Hydrogen–oxygen fuel cells- CIE iGCSE Chemistry Notes - New Syllabus
Hydrogen–oxygen fuel cells for iGCSE Chemistry Notes
Core Syllabus
- State that a hydrogen–oxygen fuel cell uses hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity with water as the only chemical product
Supplement Syllabus
- Describe the advantages and disadvantages of using hydrogen–oxygen fuel cells in comparison with gasoline / petrol engines in vehicles
Hydrogen–Oxygen Fuel Cells
Hydrogen–Oxygen Fuel Cells
A hydrogen–oxygen fuel cell is a type of chemical cell that converts the chemical energy from the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen directly into electrical energy.
Overall Chemical Reaction:
\( \text{2H}_2 + \text{O}_2 \rightarrow \text{2H}_2\text{O} \)
Key Features:
- It uses hydrogen gas as a fuel.
- Oxygen (usually from the air) is the oxidant.
- Water is the only chemical product of the reaction.
- Electricity is produced directly by the redox reaction between hydrogen and oxygen.
What Makes It Different from a Battery?
- Fuel cells can continuously produce electricity as long as hydrogen and oxygen are supplied.
- Unlike rechargeable batteries, fuel cells do not run down or require recharging.
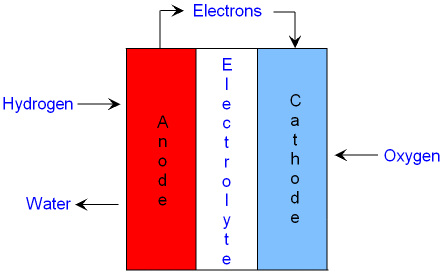
Structure of a Hydrogen–Oxygen Fuel Cell:
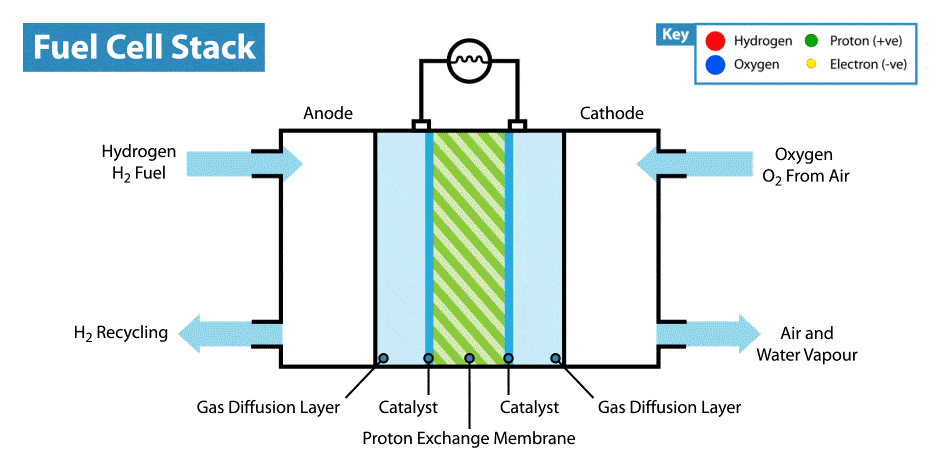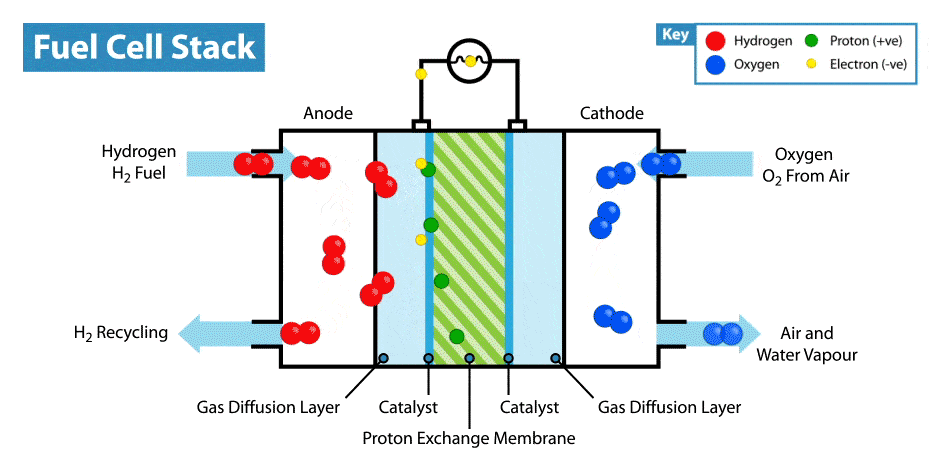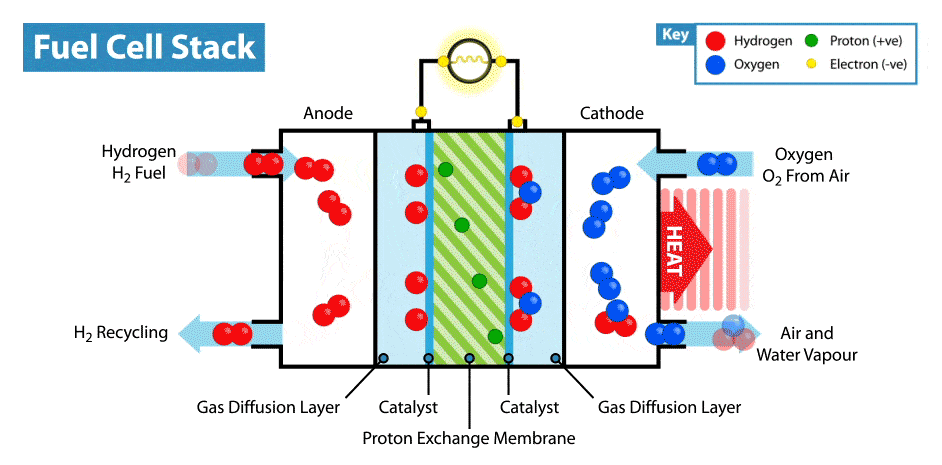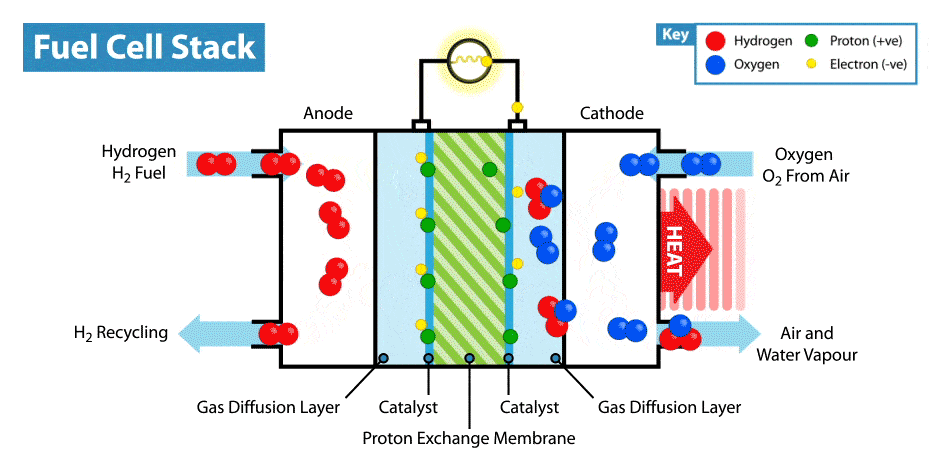
The fuel cell has two electrodes separated by an electrolyte:
- Anode (−): Hydrogen gas is supplied here and gets oxidised (loses electrons).
- Cathode (+): Oxygen gas is supplied here and gets reduced (gains electrons).
- Electrolyte: Usually an aqueous solution of potassium hydroxide (KOH) or an acid that conducts ions.
