Question
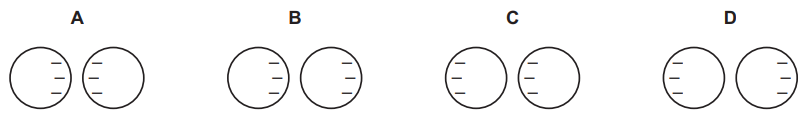
Two isolated metal spheres are both negatively charged. The spheres are brought close together but do not touch.
Which diagram shows the charge distribution on the spheres?
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
A plastic rod is rubbed with a dry cloth. The rod becomes positively charged.
Why has the rod become positively charged?
A It has gained electrons.
B It has gained neutrons.
C It has lost electrons.
D It has lost neutrons.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Two uncharged metal spheres X and Y rest on insulating stands and touch each other.
A negatively charged plastic rod is brought near to sphere X.
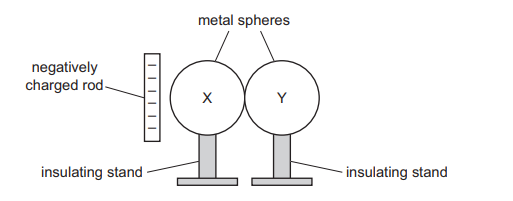
Using the insulating stand, sphere Y is moved away from sphere X.
What are the signs and the relative magnitudes of the charges induced on X and Y?
charge on X | charge on Y | relative magnitudes of charges | |
A | negative | negative | equal |
B | negative | positive | different |
C | positive | negative | equal |
D | positive | positive | different |
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
A student rubs a plastic rod with a cloth.
The rod becomes positively charged.
What has happened to the rod?
A It has gained electrons. B It has gained protons. C It has lost electrons. D It has lost protons.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
An isolated metal sphere is positively charged.
It is then brought near to another isolated metal sphere that is neutral.
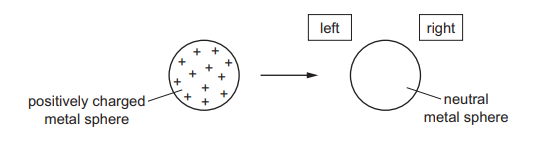
What happens to the charges on the neutral sphere as the positively charged sphere is brought close to it?
A Some positive charges move to the left and some negative charges move to the right.
B Some positive charges move to the right and some negative charges move to the left.
C Some positive charges move to the right, but the negative charges do not move.
D The positive charges do not move, but some negative charges move to the left.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
