Question
(a) Fig. 10.1 shows the cross-section of a wire carrying a current into the plane of the paper.

On Fig. 10.1, sketch the magnetic field due to the current in the wire. The detail of your sketch should suggest the variation in the strength of the field. Show the direction of the field with arrows.
(b) Fig. 10.2 shows part of a model of a d.c. motor.
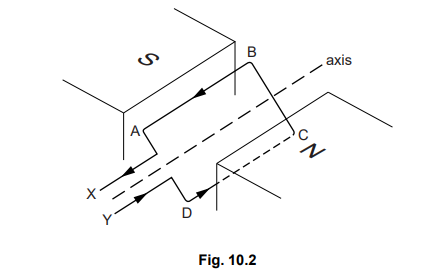
(i) On Fig. 10.2, draw arrows to show the directions of the forces acting on side AB
and on side CD of the loop.
(ii) With the loop in the position shown in Fig. 10.2, explain why the forces on AB and
CD cause the loop to rotate about the axis.
(iii) The ends X and Y of the loop are connected to a battery using brushes and a splitring commutator.
State why a split-ring commutator is used.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) at least 3 concentric circles centred on wire B1 arrows clockwise on each circle / at least one circle spacing of circles increasing as radius increases
(b) (i) arrow pointing down on side AB, up on side CD
(ii) forces on AB and CD are opposite OR up and down and separated / not in same line (so cause rotation) OR have moments in same sense / direction OR cause couple / torque
(iii) to reverse current in loop or keep current in AB or CD in the same direction OR keep current on side near a pole in the same direction when (plane of) coil is vertical OR every half turn OR when AB and CD swap sides so that: rotation continues (in same direction) OR so that rotation doesn’t reverse its direction OR to maintain sense/direction of moments/couple OR coil turns more than half a revolution
Question
(a) Fig. 11.1 shows in each of the diagrams a current-carrying conductor and a magnetic field pattern.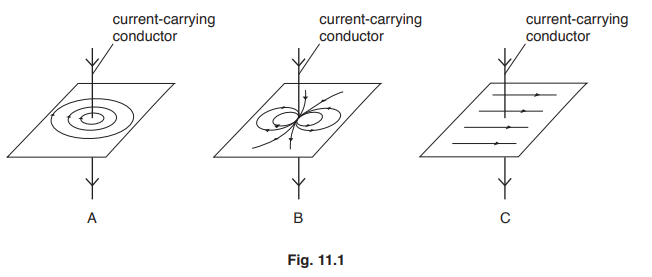
State the diagram which correctly shows the magnetic field around a current-carrying conductor.
(b) Fig. 11.2 shows three pieces of equipment.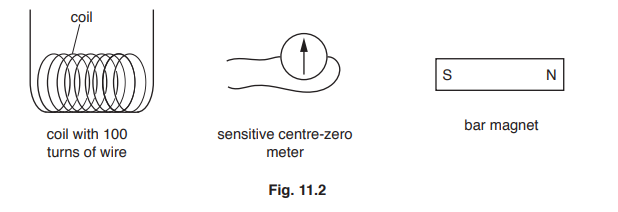
i. Describe how to generate and detect an electromotive force (e.m.f.) using the equipment in Fig. 11.2.
You may draw a diagram.
ii. Describe two changes that will generate a larger e.m.f. using similar equipment to that in Fig. 11.2.
(c) A student connects a lamp and centre-zero galvanometer in series with a generator, as shown in Fig. 11.3.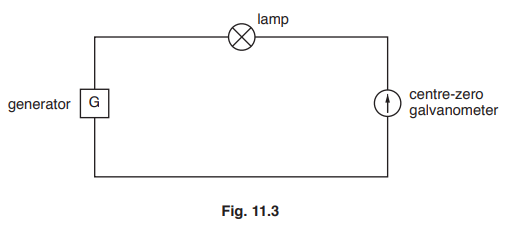
The student observes the galvanometer needle moving from side-to-side repeatedly.
Explain why the needle moves in this way.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (diagram) A
(b) (i) connect coil to (centre zero) meter
move magnet in OR / AND out of coil
(observe) deflection on meter
(ii) any two from:
use stronger magnet
move magnet faster
more turns on coil OR use more than 100 turns
(c)
