CIE iGCSE Biology Paper 3 Prediction - 2025
CIE iGCSE Biology Paper 3 Prediction – 2025
Preparing for your IGCSE exam can be daunting, but with the right approach, you can achieve your goals with CIE iGCSE Biology Paper 3 Prediction
Ace your iGCSE exam! Find exam-style questions, detailed notes, and helpful resources to boost your understanding
iGCSE Practice Questions, Past Papers , Flashcards and notes available for iGCSE Students at IITian Academy.
Question 1
Table shows some information about air pollution.
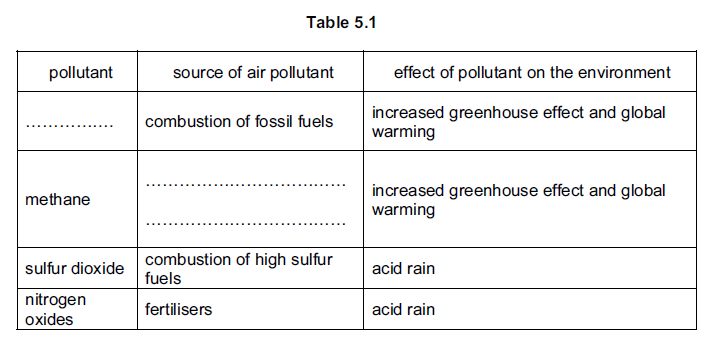
(a) Complete Table by writing answers in the spaces indicated. [2]
(b) Explain how the increased greenhouse effect is thought to lead to global warming.

(c) Figure shows changes in the emissions of sulfur dioxide in Europe between 1880 and
2004.
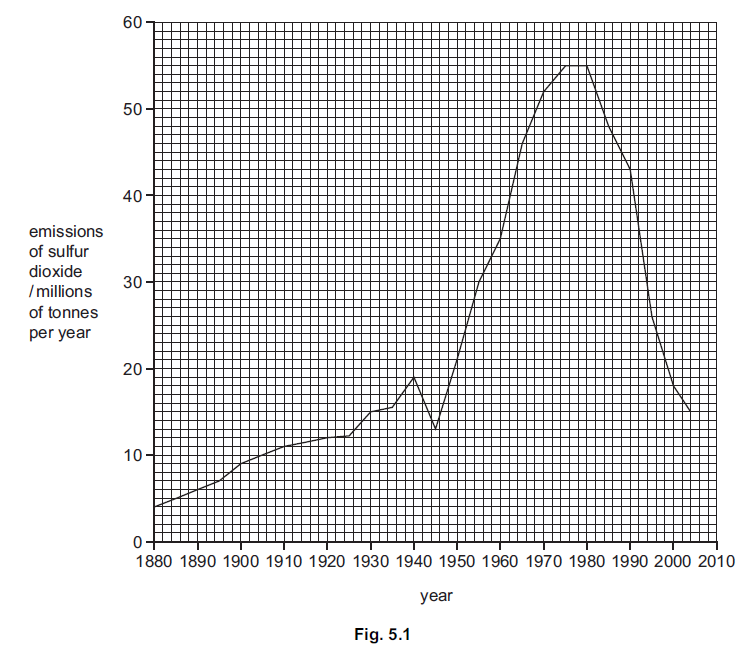
(i) Use the information in Figure to describe the changes in the emissions of sulfur
dioxide in Europe between 1880 and 2004.

(ii) Describe the effects of acid rain on the environment.

(iii) Outline the methods that have been used to reduce the emissions of sulfur dioxide.

Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question 2
(a) Define the term respiration.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..[2]
(b) A rowing machine is a piece of apparatus that is used in many fitness centres.
Fig. 4.1 shows a man training on a rowing machine. The man in the photograph has his arms
extended during the rowing stroke as shown in Fig. 4.2.
