Group VII properties- CIE iGCSE Chemistry Notes - New Syllabus
Group VII properties for iGCSE Chemistry Notes
Core Syllabus
- Describe the Group VII halogens, chlorine, bromine and iodine, as diatomic non-metals with general trends down the group, limited to:
(a) increasing density
(b) decreasing reactivity - State the appearance of the halogens at r.t.p. as:
(a) chlorine, a pale yellow-green gas
(b) bromine, a red-brown liquid
(c) iodine, a grey-black solid - Describe and explain the displacement reactions of halogens with other halide ions
- Predict the properties of other elements in Group VII, given information about the elements
Group VII halogens (Cl, Br, I) and general trends and Appearance
Group VII halogens (Cl, Br, I) and general trends
- Group VII elements are called halogens.
- They are all diatomic non-metals at standard conditions: Cl2, Br2, I2.
- They show trends in density and reactivity as you move down the group.
General trends
- Density: increases down the group. Cl₂ (gas) < Br₂ (liquid) < I₂ (solid). This is because molar mass increases and particles become larger.
- Reactivity: decreases down the group. Chlorine is the most reactive, iodine the least. Reactivity decreases because atoms become larger → outer electrons are further from the nucleus → less able to attract electrons to form negative ions.
Explanation of trends
- Halogens need one extra electron to complete their outer shell → form X⁻ ions.
- As you move down the group:
- Atomic radius increases → nucleus has weaker attraction for incoming electron.
- Electronegativity decreases → less reactive.
Example
Compare the densities of chlorine, bromine, and iodine and explain the trend.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Density increases down the group: Cl₂ < Br₂ < I₂.
This is due to increasing molar mass and stronger van der Waals forces between molecules.
Example
Explain why chlorine is more reactive than iodine.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Chlorine has a smaller atomic radius → nucleus exerts stronger attraction on electrons → more easily gains an electron to form Cl⁻ → more reactive than iodine.
Example
Predict the physical state of fluorine and astatine at room temperature.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Fluorine (top of Group VII, very light) → gas. Astatine (bottom of Group VII, heavy) → solid.
Trend is due to increasing van der Waals forces with increasing molar mass.
Appearance of halogens at room temperature
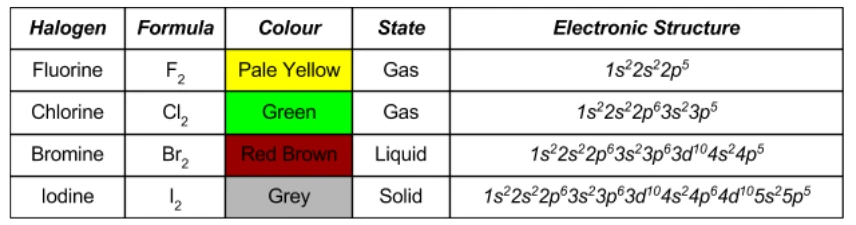
- Halogens exist as diatomic molecules at room temperature (r.t.p.): Cl₂, Br₂, I₂.
- Their physical appearance changes down the group due to increasing molecular mass and van der Waals forces:
- Chlorine: pale yellow-green gas
- Bromine: red-brown liquid
- Iodine: grey-black solid
Explanation of trend
- Van der Waals forces increase down the group as molecules become larger → require more energy to separate → changes physical state.
- Thus, chlorine is a gas, bromine is a liquid, and iodine is a solid at r.t.p.
Example
State the appearance of chlorine, bromine, and iodine at room temperature.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Chlorine → pale yellow-green gas, Bromine → red-brown liquid, Iodine → grey-black solid.
Trend is due to increasing molecular mass and van der Waals forces.
Example
Explain why bromine is a liquid while chlorine is a gas at r.t.p.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Bromine molecules are larger than chlorine molecules → stronger van der Waals forces → more energy required to separate → liquid at r.t.p., whereas chlorine has weaker forces → gas.
Displacement reactions of halogens with other halide ions
Displacement reactions of halogens with other halide ions
- Halogens can displace other halogens from solutions of their halide salts if they are more reactive.
