CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-C10.2 Air quality and climate- Study Notes- New Syllabus
CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-C10.2 Air quality and climate – Study Notes
CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-C10.2 Air quality and climate – Study Notes -CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
Core
- State the composition of clean, dry air as approximately 78% nitrogen, N₂, 21% oxygen, O₂, and the remainder as a mixture of noble gases and carbon dioxide, CO₂
- State the source of each of these air pollutants, limited to:
(a) carbon dioxide from the complete combustion of carbon-containing fuels
(b) carbon monoxide and particulates from the incomplete combustion of carbon-containing fuels
(c) methane from the decomposition of vegetation and waste gases from digestion in animals
(d) oxides of nitrogen from car engines
(e) sulfur dioxide from the combustion of fossil fuels which contain sulfur compounds - State the adverse effect of these air pollutants, limited to:
(a) carbon dioxide: higher levels of carbon dioxide leading to increased global warming, which leads to climate change
(b) carbon monoxide: toxic gas
(c) particulates: increased risk of respiratory problems and cancer
(d) methane: higher levels of methane leading to increased global warming, which leads to climate change
(e) oxides of nitrogen: acid rain and respiratory problems
(f) sulfur dioxide: acid rain - State and explain strategies to reduce the effects of climate change:
(a) planting trees
(b) reduction in livestock farming
(c) decreasing use of fossil fuels
(d) increasing use of hydrogen and renewable energy, e.g. wind, solar
Supplement
- State and explain strategies to reduce the effects of acid rain: reducing emissions of sulfur dioxide by using low-sulfur fuels and flue gas desulfurisation with calcium oxide
- Describe how the greenhouse gases carbon dioxide and methane cause global warming, limited to:
(a) the absorption, reflection and emission of thermal energy
(b) reducing thermal energy loss to space - Explain how oxides of nitrogen form in car engines and describe their removal by catalytic converters, limited to: 2CO + 2NO → 2CO₂ + N₂
CIE iGCSE Co-Ordinated Sciences-Concise Summary Notes- All Topics
Composition of Clean, Dry Air
Clean, dry air is a mixture of gases in fixed proportions. It contains mostly nitrogen and oxygen, with small amounts of other gases.![]()
Approximate Composition:
- 78% Nitrogen (\(\mathrm{N_2}\))
- 21% Oxygen (\(\mathrm{O_2}\))
- ~1% Mixture of noble gases (e.g. argon, neon) and carbon dioxide (\(\mathrm{CO_2}\))
Key Idea:
- Nitrogen is the largest component of air, followed by oxygen.
- The small proportion of carbon dioxide is essential for photosynthesis in plants.
- Noble gases (mainly argon) are chemically unreactive.
Example :
A sample of dry air has a volume of \( \mathrm{200 \, cm^3} \). Calculate the approximate volumes of nitrogen, oxygen, and other gases present.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Nitrogen = \( \mathrm{78\% \times 200 = 156 \, cm^3} \).
Step 2: Oxygen = \( \mathrm{21\% \times 200 = 42 \, cm^3} \).
Step 3: Other gases = \( \mathrm{200 – (156 + 42) = 2 \, cm^3} \).
Final Answer: Nitrogen = \( \mathrm{156 \, cm^3} \), Oxygen = \( \mathrm{42 \, cm^3} \), Others = \( \mathrm{2 \, cm^3} \).
Sources of Common Air Pollutants
Air pollutants are released from different human and natural activities. Their sources are as follows:![]()
(a) Carbon dioxide (\(\mathrm{CO_2}\))
- Source: Produced from the complete combustion of carbon-containing fuels (coal, oil, gas, petrol, wood).
- Example: \(\mathrm{C + O_2 \rightarrow CO_2}\)
- Effect: Major greenhouse gas contributing to climate change.
(b) Carbon monoxide (\(\mathrm{CO}\)) and particulates
- Source: Formed during the incomplete combustion of carbon-containing fuels.
- Example: \(\mathrm{2C + O_2 \rightarrow 2CO}\)
- Effect: CO is toxic (binds with haemoglobin in blood); particulates cause breathing problems and global dimming.