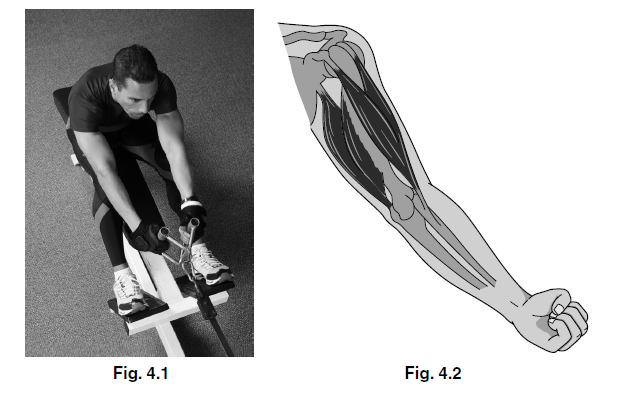
Use Fig. 4.2 to describe how the hand is moved closer to the chest during the rowing stroke.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..[3]
(c) The man has an intense workout on the rowing machine.
Fig. 4.3 shows his oxygen uptake before and during the exercise.
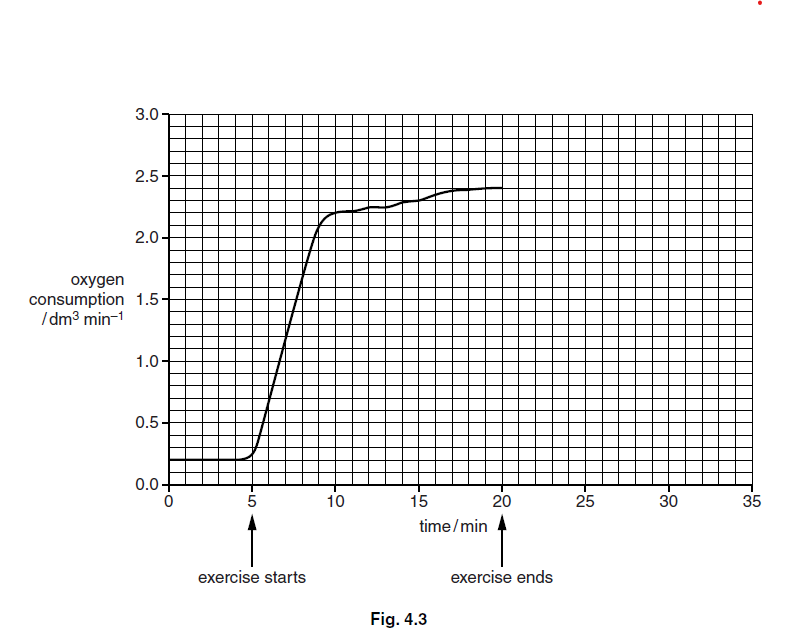
(i) Explain why there is a steep increase in the man’s oxygen consumption at the start of the
exercise.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[4]
(ii) It took 10 minutes after the man had stopped rowing for his oxygen consumption to
decrease to its resting value.
On Fig. 4.3 draw a line between 20 minutes and 35 minutes to show the change in
oxygen consumption after exercise has stopped. [2]
(iii) Explain why the man’s oxygen consumption did not return to the resting value
immediately after exercise.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[4]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question 3
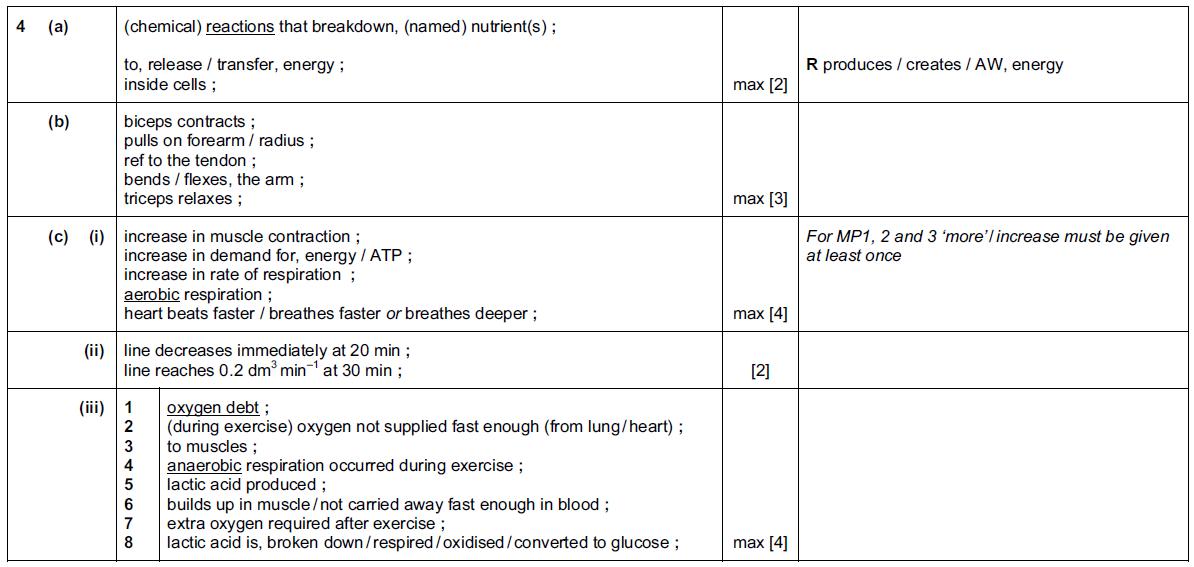
A biologist made a slide of some epidermal cells from a scale leaf of an onion bulb.
