Question
(a) In a room in a house there are four electric lamps in parallel with each other, controlled by a
single switch.
With all the lamps working, one of the lamp filaments suddenly breaks.
What, if anything happens to the remaining lamps? Explain your answer.
(b) Fig. 10.1 shows the circuit diagram for the lamp in another room. X and Y are 2-way switches.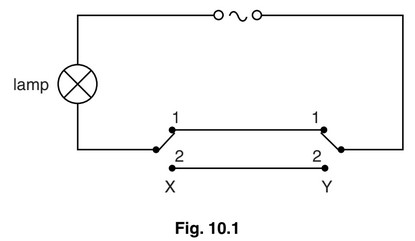
(i) Complete the table, by indicating whether the lamp is on or off for each of the switch
positions.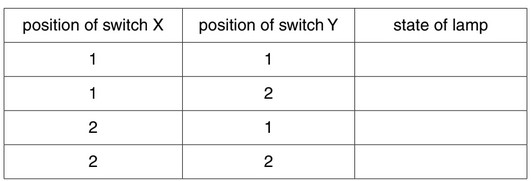
(ii) Explain why this arrangement of switches is useful.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (lamps) stay on/have same brightness as before/ nothing happens
(lamps) still connected to supply /have same voltage as before/ are connected in parallel
(b) (i) line 1: on line 2: off line 3: off line 4: on
deduct one mark for e.e.o.e.
(ii) when either switch is operated, the state of the lamp changes.
Question
(a) Fig. 10.1 shows an electron beam travelling, in a vacuum, towards the space between a
pair of oppositely-charged parallel plates.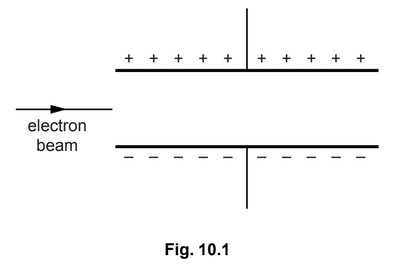
On Fig. 10.1, draw carefully the path of the beam between the plates and in the space
to the right of the plates.
(b) The screen of a cathode-ray oscilloscope (c.r.o.) has a grid of 1 cm squares. Fig. 10.2
shows the trace of an alternating voltage on this screen.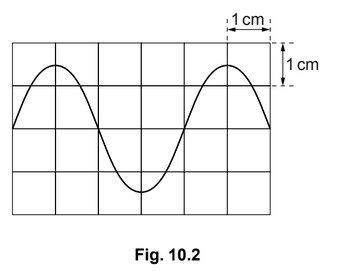
(i) A potential difference of 5.0 V across the Y-plates of the oscilloscope moves the
spot on the screen a vertical distance of 1.0 cm.
Use Fig. 10.2 to determine the maximum p.d. across the Y-plates.
(ii) The spot on the screen takes 1.0 ms to move 1.0 cm horizontally.
From Fig. 10.2, determine the time for 1 cycle of the waveform on the screen, and
use this time to find the frequency of the alternating voltage.
frequency = …………………………………………..
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) between plates path curves upwards continuously
continuation in straight line in space beyond plates
(b) (i) in range 7.0 to 7.5V
(ii) use of the number 4 (as a distance or a time)
f = 1/T OR 1⁄4 OR 1/0.004 but NOT if f = v/λ used
250Hz