(c) Methane (\(\mathrm{CH_4}\))
- Source: Released from the decomposition of vegetation and waste in landfill sites, and from digestion in animals (e.g. cows release methane in digestion).
- Effect: Potent greenhouse gas, more effective than \(\mathrm{CO_2}\) at trapping heat.
(d) Oxides of nitrogen (\(\mathrm{NO_x}\))
- Source: Produced in car engines where high temperatures cause nitrogen and oxygen in the air to react.
- Example: \(\mathrm{N_2 + O_2 \rightarrow 2NO}\), followed by \(\mathrm{2NO + O_2 \rightarrow 2NO_2}\)
- Effect: Cause respiratory problems and contribute to acid rain and smog.
(e) Sulfur dioxide (\(\mathrm{SO_2}\))
- Source: Released during the combustion of fossil fuels (coal, oil, gas) that contain sulfur compounds.
- Example: \(\mathrm{S + O_2 \rightarrow SO_2}\)
- Effect: Causes acid rain, which damages buildings, kills plants, and harms aquatic life.
Example :
State the pollutant formed from incomplete combustion of petrol in car engines and explain why it is dangerous.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: The pollutant is carbon monoxide (CO).
Step 2: It is formed when there is insufficient oxygen for complete combustion.
Step 3: Carbon monoxide is dangerous because it binds with haemoglobin in the blood, preventing oxygen transport.
Final Answer: The pollutant is CO, and it is dangerous because it is a toxic gas that prevents oxygen being carried in the blood.
Adverse Effects of Common Air Pollutants
Different air pollutants cause harm to health, the environment, and the climate. Their adverse effects are: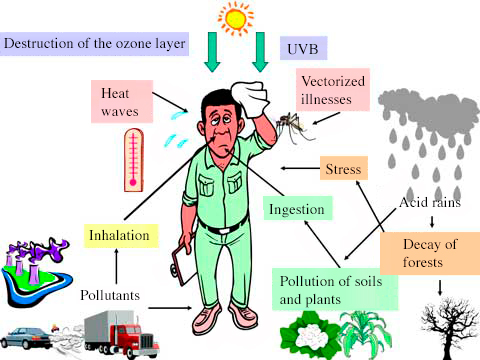
(a) Carbon dioxide (\(\mathrm{CO_2}\))
- Higher levels of \(\mathrm{CO_2}\) increase the greenhouse effect.
- This causes global warming, which leads to climate change (melting ice caps, rising sea levels, extreme weather).
(b) Carbon monoxide (\(\mathrm{CO}\))
- Carbon monoxide is a toxic gas.
- It binds to haemoglobin in the blood, reducing oxygen transport → can cause fainting, brain damage, or death.
(c) Particulates
- Tiny solid particles that pollute the air.
- Increase the risk of respiratory problems (asthma, bronchitis) and lung cancer.
- Also cause global dimming by reflecting sunlight away from Earth.
(d) Methane (\(\mathrm{CH_4}\))
- Methane is a powerful greenhouse gas.
- Higher levels of methane lead to global warming and climate change.
(e) Oxides of nitrogen (\(\mathrm{NO_x}\))
- Dissolve in rainwater to form acid rain, which damages crops, trees, aquatic life, and erodes buildings.
- Cause respiratory problems such as asthma and lung irritation.
(f) Sulfur dioxide (\(\mathrm{SO_2}\))
- Dissolves in rainwater to form acid rain.
- Acid rain damages forests, harms aquatic life, and corrodes buildings and monuments.
Example :
Which air pollutant causes both climate change and is more powerful than carbon dioxide in trapping heat?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Carbon dioxide and methane both contribute to climate change.
Step 2: Methane is a more powerful greenhouse gas than CO₂.
Final Answer: The pollutant is methane (CH₄).
