts
(ii) refraction
(iii) wavelength – decreases
frequency – stays same
speed of wave – decreases
