Question
When a beam of α-particles is incident on a thin metal foil, most of them follow a path represented by path X in the diagram. A small number of α-particles follow a path represented by path Y in the diagram.
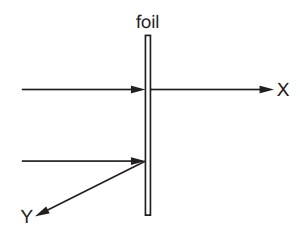
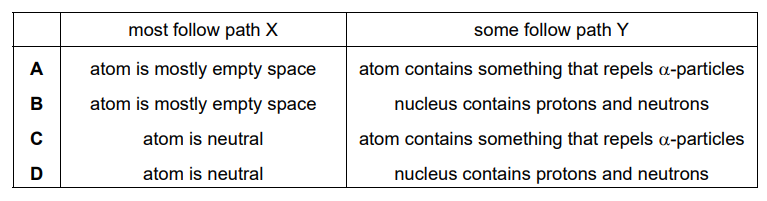
Which row correctly describes a conclusion that can be drawn from each of these observations about the structure of the atom?
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question
The diagram shows $\beta$-particles being directed between the poles of a magnet.
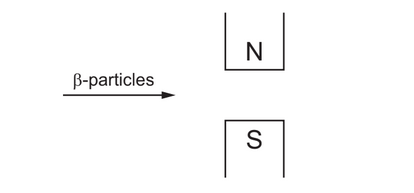
In which direction will the particles be deflected?
A into the page
B out of the page
C towards the bottom of the page
D towards the top of the page
Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
The diagram shows the path followed by α-particles as they pass between two charged plates. They are deflected downwards.
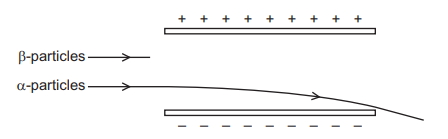
What happens to β -particles passing through the same electric field?
They are deflected downwards more than the α-particles.
They are deflected upwards.
They are not deflected at all.
They are deflected downwards by the same amount as the α-particles.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
A beta particle is a fast moving electron.
Which statement explains how beta particles are emitted from an atom?
A An electron is emitted as a beta particle from an inner electron shell of the atom.
B An electron is emitted as a beta particle from an outer electron shell of the atom.
C A neutron changes into a proton and a beta particle is emitted from the nucleus.
D A proton changes into a neutron and a beta particle is emitted from the nucleus.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
A radioactive source emits α-particles, β-particles and γ-rays into a vacuum where there is
a magnetic field.
The magnetic field acts perpendicularly into the plane of the paper.
The paths X, Y and Z of the three types of radiation through the magnetic field are shown.
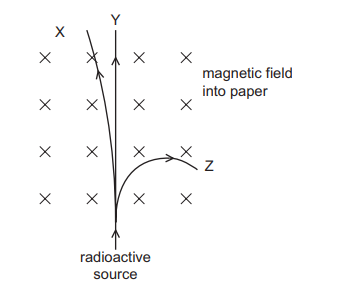
Which radiation follows path X, path Y and path Z?
| X | Y | Z |
A B C D | α-particles α-particles β-particles β-particles | β-particles γ-rays α-particles γ-rays | γ-rays β-particles γ-rays α-particles |
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
