CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-B15.5 Sexually transmitted infections- Study Notes- New Syllabus
CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-B15.5 Sexually transmitted infections – Study Notes
CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-B15.5 Sexually transmitted infections – Study Notes -CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
Core
Describe a sexually transmitted infection (STI) as an infection that is transmitted through sexual contact
State that human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a pathogen that causes an STI
State that HIV infection may lead to AIDS
Describe the methods of transmission of HIV
Explain how the spread of STIs is controlled
CIE iGCSE Co-Ordinated Sciences-Concise Summary Notes- All Topics
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
📌 Definition
A sexually transmitted infection (STI) is an infection that is passed from one person to another through sexual contact.
🌱 Key Points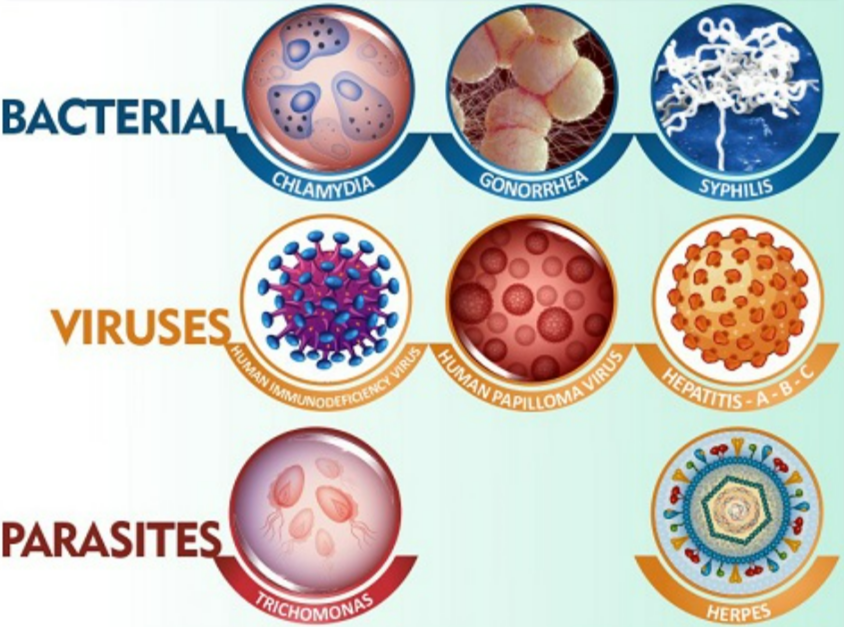
- STIs can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites.
- They affect reproductive organs but can also affect other parts of the body.
- Common examples:
Bacterial: Chlamydia, Gonorrhoea
Viral: HIV, Herpes
Parasitic: Trichomoniasis - Transmission:
Sexual intercourse (vaginal, anal, or oral)
Sometimes through body fluids like blood
📊 Summary Table
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Infection transmitted through sexual contact |
| Causes | Bacteria, viruses, parasites |
| Examples | Chlamydia, Gonorrhoea, HIV, Herpes |
| Transmission | Sexual intercourse, body fluids |
⚡ Quick Recap
STI = Sex + Infection
Can be bacterial, viral, or parasitic
Memory tip: “STI spreads through intimacy.”
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
📌 Key Statement
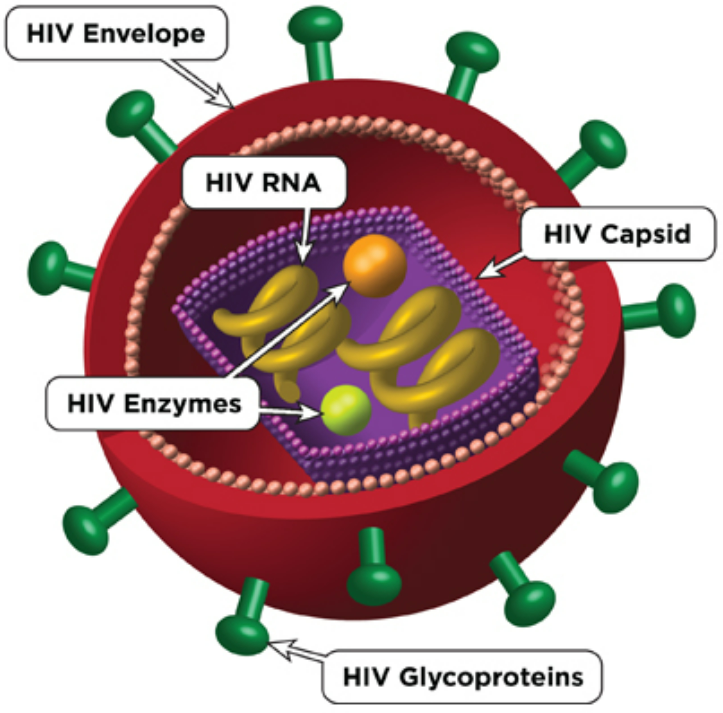
HIV is a pathogen (virus) that causes a sexually transmitted infection (STI).
🌱 Key Points
- Type of pathogen: Virus
- Transmission:
Sexual contact
Blood-to-blood contact (e.g., shared needles)
From mother to baby during pregnancy, birth, or breastfeeding - Effect on body:
Attacks immune system (destroys white blood cells).
Leads to weakened immunity → susceptible to other infections.
Can develop into AIDS if untreated.