Strategies to Reduce the Effects of Climate Change
Human activities release greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides, which contribute to global warming and climate change. Several strategies can help reduce their effects:
(a) Planting Trees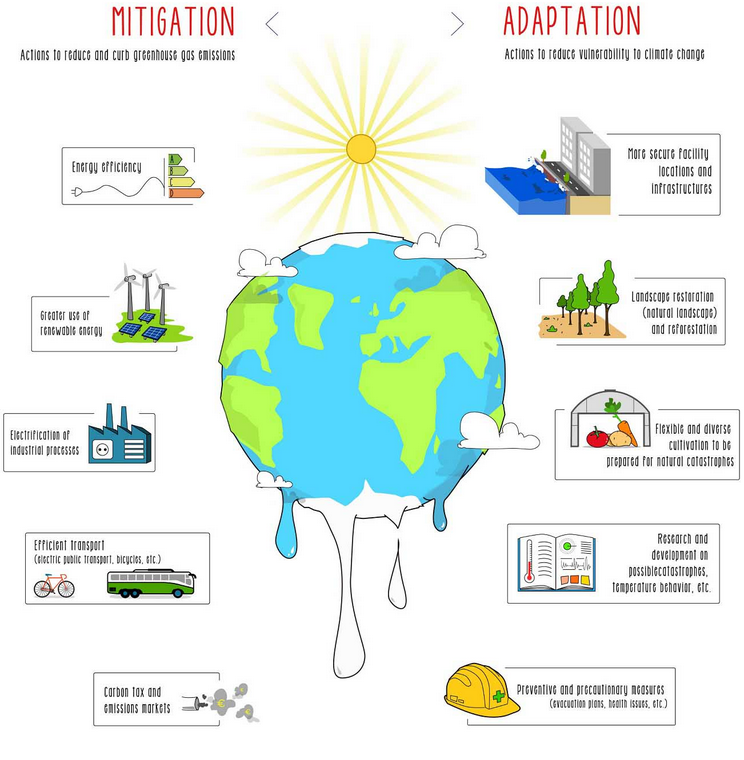
- Trees absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis.
- This reduces the concentration of \(\mathrm{CO_2}\) in the atmosphere.
- Large-scale afforestation (planting new forests) helps act as a “carbon sink”.
(b) Reduction in Livestock Farming
- Livestock such as cows and sheep release methane during digestion.
- Methane is a much stronger greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide.
- Reducing livestock farming or promoting plant-based diets helps lower methane emissions.
(c) Decreasing Use of Fossil Fuels
- Burning fossil fuels (coal, oil, gas) releases large amounts of \(\mathrm{CO_2}\).
- Reducing their use lowers carbon dioxide emissions.
- Strategies include using public transport, energy-efficient appliances, and better insulation in homes.
(d) Increasing Use of Hydrogen and Renewable Energy
- Hydrogen fuel produces only water when burned, so it does not emit \(\mathrm{CO_2}\).
- Renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power do not release greenhouse gases when generating electricity.
- Transitioning to renewables reduces dependence on fossil fuels and cuts emissions.
Example :
Explain how planting more trees helps to reduce the effects of climate change.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Trees absorb \(\mathrm{CO_2}\) from the atmosphere during photosynthesis.
Step 2: This lowers the concentration of greenhouse gases.
Step 3: With less carbon dioxide, less heat is trapped in the atmosphere.
Final Answer: Planting trees reduces the greenhouse effect, helping to slow down global warming and climate change.
Strategies to Reduce the Effects of Acid Rain
Acid rain is mainly caused by sulfur dioxide (\(\mathrm{SO_2}\)) released from burning fossil fuels that contain sulfur compounds. To reduce its effects, the following strategies are used:
(a) Using Low-Sulfur Fuels![]()
- Coal, oil, and gas often contain sulfur impurities.
- Burning fuels with less sulfur reduces the release of \(\mathrm{SO_2}\) into the atmosphere.
- This lowers the amount of acid rain formed.
(b) Flue Gas Desulfurisation (FGD)
- In power stations, waste gases (“flue gases”) released from burning fossil fuels contain \(\mathrm{SO_2}\).
- These gases are treated with calcium oxide (\(\mathrm{CaO}\)) or calcium carbonate (\(\mathrm{CaCO_3}\)).