Fig. 4.1 is a drawing that the biologist made of one of the cells.
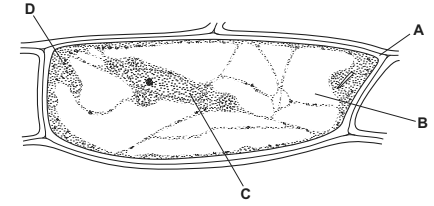
Fig. 4.1
(a) Table 4.1 shows the functions of the structures within a plant cell.
Complete the table by:
naming the part of the cell that carries out each function
using the letters from Fig. 4.1 to identify the part of the cell named.
Table 4.1
(b) The biologist added a few drops of concentrated salt solution to the cells on the slide and took a photograph of the cells, as shown in Fig. 4.2.
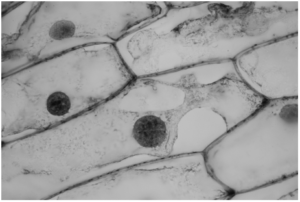
(i) With reference to Fig. 4.2, describe the effect on the plant cells of adding a concentrated salt solution.
(ii) Use the term water potential to explain the effect you have described.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) 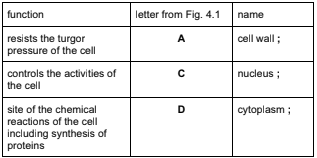
(b) (i) cytoplasm/ vacuole, decreases in, size/ volume ;
(some) cell membrane/ cytoplasm, pulls away /AW, from cell wall ;
plasmolysis / cells are plasmolysed ;
cells, are flaccid/ not turgid/ lose turgor ;
cell walls no longer, pushed outward/withstand pressure ;
(ii) salt solution has a lower water potential than the cell ; ora
water moves out of the cells, by osmosis ;
down a water potential gradient/ from a high(er) water potential to a low(er) water potential ;
through a partially permeable membrane ;
Question 4
Figure shows a diagram of a cell found in leaves.
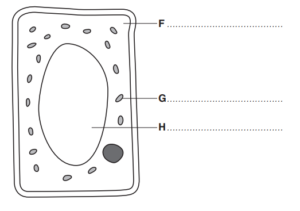
(a) (i) State the names of structures F, G and H.
Write your answers on Fig. 5.1.
(ii) On Fig. 5.1 draw:
a line labelled K to show where the chromosomes are found
a line labelled L to show the position of the cell membrane.
(iii) State the name of this type of plant cell.
(b) The cell in Fig. 5.1 was placed in a concentrated glucose solution.
Fig. 5.2 shows the appearance of the cell after ten minutes in the glucose solution.
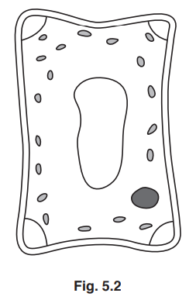
(i) State two ways in which the cell has changed.
1 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [2]
(ii) Water moves into and out of the cell by osmosis.
Osmosis is a form of diffusion.
Describe the ways in which diffusion is different to active transport.
Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a)(i) (F) cytoplasm ;
(G) chloroplast ;
(H) (sap / central) vacuole ;
(a)(ii) K line ending on the nucleus ;
L line ending exactly on inner line of cell wall ;
(a)(iii) palisade (mesophyll) cell ; 1
(b)(i) cell / it, has shrunk or is smaller / AW ;
cell walls are indented / AW ;
vacuole / AW is smaller ;
gap developed (between wall and membrane) ;
(b)(ii) 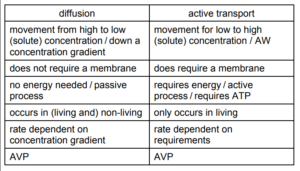
Question 5
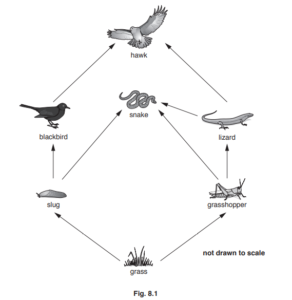
(a) (i) State the principle source of energy for this food web.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) Explain what the arrows on Fig. 8.1 represent.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(iii) State the number of different secondary consumers in this food web.
……………………………………………………….. secondary consumers
(iv) Name the organism that is both a secondary and a tertiary consumer.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(v) State what would happen to the number of hawks if the snakes in this food web all died.
Explain your answer.
number of hawks …………………………………………………………………………………………………
explanation …………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b) (i) The food web shown in Fig. 8.1 changed when eagles moved into the area.
Eagles eat snakes and lizards.
Add this information to Fig. 8.1. You do not need to draw an eagle.
(ii) State one factor that will increase the eagle population and one factor that will decrease
the eagle population.
increase ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
decrease ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(iii) Define the term population.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) (i)the Sun ;
(ii) transfer of energy ;
(iii) three ;
(iv) snake ;
(v) number of hawks: would increase /AW ;
explanation:
lizards / grasshoppers / slugs, not eaten by snakes ;
so increase in number ;
more food for hawks ;
(b) (i) line drawn from snakes to eagles and line from lizards to eagles with arrows in correct direction ;
(ii) increase eagles more snakes /more lizards / other food source ;
decrease eagles fewer snakes /fewer lizards / disease / competition (with another species)/natural disaster ;
(iii) population:
organisms of same species /type ;
living in same area / at the same time ;
Question 6
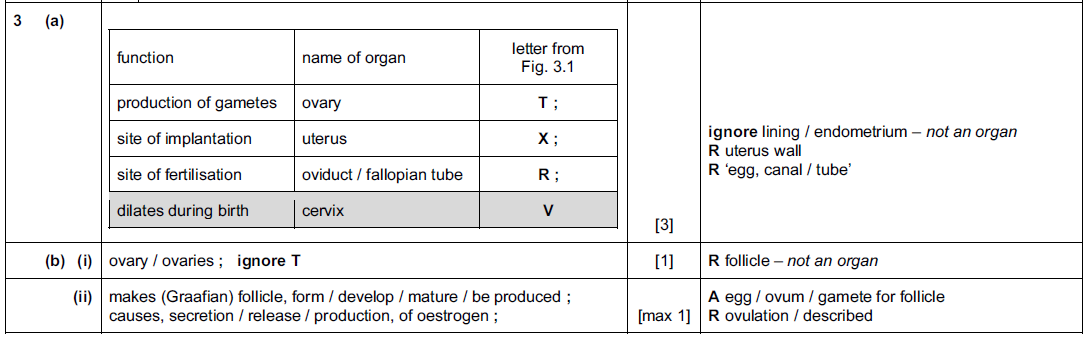
Fig. 3.1 shows the human female reproductive system.
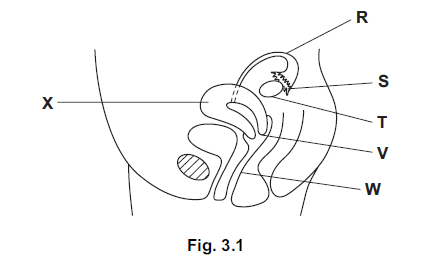
(a) Table 3.1 shows four functions of the female reproductive system.
