Question:
Fig. 5.1 shows a kitchen tap that supplies instant boiling water.
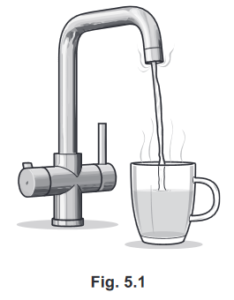
Cold water passes over an electric immersion heater inside the tap.
The boiling point of water is 100 °C.
(a) State what is meant by boiling point.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: temperature
at which liquid becomes a gas or liquid and gas exist together
(b) The immersion heater is powered by the mains at a voltage of 230 V. When the tap is opened, the heater switches on and the current in the heater is 13 A.
(i) Calculate the thermal energy produced by the heater in 60 s.
thermal energy = …………………………………………………
Answer/Explanation
Ans: 1.8 × 10 5 J
(E =) VIt (in any form) or 230 × 13 × 60 or 230 × 13 or 3000
(ii) The specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J / (kg °C). The cold water that enters the tap is at 22 °C.
Calculate the rate at which water at its boiling point emerges from the tap.
rate = …………………………………………………
Answer/Explanation
Ans: 9.1 × 10 –3 kg / s 9.1 × 10 –3 kg / s
(ΔT =) 100 – 22 or 78 or (ΔT =) 100 – 22 or 78
m = E / cΔT (in any form) or 1.8 × 105 / (4200 × 78) or (rate =) P / cΔT (in any form) or m = E / cΔT and E = Pt
1.8 × 10 5 / (4200 × 78 × 60) or or 3000 / (4200 × 78)
5.5 × 10N or 9.1/9.2 × 10N or 230 × 13 / (4200 × 78)
or 9.1 / 9.2 × 10 N
(c) The metal tap is earthed and there is a fuse in the cable that connects the heater to the mains.
1. Explain how the earth wire protects the user.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: if the tap becomes live or if the (live) cable touches the (metal) tap
there is a current to earth / in the earth wire (which blows the fuse)
2. Explain how the fuse protects the circuit.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: the current (in earth wire) is large and fuse melts / blows / stops current / breaks circuit
Question
(a) Describe, in terms of particles and the terminals of the battery, the movement of charge in an
electric circuit.
(b) Fig. 10.1 shows a lightning flash between a cloud and the ground beneath.
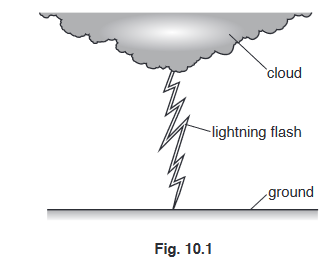
The charge built up on the cloud before the lightning flash is 0.60 C. This charge is completely
transferred to the ground by the lightning flash in 5.0 × \(10^{-5}\) s (0.000050 s).
(i) Calculate the current between the cloud and the ground.
current=
(ii) The potential difference (p.d.) between the cloud and the ground during the lightning flash is
2.5 × \(10^8\) V
Calculate the energy transferred during the lightning flash.
energy=
(iii) Suggest what happens to the energy calculated in (b)(ii).
Answer/Explanation
Answer
(a) Electrons / negative particles
Move (in circuit) from negative (terminal) to positive (terminal of battery)
(b)(i)(I =) Q / t OR 0.60 / 0.000050
12 000 A
(ii) (E=) I V t OR 12 000 × 2.5 × \(10^8\) × 0.000050
1.5 × \(10^8\) J
OR
1.5 × \(10^8\) J
(iii) Converted to any two of: thermal energy / heat, light and sound
