Question
Two separate circuits have different power supplies. Both power supplies provide the same magnitude current.
Power supply P has an electromotive force (e.m.f.) of 1.5 V and power supply Q has an e.m.f. of 3.0V.
Which statements about Q are correct when compared with P?
- Q supplies twice the charge per unit time.
- Q supplies twice the energy per unit charge.
- Q supplies twice the energy per unit time.
A 1, 2 and 3 B 1 and 2 only C 1 and 3 only D 2 and 3 only
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
A circuit contains a cell of electromotive force (e.m.f.) of $2.0 \mathrm{~V}$. The current in the circuit is $2.0 \mathrm{~A}$. How much energy is converted by the cell in $2.0$ minutes?
A $2.0 \mathrm{~J}$
B $4.0 \mathrm{~J}$
C $8.0 \mathrm{~J}$
D $480 \mathrm{~J}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Which electrical quantity is defined in terms of the energy supplied in driving charge round a complete circuit?
A current
B electromotive force
C potential difference
D power
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
A cell has an electromotive force (e.m.f.) of 1.5 V. What does this statement mean?
The cell converts 1.0 J of energy when driving 1.5 C of charge round a complete circuit.
The cell converts 1.5 J of energy when driving 1.0 C of charge round a complete circuit.
The cell converts 1.5 J of energy per second when driving 1.0 C of charge round a complete circuit.
The cell converts 1.5 W of power when driving 1.0 C of charge round a complete circuit.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Which produces an electromotive force (e.m.f.)?
A. a battery
B. a filament lamp
C. a resistor
D. a spring balance
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
The electromotive force (e.m.f.) of a rechargeable battery is 6.0 V. What does this mean?
A. 6.0 J is the maximum energy the battery can provide in 1.0 s.
B. 6.0 J is the total energy the battery can provide before it has to be recharged.
C. 6.0 J of energy is provided by the battery to drive a charge of 1.0 C around a complete circuit.
D. 6.0 J of energy is provided by the battery to drive a current of 1.0 A around a complete circuit.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
The diagram shows two voltmeters P and Q connected to a potential divider.
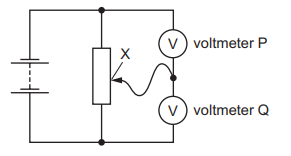
The sliding connection at point X is moved towards the top of the diagram.
What happens to the reading on P and to the reading on Q?
| reading on P | reading on Q |
A | decreases | decreases |
B | decreases | increases |
C | increases | decreases |
D | increases | increases |
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
In which unit is potential difference measured?
A. ampere
B. ohm
C. volt
D. watt
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
The diagram shows an electrical circuit.
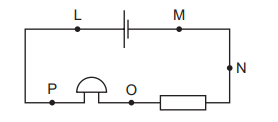
Between which two points must a voltmeter be connected to find the potential difference across
the bell?
A L and M
B M and N
C N and O
D O and P
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
The diagram shows a 10 Ω resistor and a 20 Ω resistor connected in a potential divider circuit.
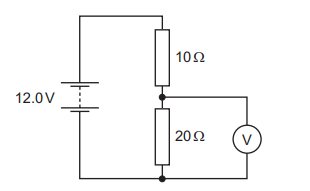
What is the reading on the voltmeter? 4.2.4
A 4.0 V
B 6.0 V
C 8.0 V
D 12.0 V
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
The diagram shows a 10 Ω resistor and a 20 Ω resistor connected in a potential divider circuit.

What is the reading on the voltmeter? 4.2.4
A 4.0 V
B 6.0 V
C 8.0 V
D 12.0 V
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
