Question
Which action will not magnetise a rod?
placing a copper rod inside a coil carrying a direct current
stroking a steel rod with a permanent magnet
hammering a steel rod aligned with the Earth’s magnetic field
placing a soft-iron rod close to a permanent magnet
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
A student wishes to demonstrate electromagnetic induction.
He has a magnet and connecting wires. Which other apparatus does he need?
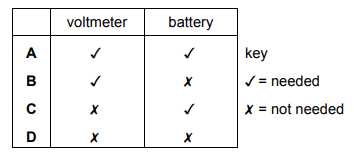
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
A bar magnet is held near a coil of wire. The coil is connected to a sensitive voltmeter. 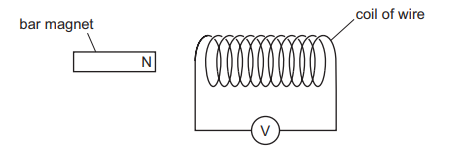
The N-pole of the magnet is moved quickly towards the coil. The voltmeter shows a reading of
+10 mV.
The N-pole of the magnet is then moved slowly away from the same end of the coil. The reading on the voltmeter is observed.
Which voltmeter reading is possible?
A –15 mV
B –5 mV
C 0 mV
D +5 mV
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Which statement about electromagnetic induction is correct?
A strong magnet that is held stationary near a stationary conductor causes a greater effect than a weak magnet.
The effect occurs when a magnet and a conductor are both moved with the same speed and in the same direction.
The effect occurs when a magnet is moved away from a nearby conductor.
The effect only occurs when a magnet is moved towards a conductor.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Electromagnetic induction is the process of generating an electromotive force by moving a conductor through a magnetic field. According to Lenz law the direction of induced e.m.f. (or) current is such that it opposes the cause which produce it.
Question
The diagram shows a coil of wire connected to a voltmeter.
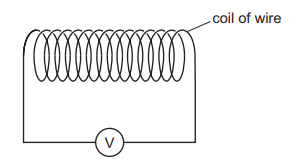
A student has a magnet and an unmagnetised iron rod.
How can an e.m.f. be induced across the coil?
A holding the magnet inside the coil
B holding the iron rod inside the coil
C pushing the magnet into the coil
D pushing the iron rod into the coil
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