- Displacement occurs because a more reactive halogen can gain electrons from a halide ion of a less reactive halogen:
General rule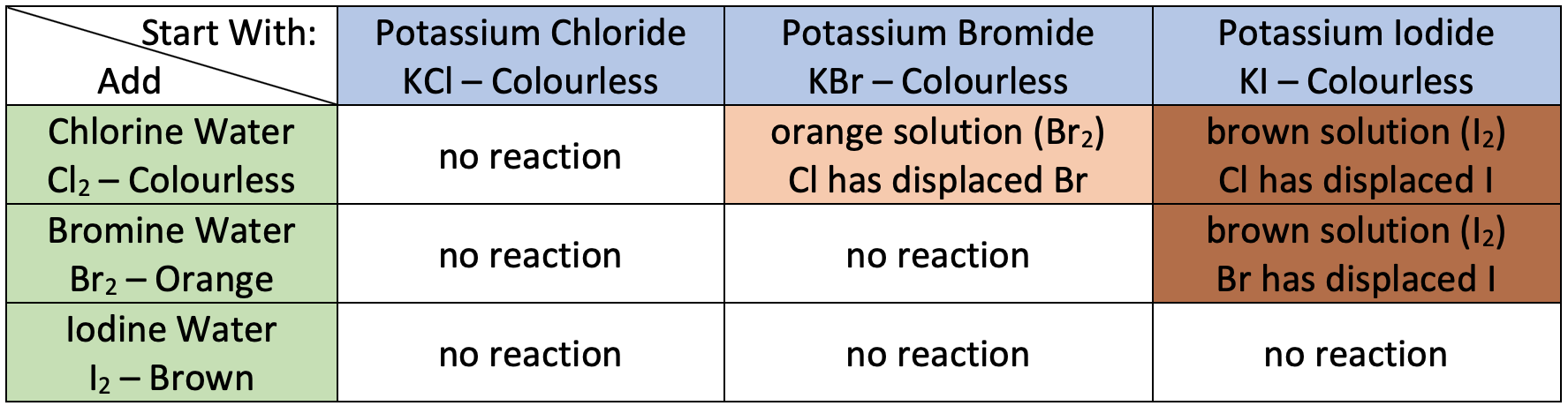
- Reactivity decreases down the group: Cl₂ > Br₂ > I₂.
- A halogen can displace any halide below it in the group:
- Chlorine displaces bromide and iodide ions.
- Bromine displaces iodide ions, but not chloride ions.
- Iodine does not displace chloride or bromide ions.
Example reactions
- Cl₂ + 2NaBr → 2NaCl + Br₂
- Br₂ + 2NaI → 2NaBr + I₂
- I₂ + 2NaCl → No reaction
Explanation
- The more reactive halogen is a stronger oxidising agent → oxidises the halide ion of the less reactive halogen → halogen displacement.
Example
Predict the products and observations when chlorine is added to a solution of potassium bromide.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Reaction: Cl₂ + 2KBr → 2KCl + Br₂. Observation: orange-brown solution due to liberated bromine.
Example
Explain why iodine does not displace bromine from a bromide solution.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Iodine is less reactive than bromine → cannot oxidise Br⁻ ions → no reaction occurs.
Example
Predict the products when bromine is added to a solution of potassium iodide.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Reaction: Br₂ + 2KI → 2KBr + I₂. Observation: brown solution of iodine forms, confirming displacement.
The properties of other elements in Group VII
The properties of other elements in Group VII
- Properties of halogens can be predicted based on the trends observed in chlorine, bromine, and iodine.
- As you move down Group VII (F → Cl → Br → I → At):
1. Density: increases down the group due to increasing molar mass and stronger van der Waals forces.
2. Reactivity: decreases down the group because atoms are larger → nucleus has weaker attraction for additional electrons → less oxidising.
3. Physical state: changes down the group due to van der Waals forces: fluorine and chlorine are gases, bromine is a liquid, iodine and astatine are solids at r.t.p.
4. Appearance: varies down the group: F₂ pale yellow, Cl₂ pale yellow-green, Br₂ red-brown, I₂ grey-black, At dark solid.
5. Displacement reactions: more reactive halogens can displace less reactive halide ions from their salts.
Example
Predict the reactivity of fluorine and astatine compared to chlorine.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Fluorine is more reactive than chlorine → strongest oxidising halogen. Astatine is less reactive than iodine → weakest among halogens.
Example
Predict the physical state of fluorine and astatine at room temperature.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Fluorine → pale yellow gas (small molecule, weak van der Waals forces). Astatine → dark solid (large molecule, strong van der Waals forces).
Example
Predict whether fluorine can displace iodine from a solution of potassium iodide.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Fluorine is more reactive than iodine → will displace iodide ions → reaction occurs: F₂ + 2KI → 2KF + I₂.