📊 Summary Table
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Pathogen | Virus |
| Disease caused | HIV infection → can lead to AIDS |
| Transmission | Sexual contact, blood, mother to baby |
| Effect on body | Weakens immune system, increases risk of other infections |
⚡ Quick Recap
HIV = Virus causing STI
Weakens immune system → may lead to AIDS
Memory tip: “HIV hides in white blood cells → immune system falls.”
HIV and AIDS
📌 Key Statement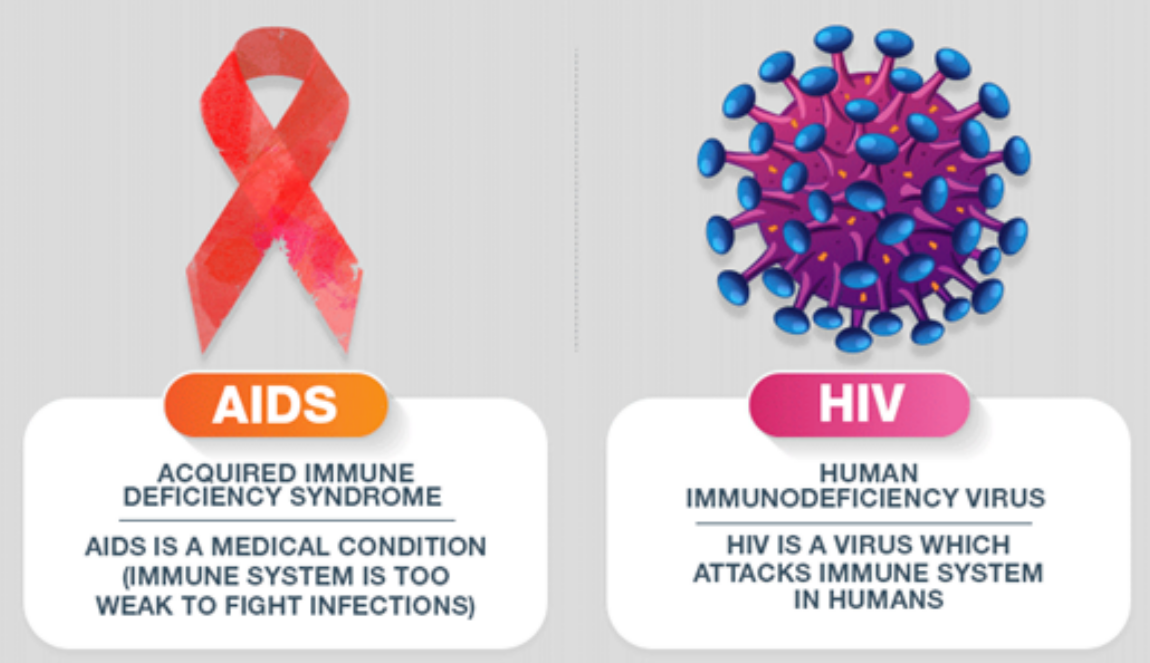
HIV infection may progress to AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) if untreated.
🌱 Key Points
- HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) attacks white blood cells → weakens immunity.
- Over time, the immune system becomes too weak to fight infections.
- At this stage, the condition is called AIDS.
- People with AIDS are vulnerable to opportunistic infections (e.g., tuberculosis, pneumonia).
📊 Summary Table
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| HIV | Virus that infects white blood cells |
| AIDS | Advanced stage of HIV infection; immune system severely weakened |
| Risk | Susceptible to other infections and diseases |
⚡ Quick Recap
HIV → attacks immunity → may lead to AIDS
Memory tip: “HIV hides, immunity slides, AIDS arrives.”
Transmission of HIV
📌 Introduction
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is transmitted when infected body fluids enter another person’s body.
🌱 Main Methods of Transmission
- Sexual contact
Vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected person. - Blood-to-blood contact
Sharing needles or syringes (e.g., in drug use).
Receiving contaminated blood transfusions. - Mother-to-child
During pregnancy, birth, or breastfeeding.
📊 Summary Table
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Sexual contact | HIV present in semen, vaginal fluids |
| Blood contact | Needles, transfusions, cuts with infected blood |
| Mother-to-child | Transmitted before, during, or after birth |
⚡ Quick Recap
HIV spreads through sex, blood, and mother → baby.
Memory tip: “Sex, blood, baby – three paths HIV may take.”
Control of STIs
📌 Introduction
STIs (Sexually Transmitted Infections) can spread easily through sexual contact.
Control measures aim to reduce transmission and protect health.
🌱 Methods of Control
- Safe sexual practices
Use condoms → prevent direct contact with infected fluids.
Limit number of sexual partners → reduce exposure. - Screening and early treatment
Regular testing → identify infections early.
Treat infections promptly → reduce risk of passing them to others. - Education and awareness
Inform people about STIs, symptoms, and prevention.
Encourage responsible sexual behaviour. - Preventing mother-to-child transmission
Treatment during pregnancy → reduces HIV transmission to baby. - Avoid sharing needles
Especially for drug users, to prevent blood-borne infections.
📊 Summary Table
| Control Measure | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Condoms / safe sex | Reduce sexual transmission |
| Screening & treatment | Detect & treat infections early |
| Education | Awareness & responsible behaviour |
| Prevent mother-to-child | Reduce HIV in newborns |
| Avoid needle sharing | Prevent blood-borne infections |
⚡ Quick Recap
STI control = Safe sex + Testing + Education + Avoid needles + Mother care
Memory tip: “Condoms, check-ups, teach, no needles, protect baby.”
