Question
Fig. 7.1 shows a circuit including a 12V battery and two identical lamps.
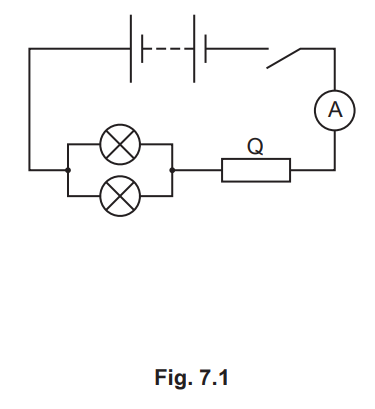
(a) The 12V battery consists of cells connected in series. Each cell in the battery has an electromotive force (e.m.f.) of 1.5V.
Determine how many cells are in the battery.
number of cells = [1]
(b) (i) When the switch is closed, the ammeter reading is 2.4A.
Calculate the total resistance of the circuit.
resistance = [2]
(ii) Each lamp has a resistance of 3.0Ω.
Calculate the resistance of Q.
resistance of Q = [2]
(c) (i) On Fig. 7.1, draw the symbol for a voltmeter that measures the potential difference (p.d.) across the two lamps. [1]
(ii) Calculate the power supplied to one lamp.
power = [3] [Total: 9]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) 8 (cells)
(b)(i) (12 / 2.4 =) 5.0 Ω
R = V / I in any form
(b)(ii) (Resistance of Q = 5–1.5) = 3.5 Ω
1 / R = 1 / R1 + 1 / R2 OR R= R1R2 / (R1+R2)
(c)(i) correct voltmeter symbol connected correctly across both lamps B1
(c)(ii) 4.3 W
(P = ) IV in any form OR 1.2 × 3.6
3.6 V OR 1.2 A
Question
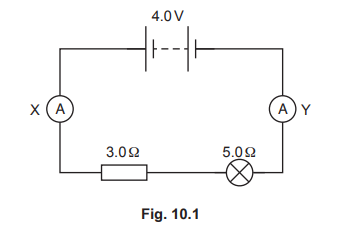
(a) Fig. 10.1 shows a lamp and a resistor connected in a circuit.
-
Determine the combined resistance of the 3.0 Ω resistor and the 5.0 Ω lamp.
combined resistance = ………………………………………………………………………… Ω [1]
-
The reading on ammeter X is 0.50 A. State the reading on ammeter Y.
reading on ammeter Y = ………………………………………………………………………….. A [1]
(b) In another circuit, the 3.0 Ω resistor and the 5.0 Ω lamp are connected in parallel, as shown in Fig. 10.2.
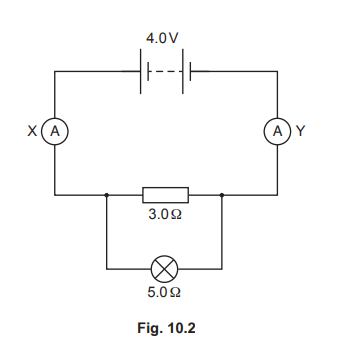
The lamp and resistor have changed from a series to a parallel combination.
State and explain the effect of this change on the current in ammeter X.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [c]
(c) The current in a different lamp is 0.40 A when the potential difference (p.d.) across the lamp is 6.0 V.
Calculate the resistance of the lamp.
resistance of lamp = …………………………………………….. Ω [3] [Total: 8]
Answer/Explanation
Ans: (a)(i) (3.0 + 5.0 =) 8.0 (Ω)
(a)(ii) 0.5(0) (A)
(b) (current/reading) increases B1(because circuit)
resistance decreases (circuit)resistance becomes less than 3(.0)Ω OR less than smallest resistor (value)
OR current/reading more than doubles
(c) V= IR or (R =) V/I 6.0 ÷ 0.4 C1 15 (Ω)
