Question
The diagram shows a uniform metre rule, MN, pivoted at its midpoint P.
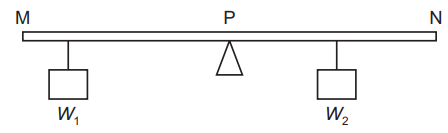
Two weights, W1 and W2, are hung either side of the pivot.
The rule remains balanced.
Which row is correct?
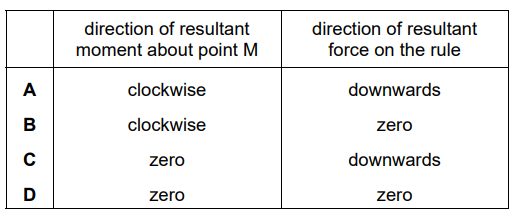
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
Which statement gives a complete description of any object that is in equilibrium?
A There are no forces acting.
B There is no resultant force.
C There is no resultant force and no resultant turning effect.
D There is no resultant turning effect.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
A uniform rod XY of weight 2.0 N has a length of 80 cm.
The rod is suspended by a thread 20 cm from end X. A weight of 5.0 N is suspended from end X.
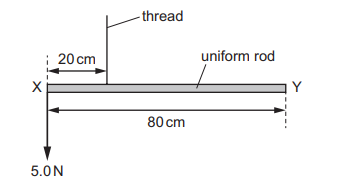
A student hangs a 6.0 N weight on the rod so that it is in equilibrium.
What is the distance of the 6.0 N weight from end X?
A 6 cm
B 10 cm
C 26 cm
D 30 cm
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
A wooden plank rests in equilibrium on two rocks on opposite sides of a narrow stream.
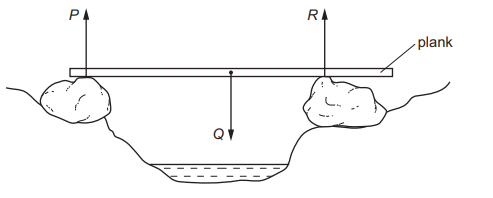
How are the sizes of the forces related?
A P + Q = R
B P + R = Q
C P = Q = R
D P = Q + R
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
A balloon and a mass are attached to a rod that is pivoted at P.
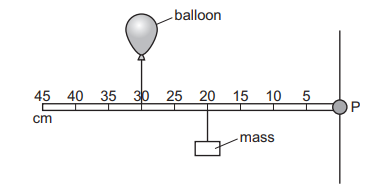
The balloon is filled with helium, a gas less dense than air, so that it applies an upward force on the rod.
The rod is horizontal and stationary.
Which action causes the rod to rotate clockwise?
A Move both the balloon and mass 10 cm to the left.
B Move both the balloon and mass 10 cm to the right.
C Move both the balloon and mass to the 25 cm mark.
D Move the balloon to the 20 cm mark and the mass to the 30 cm mark.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
A wooden plank rests in equilibrium on two rocks on opposite sides of a narrow stream.

How are the sizes of the forces related?
A P + Q = R
B P + R = Q
C P = Q = R
D P = Q + R
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
A plane lamina with centre of mass X touches the ground at point P.
Which diagram shows the lamina in equilibrium?
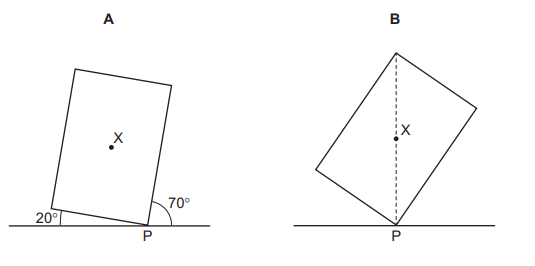
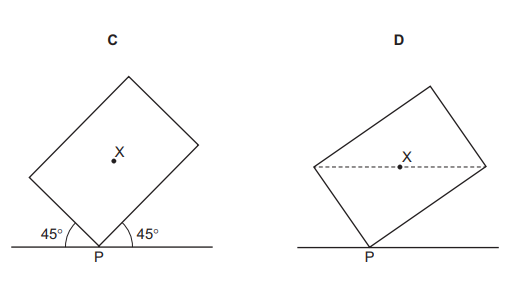
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
The diagram shows sections of four objects of equal mass. The position of the centre of mass
of each object has been marked with a cross.
Which object is the most stable?
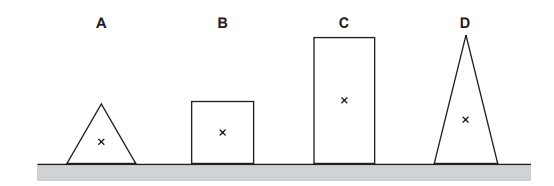
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
A see-saw is made by resting a long plank of wood with its centre of mass on a barrel.
A boy sits on one side of the barrel and a girl sits on the other side so that the see-saw is balanced.
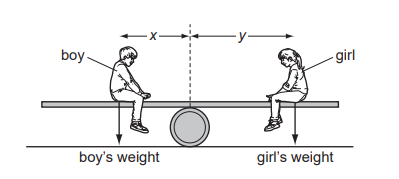
Which statement must be true?
A boy’s weight = girl’s weight
B distance x = distance y
C total downward force = total moment about the barrel
D resultant force and resultant moment are both zero
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