Complete the table by:
• naming the part of the system that carries out each of the functions;
• using the letters from Fig. 3.1 to identify the part of the system named.
One row has been completed for you.
The hormone FSH is important in regulating the menstrual cycle.
(b) (i) State the target organ of FSH.
![]()
(ii) State one effect of FSH.

(c) The drug clomiphene is given to women who have difficulty in having children. The
drug increases the secretion of FSH.
As part of treatment for infertility, a woman was given clomiphene for five days. The
concentration of oestrogen in her blood was measured every day for 27 days.
The results are shown in Fig. 3.2.
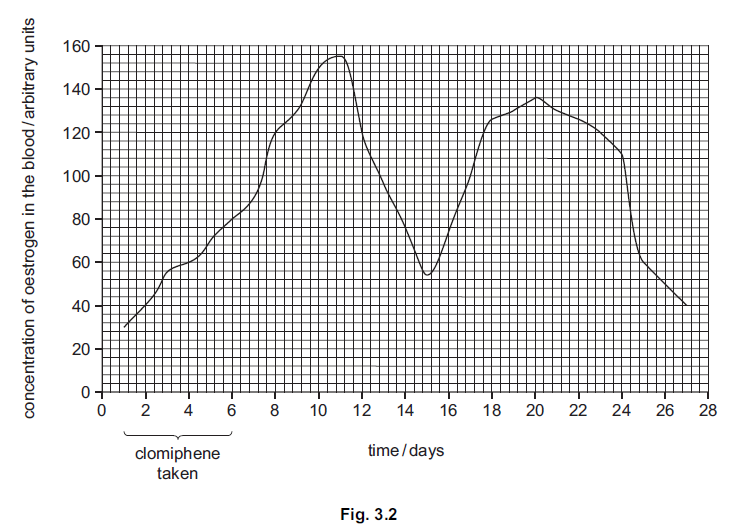
(i) Describe the changes in oestrogen in the blood over the 27 days.
You will gain credit if you use results from Fig. 3.2 in your answer.

(ii) Doctors thought that ovulation occurred around day 15.
Explain what is meant by the term ovulation.

(d) The treatment was not successful on the first occasion.
As an alternative to this treatment, women may be offered in vitro fertilisation (IVF)
treatment.
In IVF treatment, an egg is fertilised outside the body and the resulting embryo is
placed into the uterus.
Describe what happens when an egg is fertilised by a sperm.

(e) Some embryos produced by IVF do not develop because there are problems with their
chromosomes, such as having the wrong number.
(i) Define the term chromosome.

(ii) State the correct number of chromosomes that should be in a cell of a human
embryo.
![]()
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question 7
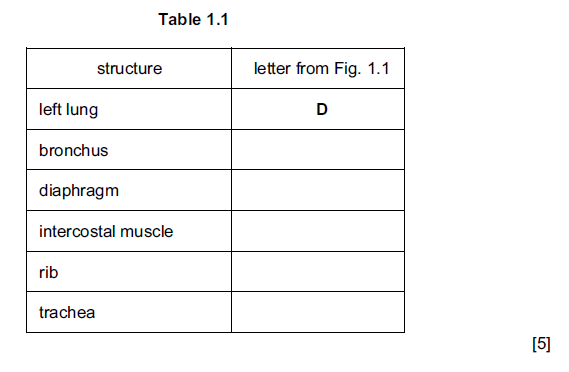
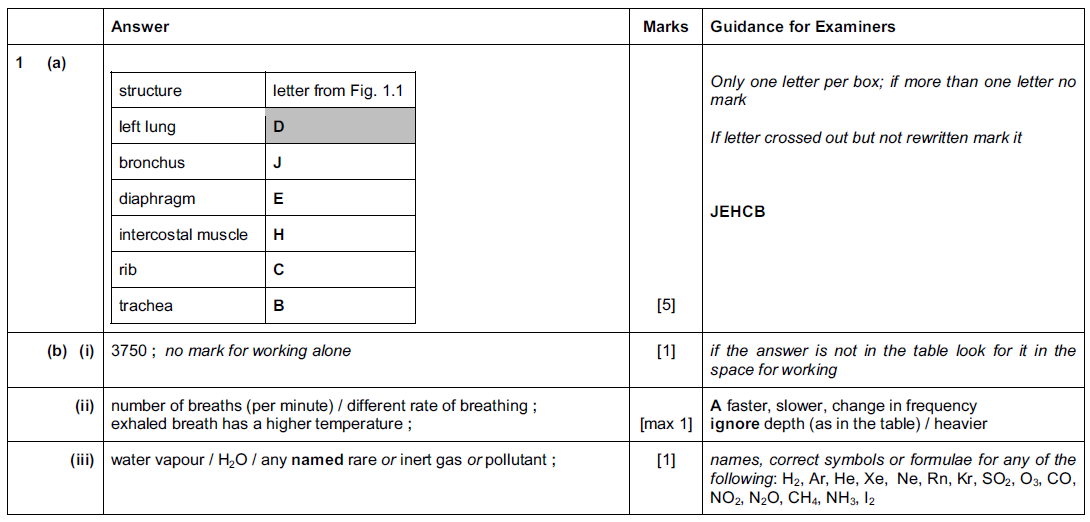
(a) Fig. 1.1 shows the human head, neck and thorax.
