CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-B19.1 Habitat destruction - Study Notes- New Syllabus
CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-B19.1 Habitat destruction – Study Notes
CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-B19.1 Habitat destruction – Study Notes -CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
Core
- Describe an ecosystem as a unit containing the community of organisms and their environment, interacting together
- Describe biodiversity as the number of different species that live in an area
- Describe the reasons for habitat destruction, including:
(a) increased area for housing, crop plant production and livestock production
(b) extraction of natural resources
(c) freshwater and marine pollution (a detailed description of eutrophication is not required) - State the undesirable effects of deforestation as an example of habitat destruction, to include: reducing biodiversity, extinction, loss of soil, flooding and increase of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
Supplement
- Explain the undesirable effects of deforestation as an example of habitat destruction, to include: reducing biodiversity, extinction, loss of soil, flooding and increase of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
CIE iGCSE Co-Ordinated Sciences-Concise Summary Notes- All Topics
Ecosystem
📌 Definition
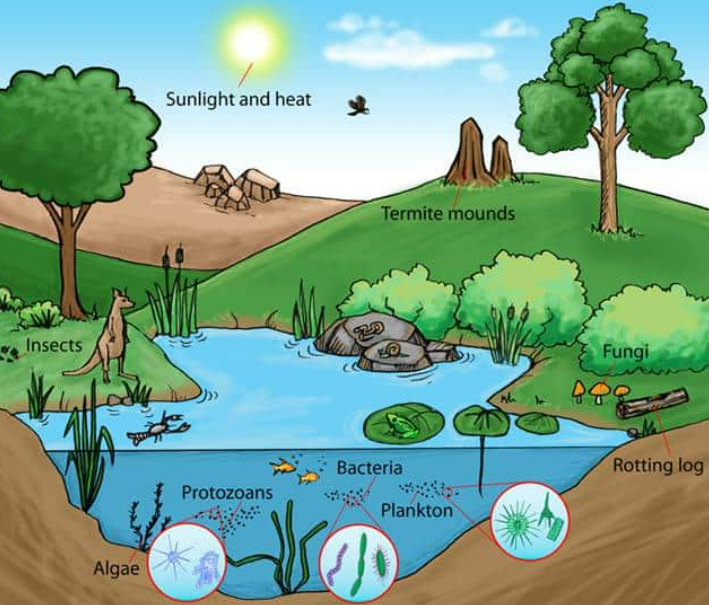
An ecosystem is a unit containing a community of living organisms and their physical environment, all interacting together.
🌱 Key Points
- Living components (biotic): plants, animals, fungi, bacteria.
- Non-living components (abiotic): sunlight, air, water, soil, temperature.
- Interactions:
- Organisms depend on each other for food, shelter, and reproduction.
- Organisms interact with the environment for nutrients, energy, and habitat.
- Examples: Pond ecosystem, Forest ecosystem, Grassland ecosystem
📊 Summary Table
| Component | Examples | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Biotic | Plants, animals, microbes | Energy transfer, food chains, reproduction |
| Abiotic | Sunlight, water, soil, air | Provides resources for survival |
⚡ Quick Recap
Ecosystem = community + environment + interactions.
Energy and nutrients flow and cycle within the ecosystem.
Memory tip: “All living + non-living things interacting as one unit.”
Biodiversity
📌 Definition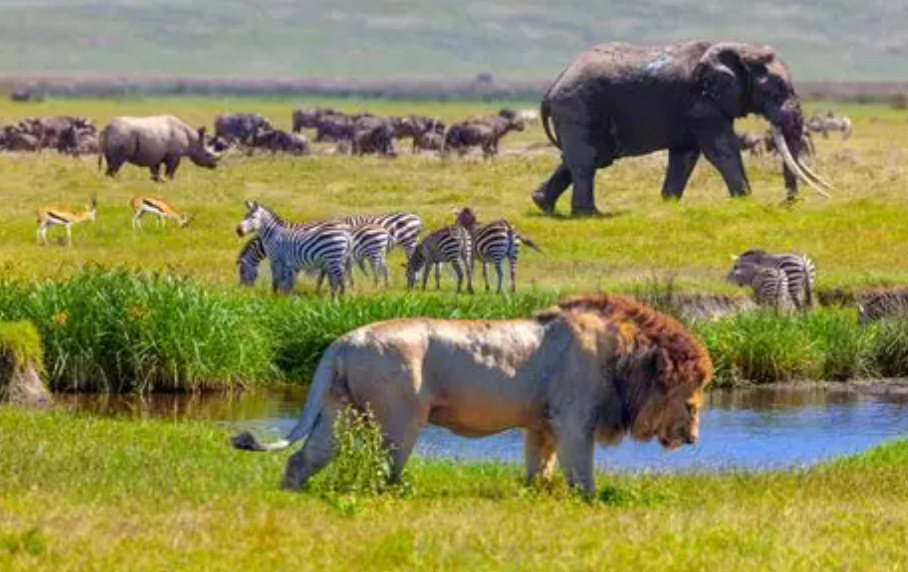
Biodiversity is the number of different species that live in a particular area.
🌱 Key Points
- Higher biodiversity → more species variety and ecosystem stability.
- Includes:
- Plants
- Animals
- Microorganisms
- Important for:
- Maintaining food chains and webs
- Providing resources (food, medicine, materials)
- Supporting ecosystem services (pollination, decomposition)
📊 Summary Table
| Term | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Biodiversity | Number of species in an area | Rainforest has high biodiversity; desert has lower biodiversity |
⚡ Quick Recap
Biodiversity = species variety in an area.
More species → more stable and resilient ecosystems.
Memory tip: “Bio = life, diversity = variety → life variety.”
Habitat Destruction
📌 Definition
Habitat destruction occurs when natural environments are damaged or removed, making them unsuitable for the species that live there.
🌱 Main Reasons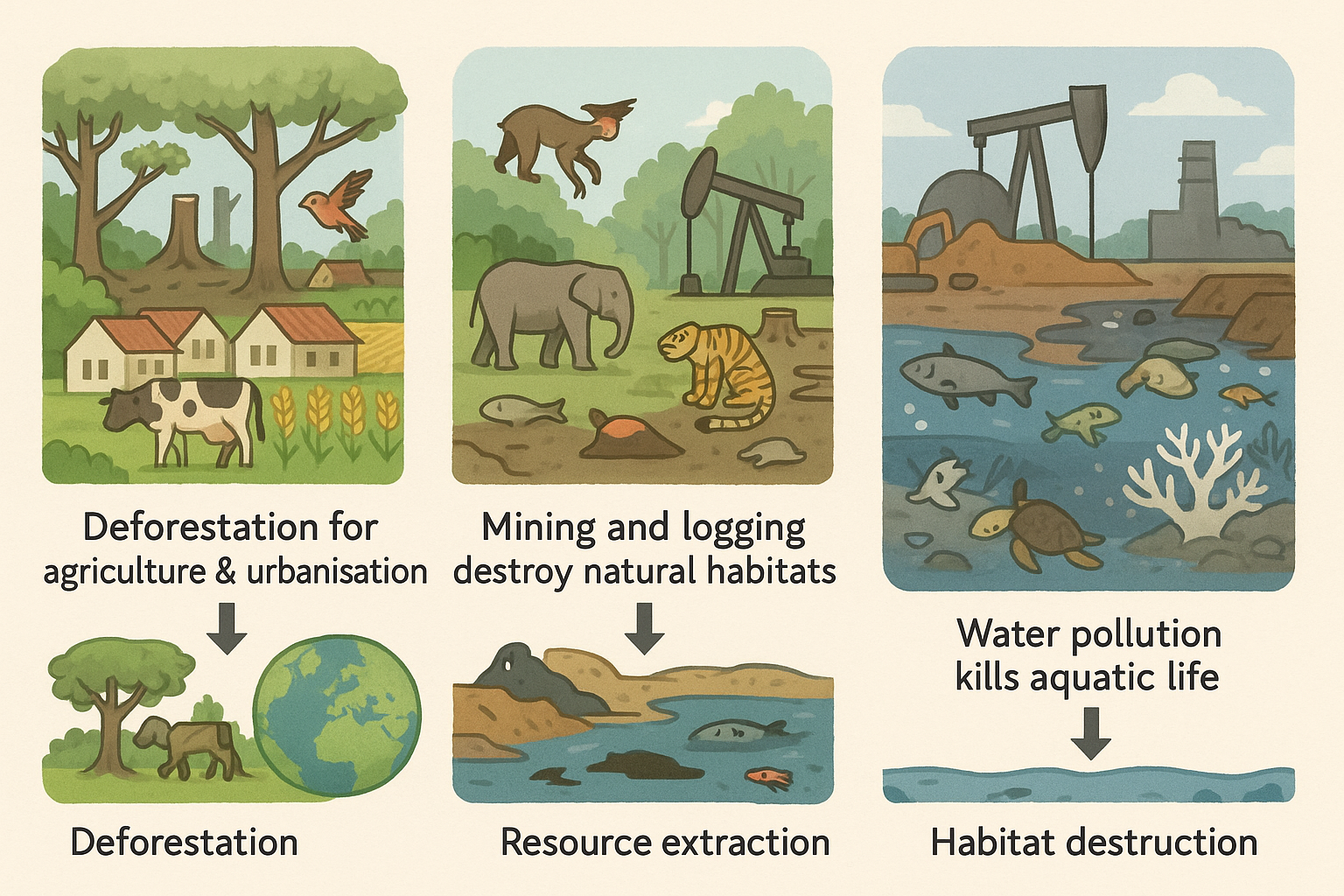
- Increased land use
Housing → forests and grasslands cleared for buildings.
Crop production → natural habitats converted into farmland.
Livestock production → grazing land replaces forests or grasslands. - Extraction of natural resources
Mining, quarrying, and logging destroy habitats.
Reduces shelter and food for species. - Freshwater and marine pollution
Pollutants from industry, agriculture, and sewage damage aquatic habitats.
E.g., chemicals or waste in rivers and oceans make water uninhabitable for many organisms.
Note: Detailed eutrophication description not required.
📊 Summary Table
| Cause | How it affects habitats | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Housing, crops, livestock | Natural areas cleared | Deforestation for cities or farms |
| Resource extraction | Land destroyed, ecosystems disrupted | Mining, logging |
| Pollution | Water quality declines, species die | Chemical runoff, oil spills |
⚡ Quick Recap
Habitat destruction = human activity makes environment unlivable.
Main reasons:
Land use (housing, farming, livestock)
Resource extraction (mining, logging)
Pollution (freshwater/marine)
Memory tip: “Land, resources, water → habitats suffer.”
Deforestation – Causes and Effects
📌 Definition
Deforestation is the large-scale removal of trees from forests or woodlands.
It is a major form of habitat destruction caused by human activity.
🌱 Main Causes of Deforestation
- Land Clearance for Agriculture
Forests cleared to grow crop plants or for livestock grazing. - Urban Development
Trees removed to make space for houses, roads, and industries. - Logging and Resource Extraction
Trees cut for timber, paper, and fuel. - Pollution & Fires
Forests damaged by pollution, accidental or deliberate fires.
🐾 Undesirable Effects of Deforestation

- Reduction in Biodiversity
Many species depend on forests for food and shelter.
Removing trees reduces the number of habitats, leading to fewer species. - Extinction of Species
Some species live only in specific forests.
Loss of habitat can cause permanent disappearance of species. - Soil Loss and Erosion
Tree roots hold soil together.
Without trees, rain washes soil away, leading to loss of fertile topsoil.
Makes land less suitable for future plant growth. - Flooding
Trees absorb and store rainwater.
Deforestation → more surface runoff → rivers overflow → floods. - Increase of Carbon Dioxide in the Atmosphere
Trees store carbon in their wood.
Cutting and burning trees releases CO₂ → contributes to global warming.
📊 Summary Table
| Effect | Explanation | Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced biodiversity | Fewer habitats | Ecosystem becomes unstable |
| Extinction | Loss of specific habitats | Permanent loss of species |
| Soil loss | Roots no longer hold soil | Land degradation and erosion |
| Flooding | Less water absorption | Damage to human settlements and crops |
| Increased CO₂ | Carbon released | Climate change and global warming |
⚡ Quick Recap
Deforestation = cutting forests → habitat destruction → ecological problems.
Main impacts: biodiversity ↓, extinction, soil loss, flooding, CO₂ ↑.
Memory tip: “No trees → less life, more floods, more CO₂.”
Deforestation – Effects on Habitats
📌 Definition
Deforestation is the large-scale removal of trees from forests.
It is a major cause of habitat destruction, affecting both living organisms and the environment.
🌱 Undesirable Effects
- Reducing Biodiversity
Trees provide food, shelter, and breeding grounds.
Removing forests reduces the number of habitats, causing a decline in species variety. - Extinction of Species
Some species live only in specific forest areas.
Loss of habitat can lead to species disappearing permanently. - Loss of Soil / Soil Erosion
Tree roots hold soil together.
Without trees, rain washes soil away, reducing soil fertility and harming plant growth. - Flooding
Trees absorb water during rainfall.
Deforestation → more surface runoff → rivers overflow → increased risk of floods. - Increase of Carbon Dioxide in the Atmosphere
Trees store carbon in their biomass.
Cutting or burning trees releases CO₂ → contributes to global warming.
📊 Summary Table
| Effect | Explanation | Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced biodiversity | Fewer habitats available | Ecosystem becomes unstable |
| Extinction | Species lose their only habitat | Permanent species loss |
| Soil loss | Roots absent → soil washed away | Land degradation |
| Flooding | Less water absorption | Damage to settlements and crops |
| Increased CO₂ | Carbon released from trees | Climate change |
⚡ Quick Recap
Deforestation = tree loss → habitat destruction → ecological problems.
Key impacts: biodiversity ↓, extinction, soil loss, flooding, CO₂ ↑
Memory tip: “No trees → less life, more floods, more CO₂.”
