CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-B16.1 Chromosomes and genes - Study Notes- New Syllabus
CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-B16.1 Chromosomes and genes – Study Notes
CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-B16.1 Chromosomes and genes – Study Notes -CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
Core
State that chromosomes are made of DNA, which contains genetic information in the form of genes
Supplement
Define a gene as a length of DNA that codes for a protein
Define an allele as an alternative form of a gene
Describe the inheritance of sex in humans with reference to XX and XY chromosomes
Describe a haploid nucleus as a nucleus containing a single set of chromosomes
Describe a diploid nucleus as a nucleus containing two sets of chromosomes
State that in a diploid cell, there is a pair of each type of chromosome and in a human diploid cell there are 23 pairs
CIE iGCSE Co-Ordinated Sciences-Concise Summary Notes- All Topics
Chromosomes and DNA
📌 Key Statement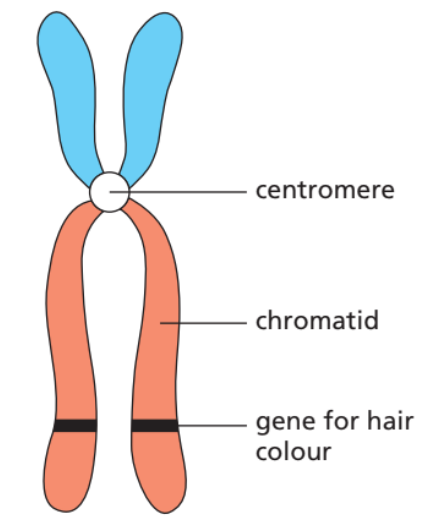
Chromosomes are structures in the nucleus of cells made of DNA.
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) contains genetic information.
Genes are segments of DNA that carry instructions for specific traits.
🌱 Key Points
- Each chromosome contains many genes.
- Genes determine characteristics such as eye colour, blood group, or height.
- DNA is the hereditary material passed from parents to offspring.
📊 Summary Table
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Chromosome | Thread-like structure of DNA in the nucleus |
| DNA | Carries genetic instructions |
| Gene | Segment of DNA coding for a specific trait |
⚡ Quick Recap
Chromosome = DNA bundle
DNA = genetic instructions
Gene = specific trait code
Memory tip: “Chromosome holds DNA; DNA holds genes; genes hold traits.”
Gene
📌 Definition
A gene is a length of DNA that carries the instructions to make a specific protein.
🌱 Key Points
- Proteins determine traits (e.g., eye colour, enzymes, hormones).
- Each gene occupies a specific position (locus) on a chromosome.
- Genes are the functional units of heredity.
📊 Summary Table
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Gene | Length of DNA coding for a protein |
| Function | Determines traits by producing proteins |
| Location | Specific position (locus) on a chromosome |
⚡ Quick Recap
Gene = DNA segment → protein
Memory tip: “Genes are DNA instructions for proteins → traits.”
Allele
📌 Definition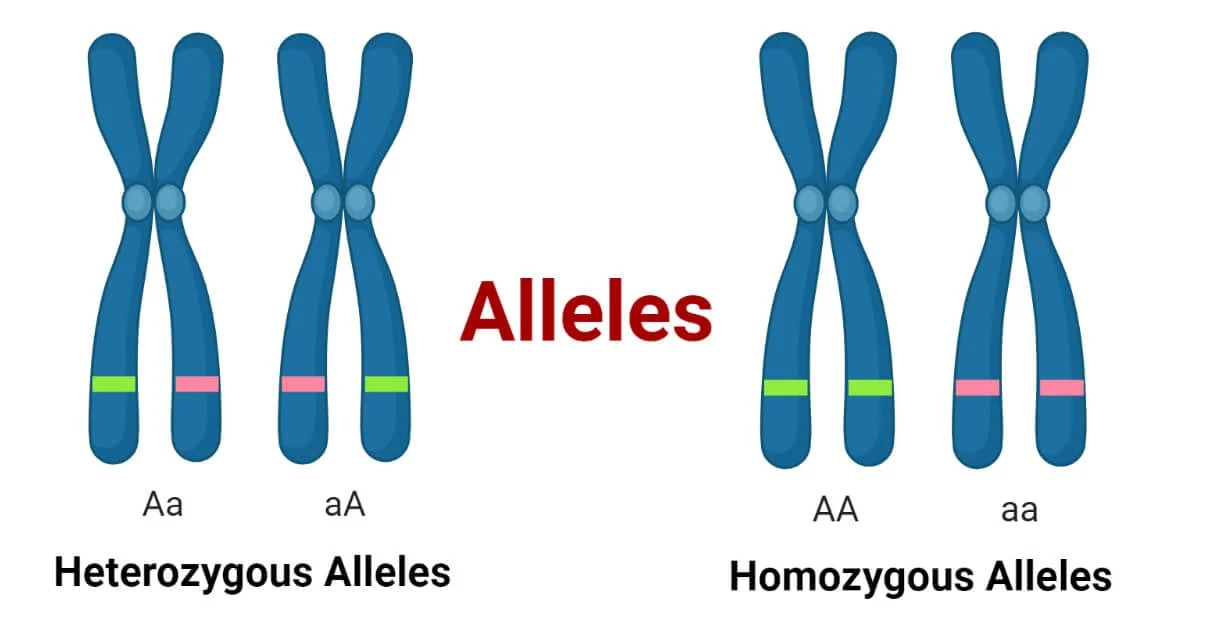
An allele is an alternative form of a gene.
🌱 Key Points
- Each gene may have two or more alleles.
- Alleles determine different variations of the same trait.
- Example: Gene for eye colour → alleles could be brown or blue.