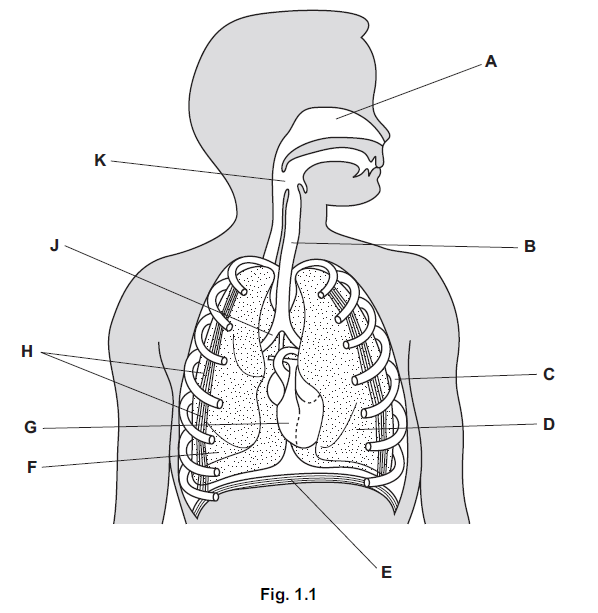
Complete Table 1.1 by writing one letter from Fig. 1.1 to identify the named structures.
The first one has been done for you.
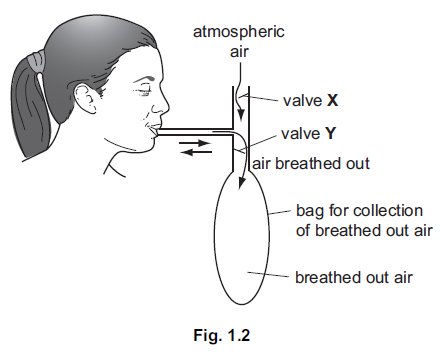
(b) In an investigation, a student breathed in and out of the apparatus shown in Fig. 1.2.
Valve X opens to allow atmospheric air in while valve Y is closed.
When the student breathes out, valve X is closed and valve Y opens to allow breathed
out air into the bag.
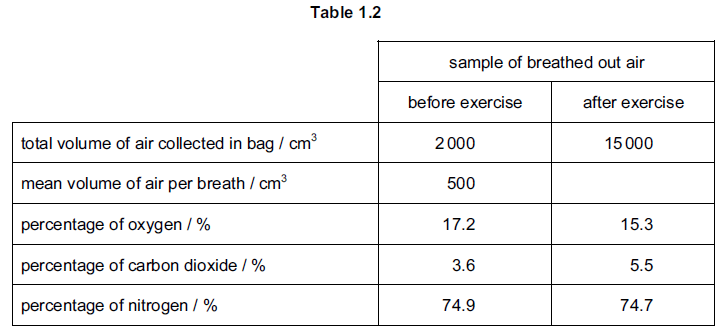
The student breathed in and out four times. The bag was sealed and the volume of air
inside the bag was measured.
