Question
An electromagnet consists of a solenoid X that is made of copper wire. The solenoid contains an iron core.
(a) Explain why:
(i) the structure of copper makes it a suitable material for the wire
(ii) iron is a suitable material for the core of an electromagnet.
(b) Fig. 7.1 shows the electromagnet inside a second solenoid Y.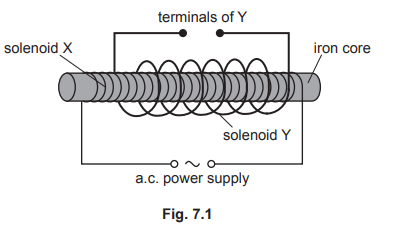
(i) Describe and explain what happens in solenoid Y when solenoid X is connected to an alternating current (a.c.) power supply.
(ii) A switch and a lamp are connected in series with the terminals of solenoid Y. When the switch is closed, the lamp lights up at normal brightness.
Describe and explain what happens to the current in solenoid X when the switch is closed.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) (copper) contains free electrons
good electrical conductor
(a) (ii) magnetic material OR easily magnetised
temporary magnetic material OR easily demagnetised
(b) (i) alternating / changing / varying magnetic field (produced by X)
(electromagnetic) induction in Y
(alternating) electromotive force (e.m.f.) between terminals of Y / in Y
(b) (ii) current in X increases
to supply the power used in Y / the lamp
Question
(a) Fig. 10.1 is a simplified top view of a flat coil. There is an alternating current (a.c.) in the coil.
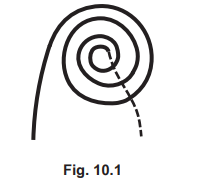
Describe the magnetic effect of this alternating current.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) Fig. 10.2 shows a pan placed above the coil. The base of the pan is made of steel.
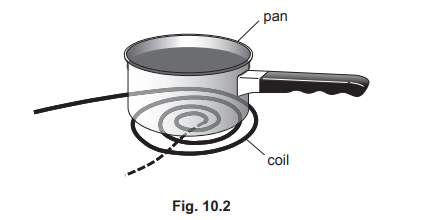
State what quantity is induced in the base of the pan.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(c) The pan contains water.
State and explain the effect of the quantity induced in part (b) on the temperature of the water in the pan.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) magnetic field (produced)
(magnetic field / magnetic flux / magnetic effect / magnetism) (it) alternates / changes direction / reverses
(b) e.m.f. / p.d. / voltage
(c) (temperature) increased
current in base of pan o.w.t.t.e
thermal energy (produced in base of pan)