- Individuals inherit one allele from each parent.
📊 Summary Table
| Term | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Allele | Alternative form of a gene | Eye colour: brown or blue |
| Inheritance | One allele from mother, one from father | Bb, BB, or bb |
⚡ Quick Recap
Allele = Gene variant
Memory tip: “Gene = trait instructions; Allele = version of instruction.”
Inheritance of Sex in Humans
📌 Introduction
Human sex is determined by sex chromosomes.
Females have XX, males have XY.
🌱 Key Points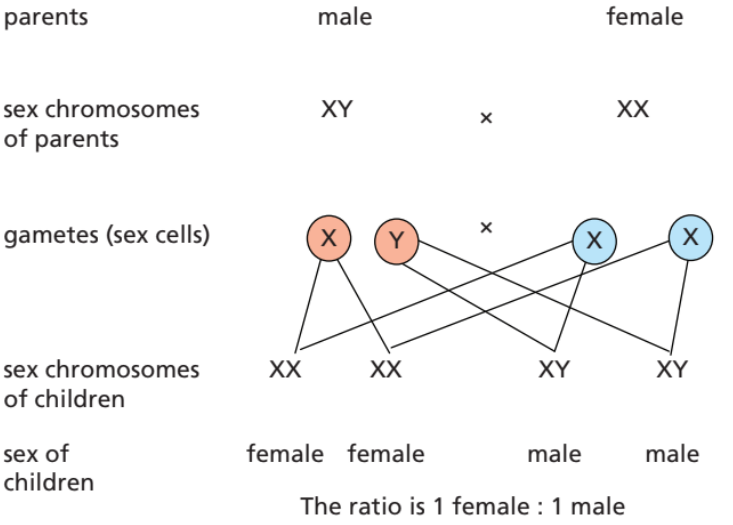
- Chromosome pairs: Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total).
- 22 pairs → autosomes
- 1 pair → sex chromosomes
- Female (XX): Egg cells always carry an X chromosome.
- Male (XY): Sperm cells carry X or Y chromosome.
- Fertilisation and sex:
- X egg + X sperm → XX → female
- X egg + Y sperm → XY → male
- Probability: Chance of male or female offspring = 50% each.
📊 Summary Table
| Parent | Gametes | Offspring Genotype | Sex |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female | X | XX | Female |
| Male | X or Y | XY | Male |
| Male | X or Y | XX | Female |
⚡ Quick Recap
XX = female, XY = male
Mother always contributes X, father contributes X or Y
Haploid Nucleus
📌 Definition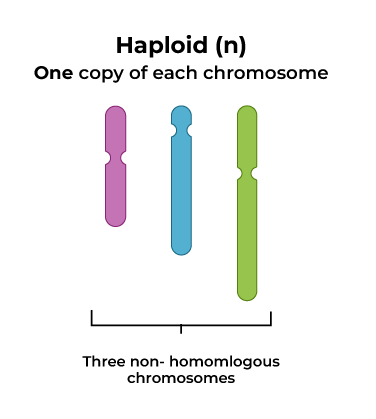
A haploid nucleus contains a single set of chromosomes.
🌱 Key Points
- Represented as n.
- Found in gametes (sperm and egg cells).
- Ensures that after fertilisation, the resulting zygote has a diploid nucleus (2n).
📊 Summary Table
| Term | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Haploid (n) | Single set of chromosomes | Sperm, Egg |
| Diploid (2n) | Two sets of chromosomes | Zygote, body cells |
⚡ Quick Recap
Haploid = 1 set of chromosomes
Found in gametes
Memory tip: “Haploid gametes meet → diploid zygote formed.”
Diploid Nucleus
📌 Definition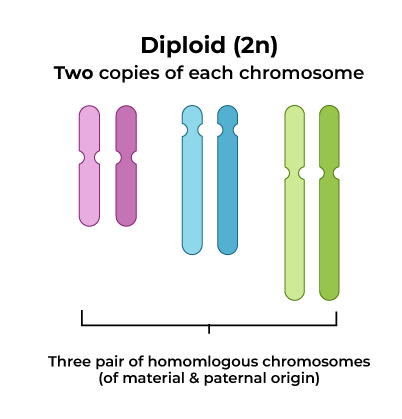
A diploid nucleus contains two sets of chromosomes (one set from each parent).
🌱 Key Points
- Represented as 2n.
- Found in body (somatic) cells of humans.
- Ensures that each generation maintains the correct chromosome number.
- Formed when two haploid gametes fuse during fertilisation.
📊 Summary Table
| Term | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Diploid (2n) | Two sets of chromosomes | Zygote, body cells |
| Haploid (n) | One set of chromosomes | Sperm, Egg |
⚡ Quick Recap
Diploid = 2 sets of chromosomes
Found in all body cells
Memory tip: “Haploid + Haploid → Diploid zygote → body cells 2n.”
Diploid Cells and Chromosome Pairs
📌 Key Statement
In a diploid cell, there is a pair of each type of chromosome.
In humans, a diploid cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total).
🌱 Key Points
- One chromosome of each pair comes from the mother, the other from the father.
- The 23 pairs include:
- 22 pairs of autosomes → control body traits
- 1 pair of sex chromosomes → determines sex (XX or XY)
📊 Summary Table
| Feature | Humans |
|---|---|
| Total chromosomes in diploid cell | 46 |
| Number of pairs | 23 |
| Autosomes | 22 pairs |
| Sex chromosomes | 1 pair (XX or XY) |
⚡ Quick Recap
Diploid = 2 sets of chromosomes → 23 pairs in humans
One from mom, one from dad
Memory tip: “46 chromosomes, 23 pairs, one from each parent for every pair.”