- The calcium compounds react with \(\mathrm{SO_2}\) to form calcium sulfite, which is harmless.
\(\mathrm{CaO + SO_2 \rightarrow CaSO_3}\)
\(\mathrm{CaCO_3 + SO_2 \rightarrow CaSO_3 + CO_2}\)
Key Idea:
- Both methods reduce the release of sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere.
- This prevents the formation of acid rain, protecting forests, aquatic life, and buildings.
Example :
How does flue gas desulfurisation help reduce acid rain?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Flue gases from burning fuels contain \(\mathrm{SO_2}\).
Step 2: The gases are treated with calcium oxide or calcium carbonate.
Step 3: They react with \(\mathrm{SO_2}\) to form harmless calcium sulfite.
Final Answer: Flue gas desulfurisation removes \(\mathrm{SO_2}\), reducing acid rain formation.
How Carbon Dioxide and Methane Cause Global Warming
Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (\(\mathrm{CO_2}\)) and methane (\(\mathrm{CH_4}\)) trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere. This process is called the greenhouse effect, and it leads to global warming.
(a) Absorption, Reflection and Emission of Thermal Energy![]()
- The Sun emits short-wave radiation (light and heat) which passes through the atmosphere and warms the Earth’s surface.
- The warmed Earth re-emits this energy as long-wave infrared (IR) radiation.
- \(\mathrm{CO_2}\) and \(\mathrm{CH_4}\) absorb and re-emit some of this infrared radiation back towards the Earth’s surface.
- This increases the thermal energy retained in the atmosphere.
(b) Reducing Thermal Energy Loss to Space
- Without greenhouse gases, much of the Earth’s heat would escape into space.
- Greenhouse gases form a “blanket” in the atmosphere, preventing heat loss.
- Higher concentrations of \(\mathrm{CO_2}\) and \(\mathrm{CH_4}\) mean more heat is trapped, leading to global warming and climate change.
Example :
Explain why an increase in carbon dioxide levels leads to higher global temperatures.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: The Earth’s surface absorbs sunlight and re-emits it as infrared radiation.
Step 2: Carbon dioxide absorbs and re-emits infrared radiation back towards Earth.
Step 3: This reduces the amount of heat energy lost to space.
Final Answer: Higher levels of \(\mathrm{CO_2}\) trap more heat, causing global warming.
Oxides of Nitrogen and Their Removal
Formation of Oxides of Nitrogen:
Inside a car engine, the temperature is extremely high.
![]()
- At these high temperatures, nitrogen (\(\mathrm{N_2}\)) and oxygen (\(\mathrm{O_2}\)) from the air react together.
- This forms nitrogen monoxide (\(\mathrm{NO}\)) and nitrogen dioxide (\(\mathrm{NO_2}\)), collectively called oxides of nitrogen (\(\mathrm{NO_x}\)).
\(\mathrm{N_2 + O_2 \;\;\rightarrow\;\; 2NO}\)
\(\mathrm{2NO + O_2 \;\;\rightarrow\;\; 2NO_2}\)
Problems Caused by Oxides of Nitrogen:
- They cause respiratory problems in humans.
- They contribute to the formation of acid rain when dissolved in water.
- They also contribute to photochemical smog.
Removal by Catalytic Converters:
![]()
- Modern cars are fitted with catalytic converters in the exhaust system.
- These contain platinum or rhodium catalysts that speed up reactions.
- Oxides of nitrogen react with carbon monoxide in the converter to form harmless gases.
\(\mathrm{2CO + 2NO \;\;\rightarrow\;\; 2CO_2 + N_2}\)
Example :
Explain why catalytic converters are fitted to car exhaust systems.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Oxides of nitrogen form in car engines due to high temperatures.
Step 2: Carbon monoxide is also produced from incomplete combustion.
Step 3: In the catalytic converter, \(\mathrm{2CO + 2NO \;\;\rightarrow\;\; 2CO_2 + N_2}\).
Final Answer: Catalytic converters reduce air pollution by removing both CO and NO_x, producing less harmful gases.