A sample of air from the bag was analysed for the percentage composition of oxygen,
carbon dioxide and nitrogen.
The student then did some vigorous exercise for five minutes. After the exercise, the
student repeated the procedure.
The results of the investigation are shown in Table 1.2.
(i) Calculate the mean volume of air per breath after exercise.
Write your answer in Table 1.2.
Show your working.
[1]
(ii) Suggest one way, not shown in Table 1.2, in which the student’s breathing
changed after exercise.

(iii) The figures in Table 1.2 for the percentage composition of air in each sample do
not add up to 100 %.
Name one other gas that would be present in both samples of air.
![]()
(iv) The results for oxygen and carbon dioxide in the samples of breathed out air taken
before and after exercise are different.
Describe and explain these differences.

Answer/Explanation
Ans:
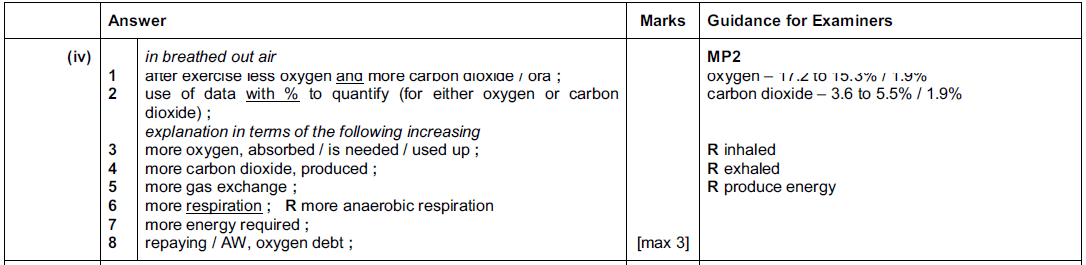
Question 8
An adaptive feature helps an organism survive in its environment.
Adaptive features are inherited.
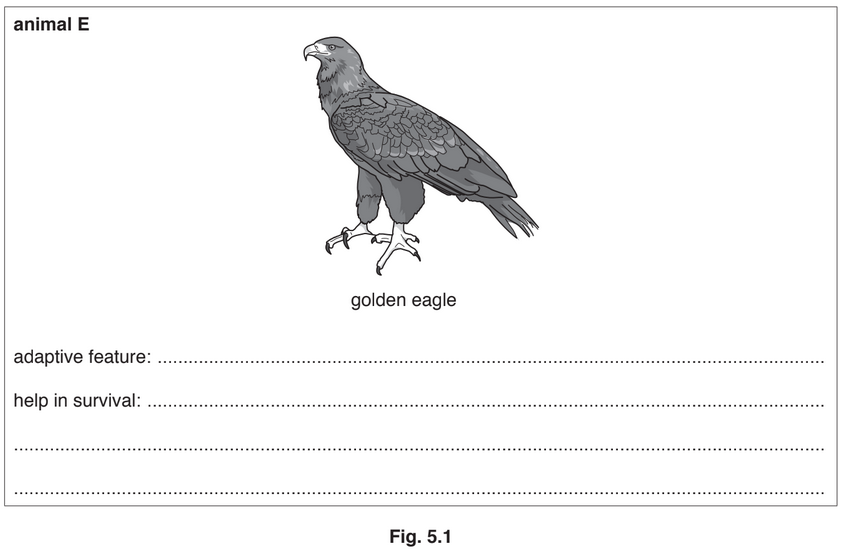
Fig. 5.1 contains diagrams of three animals.
(a) For each animal, select one adaptive feature visible in Fig. 5.1 and briefly suggest how it
helps the animal to survive.