Electrode Reactions:
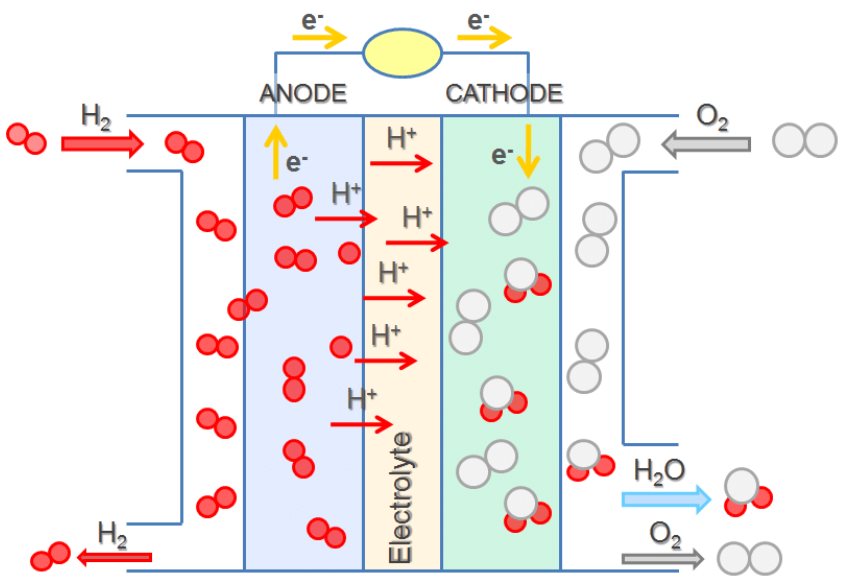
- At the anode (oxidation):
\( \text{H}_2 \rightarrow 2\text{H}^+ + 2e^- \) - At the cathode (reduction):
\( \text{O}_2 + 4\text{H}^+ + 4e^- \rightarrow 2\text{H}_2\text{O} \) - Overall reaction:
\( 2\text{H}_2 + \text{O}_2 \rightarrow 2\text{H}_2\text{O} \)
Environmental Benefit:
The only chemical product is water, making it a clean energy source with no emissions of greenhouse gases or pollutants like carbon dioxide or sulfur dioxide.
Example
State what is meant by a hydrogen–oxygen fuel cell and write the overall equation for the reaction in the cell.
▶️Answer/Explanation
A hydrogen–oxygen fuel cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy through a redox reaction between hydrogen and oxygen.
The only chemical product is water.
Overall reaction:
\( 2\text{H}_2 + \text{O}_2 \rightarrow 2\text{H}_2\text{O} \)
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hydrogen–Oxygen Fuel Cells Compared to Gasoline / Petrol Engines
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hydrogen–Oxygen Fuel Cells Compared to Gasoline / Petrol Engines
Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs) vs. Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles:
Hydrogen–oxygen fuel cells and petrol engines both power vehicles, but they differ in how energy is generated and the environmental impact.
Advantages of Hydrogen–Oxygen Fuel Cells:
- Only water is produced:
The only waste product is \( \text{H}_2\text{O} \), so they cause no air pollution.
- No carbon dioxide emissions:
Unlike petrol engines, they do not contribute to global warming.
- High efficiency:
Fuel cells convert chemical energy directly into electrical energy with less energy loss as heat.
- Quiet operation:
Fuel cells operate silently, unlike noisy combustion engines.
- Renewable fuel source:
Hydrogen can be obtained from water by electrolysis using renewable electricity.
Disadvantages of Hydrogen–Oxygen Fuel Cells:
- Hydrogen is difficult to store:
It must be stored under high pressure or at very low temperatures, requiring special tanks.
- Hydrogen is not readily available:
It is usually made from natural gas (non-renewable) or by electrolysis (expensive if not renewable).
- Fuel cells are expensive:
The cost of materials and manufacturing is higher than petrol engines.
- Lack of infrastructure:
Hydrogen refuelling stations are rare compared to petrol stations.
Comparison Table:
| Feature | Hydrogen–Oxygen Fuel Cell | Petrol Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Main Product | Water | \( \text{CO}_2 \), water, pollutants |
| Fuel Availability | Limited | Widespread |
| Emissions | Clean (zero-emission) | Pollutants and greenhouse gases |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher | Lower (energy lost as heat) |
| Noise | Quiet | Loud |
Example
State one environmental advantage and one practical disadvantage of using hydrogen fuel cells in vehicles.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Advantage: No harmful emissions – only water is produced.
Disadvantage: Hydrogen is difficult to store and not readily available.
