CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-B8.1 Xylem and phloem- Study Notes- New Syllabus
CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-B8.1 Xylem and phloem – Study Notes
CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-B8.1 Xylem and phloem – Study Notes -CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
Core
- State the functions of xylem and phloem:
(a) xylem – transport of water and mineral ions, and support
(b) phloem – transport of sucrose and amino acids - Identify in diagrams and images the position of xylem and phloem as seen in sections of roots, stems and leaves of non-woody dicotyledonous plants
CIE iGCSE Co-Ordinated Sciences-Concise Summary Notes- All Topics
Transport in Plants: Xylem and Phloem
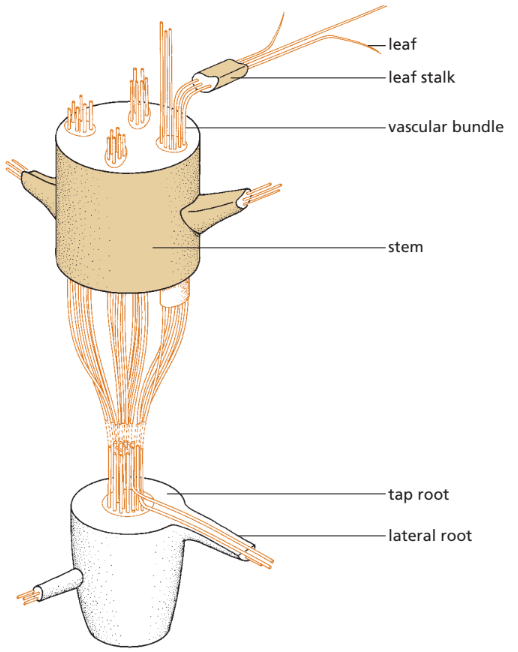
📌 Vascular bundles
- Found in roots, stems, leaf stalks, and leaf veins.
- Connect throughout the plant to form a transport system.
- Made up of xylem and phloem, surrounded by supporting cells.
1. Xylem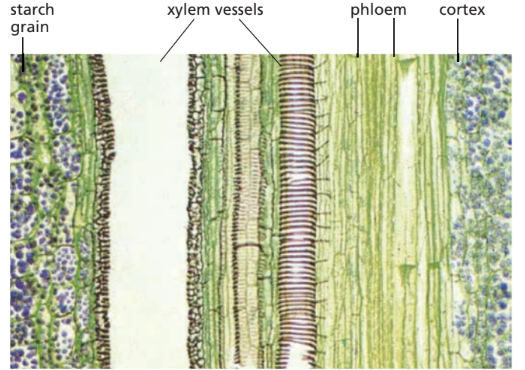
- Functions:
- Transport of water from roots → stem → leaves.
- Transport of mineral ions (dissolved salts) absorbed from the soil.
- Support: Thickened walls of xylem vessels provide mechanical strength to the plant.
- Key features:
- Made of elongated vessels.
- Lignified walls help in support and prevent collapse under tension.
- Pathway: Water enters root hairs → passes through root cortex → enters xylem → moves up to stem and leaves.
- Example: Water moves by transpiration pull and cohesion-tension.
2. Phloem
- Functions:
- Transport of sucrose (from leaves, where photosynthesis occurs) to other parts of the plant.
- Transport of amino acids (for growth and protein synthesis).
- Key features: Made of sieve tube elements with companion cells.
- Flow: Can be upwards or downwards (source → sink).
- Pathway: Sugars produced in leaves → transported via phloem → delivered to roots, stems, growing regions, or storage organs.
- Example: Food stored in roots (like carrots or turnips) comes from leaf phloem transport.
🔹 Quick Comparison
| Tissue | Main Function | Direction | Structure Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xylem | Water & mineral transport + support | Roots → leaves | Lignified vessels |
| Phloem | Sugar & amino acid transport | Up & down | Sieve tubes + companion cells |
💡 Memory Tip:
Xylem → X = eXits from roots (upwards), carries water/minerals.
Phloem → Phood = carries food (sugars/amino acids) to all parts.
Xylem & Phloem in Non-Woody Dicot Plants
In non-woody dicotyledons, xylem and phloem are part of vascular bundles, which are arranged differently in roots, stems, and leaves.
1. Root (Transverse Section)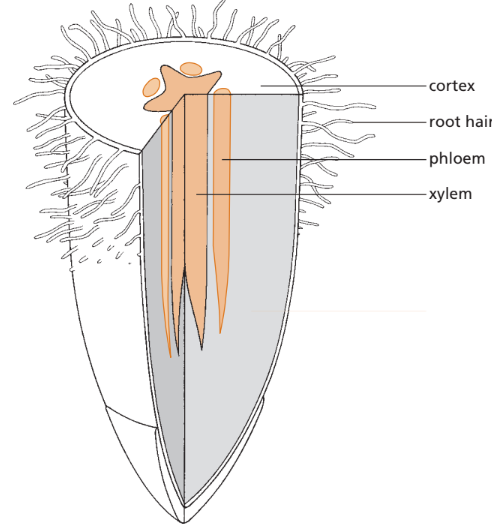
- Xylem: Central star-shaped or cross-shaped in the middle.
- Phloem: Found in between the arms of the xylem star.
- Vascular bundle: Xylem + Phloem together.
- Function: Xylem carries water/minerals upward; phloem carries food downward.
2. Stem (Transverse Section)
- Vascular bundles: Arranged in a ring around the central pith.

- Xylem: Faces toward the center of the stem.
- Phloem: Faces toward the outside of the stem.
- Cambium: Lies between xylem and phloem for secondary growth.
- Position: Outside → Phloem → Cambium → Xylem → Pith ← Center
3. Leaf (Transverse Section through Vein / Midrib)
- Xylem: Located on the upper side of the vascular bundle (closer to the upper epidermis).
- Phloem: Located on the lower side (closer to the lower epidermis).
- Vein structure: Ensures water reaches mesophyll for photosynthesis; sugar moves to phloem.
🔹 Quick Tip:
Root: Xylem in center, phloem between xylem arms.
Stem: Vascular bundles in a ring; xylem inner, phloem outer.
Leaf: Xylem on top, phloem on bottom.