An example has been done for you.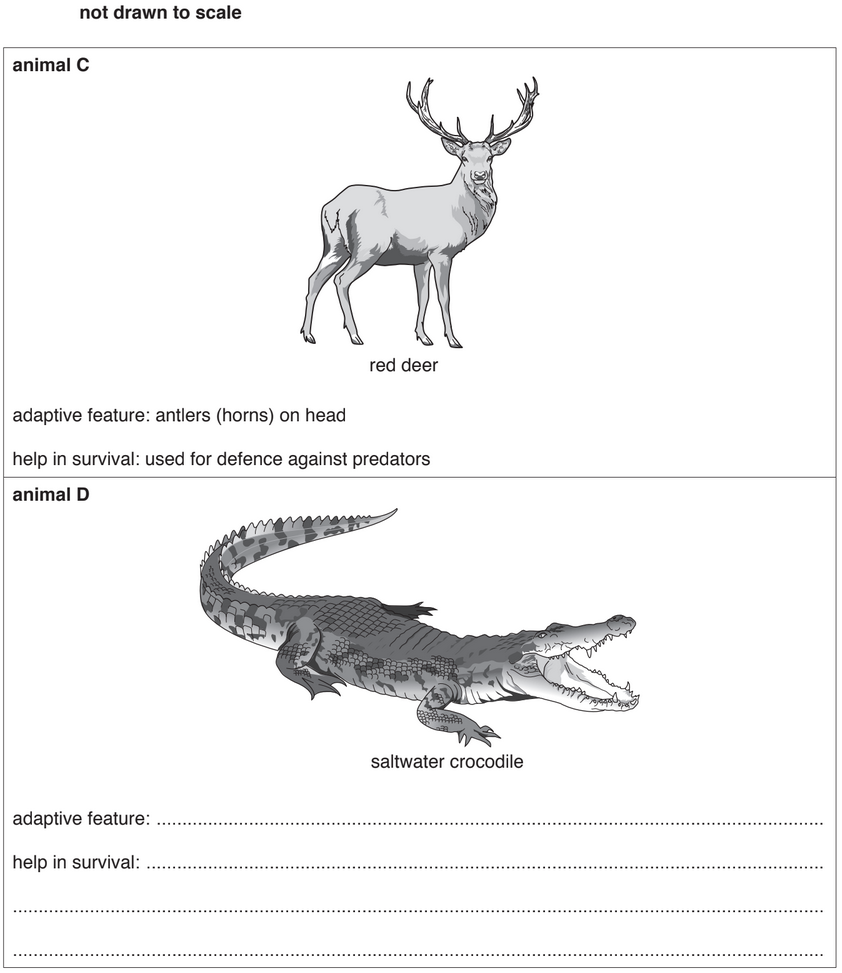
(b) Fig. 5.2 shows a giraffe and an okapi.
The long neck is an adaptive feature for giraffes.
It helps them feed on leaves that other animals like the okapi cannot reach.
Giraffes developed long necks by the process of natural selection.
The statements in Table 5.1 are about how natural selection occurred in giraffes.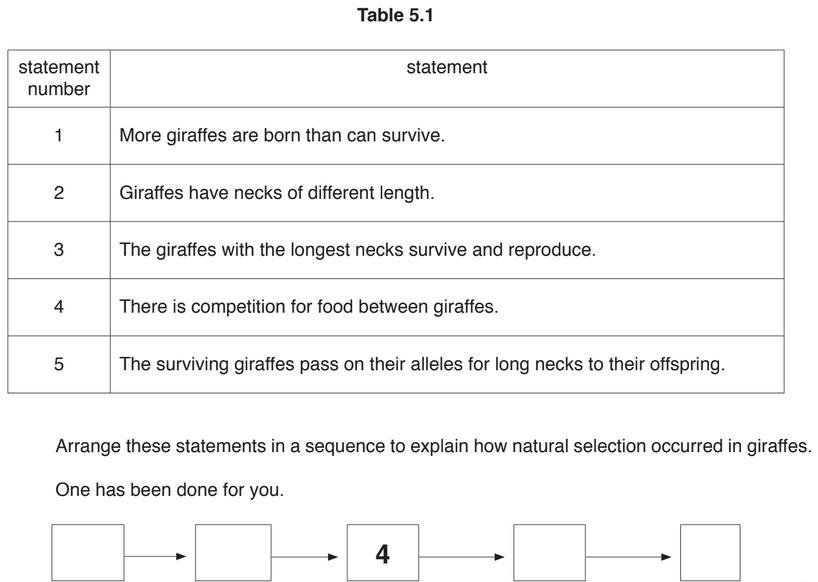
Answer/Explanation
Ans: