CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-B4. Biological molecules - Study Notes- New Syllabus
CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-B4. Biological molecules – Study Notes
CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-B4. Biological molecules – Study Notes -CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- List the chemical elements that make up: carbohydrates, fats and proteins
- State that large molecules are made from smaller molecules, limited to:
(a) starch, glycogen and cellulose from glucose
(b) proteins from amino acids
(c) fats and oils from fatty acids and glycerol - Describe the use of:
(a) iodine solution test for starch
(b) Benedict’s solution test for reducing sugars
(c) biuret test for proteins
(d) ethanol emulsion test for fats and oils
CIE iGCSE Co-Ordinated Sciences-Concise Summary Notes- All Topics
Chemical Elements of Biological Molecules
📌 Key Idea
All biological molecules contain Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O). Some also contain Nitrogen (N) and Sulfur (S).
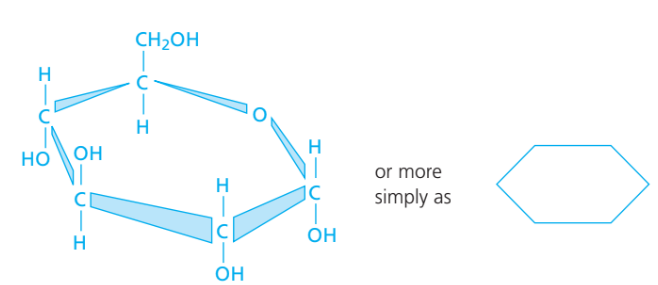
Carbohydrates
- Elements: C, H, O only
- Ratio → H:O ≈ 2:1 (like water)
- Basic unit: Monosaccharide (e.g. glucose, C₆H₁₂O₆)
- Examples: Starch, glycogen, cellulose
Fats (Lipids)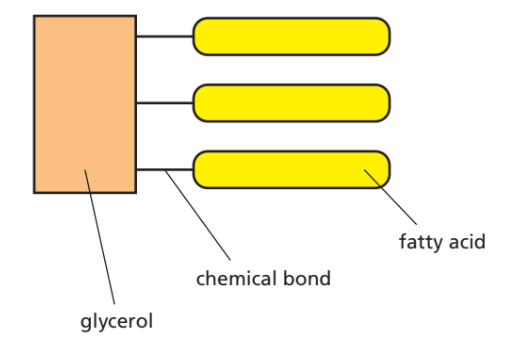
- Elements: C, H, O (but less oxygen than carbohydrates)
- Structure: 1 glycerol + 3 fatty acids
- Examples: Oils, waxes, animal fats
Proteins
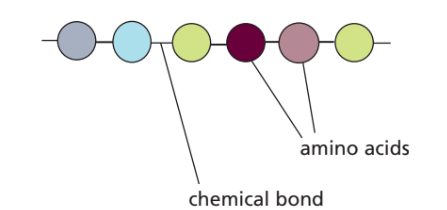
- Elements: C, H, O, N (often S too)
- Basic unit: Amino acids (20 types)
- Functions: – Structural: muscles, membranes – Functional: enzymes (biological catalysts)
📊 Summary Table
| Molecule | Elements Present | Sub-units | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | C, H, O | Monosaccharides (e.g. glucose) | Starch, glycogen, cellulose |
| Fats (Lipids) | C, H, O (low O) | Glycerol + fatty acids | Oils, waxes, fats |
| Proteins | C, H, O, N, (S) | Amino acids | Enzymes, muscle, haemoglobin |
📝 Quick Recap
Carbs = C, H, O → quick energy + storage
Fats = C, H, O (less O) → long-term energy, insulation
Proteins = C, H, O, N (+S) → structure + enzymes
💡 Mnemonic: “CHON(S) = Life’s Recipe”
Large Molecules from Small Molecules
📌 Key Idea
In living organisms, macromolecules (large molecules) are built by joining together smaller units (monomers). This process is called synthesis.
(a) Carbohydrates (Polysaccharides)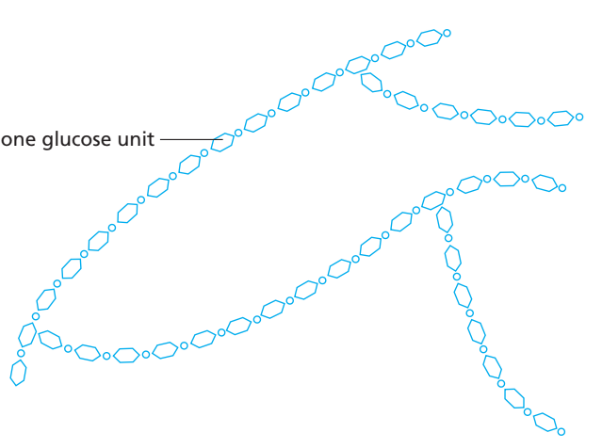
- Monomer: Glucose (a simple sugar).
- Large molecules formed:
- Starch → storage in plants.
- Glycogen → storage in animals.
- Cellulose → structural component of plant cell walls.
- All are polysaccharides, made by joining many glucose units in chains.
(b) Proteins
- Monomers: Amino acids (20 types).
- Large molecule: Proteins (long chains of amino acids joined by peptide bonds).
- Functions: Enzymes, hormones, structural proteins (e.g. muscle, collagen).
(c) Fats & Oils (Lipids)
- Sub-units:
- 1 glycerol molecule
- 3 fatty acids molecules
- Joined together to form a triglyceride (basic fat/oil structure).
- Fats → solid at room temp; Oils → liquid at room temp.
📊 Summary Table
| Large Molecule | Made From (Small Units) | Function/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Starch | Glucose | Energy store in plants |
| Glycogen | Glucose | Energy store in animals |
| Cellulose | Glucose | Plant cell wall (strength) |
| Proteins | Amino acids | Enzymes, muscle, hormones |
| Fats/Oils | Fatty acids + glycerol | Energy store, insulation |
📝 Quick Recap
Carbs: Glucose → Starch, Glycogen, Cellulose
Proteins: Amino acids → Proteins
Lipids: Fatty acids + Glycerol → Fats & Oils
💡 Trick: “Good Students Get Clever” = Glucose → Starch, Glycogen, Cellulose
Food Tests for Biological Molecules
📌 Key Idea
These are standard lab tests used to detect starch, sugars, proteins, and fats/oils in food samples.
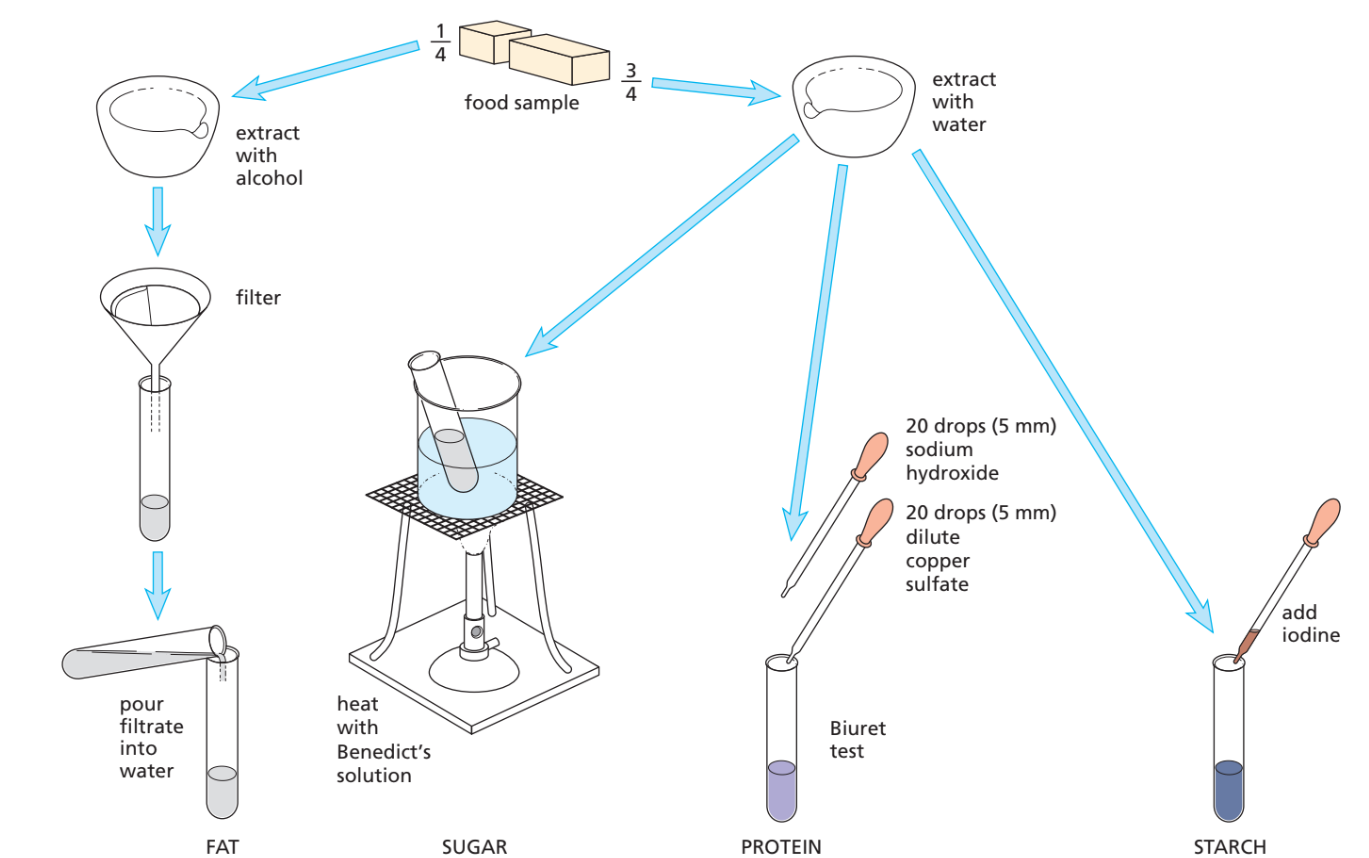
(a) Iodine Solution Test → Starch
- Add a few drops of iodine solution to the sample.
- Observation:
- Starch absent → iodine stays brown/yellow
- Starch present → iodine turns blue-black
(b) Benedict’s Solution Test → Reducing Sugars (e.g. glucose, maltose)
- Add food sample to Benedict’s solution.
- Heat mixture in a water bath (not direct flame!).
- Observation:
- No sugar → solution stays blue
- Sugar present → colour changes (with increasing sugar conc.):
Green → Yellow → Orange → Brick-red precipitate
(c) Biuret Test → Proteins
- Add a few drops of Biuret solution (sodium hydroxide + copper sulfate).
- Observation:
- Protein absent → stays blue
- Protein present → turns purple/violet
(d) Ethanol Emulsion Test → Fats & Oils
- Mix food sample with ethanol, then add water.
- Shake well.
- Observation:
- Fat absent → solution stays clear
- Fat present → forms a white/milky emulsion
📊 Summary Table
| Test | Detects | Procedure | Positive Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iodine | Starch | Add iodine solution | Blue-black colour |
| Benedict’s | Reducing sugars | Heat with Benedict’s solution | Green → Yellow → Orange → Brick-red |
| Biuret | Proteins | Add Biuret solution | Purple/violet |
| Ethanol Emulsion | Fats & Oils | Add ethanol + water | White milky emulsion |
📝 Quick Recap
Iodine → Starch → Blue-black
Benedict’s + Heat → Reducing sugar → Brick-red ppt
Biuret → Protein → Purple
Ethanol + Water → Fat → Milky white
💡 Trick: “I See Big Eggs”
I = Iodine (Starch)
C = Colour change (Blue-black)
B = Benedict’s (Sugar)
E = Ethanol (Fat)
