Question
The speed of sound in air is 340 m / s.
(a) Calculate the range of wavelengths for sounds that are audible by a healthy human ear.
wavelengths range from …………………………… to………………………………
(b) Sound waves are longitudinal waves.
Describe how a longitudinal wave differs from a transverse wave.
(c) Fig. 6.1 shows a band in front of a building.
The drum produces a low frequency sound. Other musical instruments produce a high frequency sound. These sounds are equally loud.
A young man at the side of the building hears the drum but not the high frequency sounds from the other musical instruments.
Explain why this happens.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (λ =) v / f OR 340 / 20 000 OR 340 / 20
0.017 m AND 17 m
(b) (longitudinal wave) vibration direction parallel to propagation / energy travel direction
transverse wave vibration direction perpendicular to propagation / energy travel direction
consists of rarefactions AND compressions
(c) diffraction mentioned
wavelength of sound from drum / low frequency sound greater (than wavelength of high frequency sound)
more diffraction of sound from drum OR less diffraction of high frequency sound
Question
A loudspeaker produces a sound wave of constant frequency.
(a) State what is meant by frequency.
(b) The sound wave travels in air towards a barrier with a small gap at its centre. Fig. 7.1
represents the compressions of the wave travelling towards the barrier.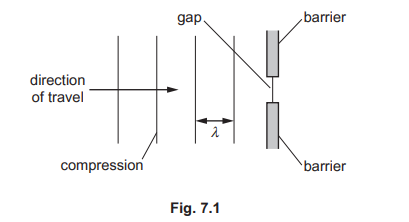
i. State what is meant by a compression.
ii. The width of the gap is smaller than the wavelength λ of the wave.
On Fig. 7.1, draw the pattern of the compressions after the sound wave has passed through the gap.
iii. The barrier is adjusted so that the gap becomes wider.
Describe how this affects the pattern of the compressions after the sound wave has passed through the gap.
(c) The frequency of the sound wave is 6800 Hz. The speed of sound in air is 340 m / s.
(i) Calculate the wavelength of the sound wave in air.
wavelength =
(ii) State a typical value for the speed of sound in a liquid.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) Number of wavefronts (generated/produced/passing a point) in 1 sec/per sec/in unit time
(b)(i) (Part of wave where) pressure/density is higher
OR molecules are closer together
(b)(ii) At least 3 wavefronts shown as part semi-circles
Same separation between wavefronts drawn by candidate
as for incident wavefronts
(b)(iii) Less spreading out OR less diffraction
(c)(i) (λ =) v / f OR 340 / 6800
0.050 m
(c)(ii) In range 900 – 2000 m / s
