CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-C2.3 Isotopes- Study Notes- New Syllabus
CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-C2.3 Isotopes – Study Notes
CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences-C2.3 Isotopes – Study Notes -CIE iGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
Core
- Define isotopes as different atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
- Interpret and use symbols for atoms, e.g. C⁶₁₂, and ions, e.g. Cl¹⁷₃₅⁻
Supplement
- State that isotopes of the same element have the same chemical properties because they have the same number of electrons and therefore the same electronic configuration
CIE iGCSE Co-Ordinated Sciences-Concise Summary Notes- All Topics
Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that contain the same number of protons (same atomic number) but differ in the number of neutrons. This results in different mass numbers for each isotope.
![]()
Examples:
- Carbon-12 (\( ^{12}\text{C} \)) → 6 protons, 6 neutrons
- Carbon-13 (\( ^{13}\text{C} \)) → 6 protons, 7 neutrons
- Carbon-14 (\( ^{14}\text{C} \)) → 6 protons, 8 neutrons
Example
Explain why Carbon-12 and Carbon-14 are isotopes of the same element.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Both Carbon-12 and Carbon-14 have 6 protons, so they are the same element (carbon). However, Carbon-12 has 6 neutrons, while Carbon-14 has 8 neutrons. The difference in neutrons gives them different mass numbers (12 and 14), making them isotopes of carbon.
Same chemical properties of isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Because chemical properties depend on the number and arrangement of electrons:
- All isotopes of an element have the same number of electrons.
- Electrons occupy the same shells and have the same configuration.
- Therefore, isotopes undergo the same chemical reactions and form the same compounds, even though their physical properties (like mass or stability) may differ.
Example
Explain why Carbon-12 and Carbon-14 react identically with oxygen.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Both Carbon-12 (\( ^{12}\text{C} \)) and Carbon-14 (\( ^{14}\text{C} \)) have 6 electrons arranged in the same configuration (2,4). The chemical properties of carbon depend on the valence electrons (outer shell electrons), which are the same for both isotopes. Therefore, both isotopes react identically with oxygen to form carbon dioxide (\( \text{CO}_2 \)), despite having different numbers of neutrons.
Symbols for atoms and ions
Atomic and ionic symbols provide information about the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons:![]()
- The subscript (bottom number) is the atomic number, representing the number of protons. In a neutral atom, it also equals the number of electrons.
- The superscript (top number) is the mass number, representing the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
- An ion is an atom that has gained or lost electrons, indicated by a charge symbol (\( + \) or \( – \)) next to the element symbol. A negative charge means extra electrons, and a positive charge means electrons are missing.
Examples:
- \( ^{12}_6\text{C} \) – Carbon atom: 6 protons, 6 neutrons (12 − 6), 6 electrons.
- \( ^{35}_{17}\text{Cl}^- \) – Chloride ion: 17 protons, 18 neutrons (35 − 17), 18 electrons (1 extra due to negative charge).
Example
Given \( ^{23}_{11}\text{Na}^+ \), identify the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Protons = 11 (atomic number)
Neutrons = 23 − 11 = 12
Electrons = 11 − 1 = 10 (because of the positive charge)
This shows how atomic and ionic symbols convey detailed information about subatomic particles.
Isotopes and Their Chemical Properties
Isotopes of the same element have the same chemical properties because they have the same number of electrons and therefore the same electronic configuration.
Understanding Isotopes:
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have: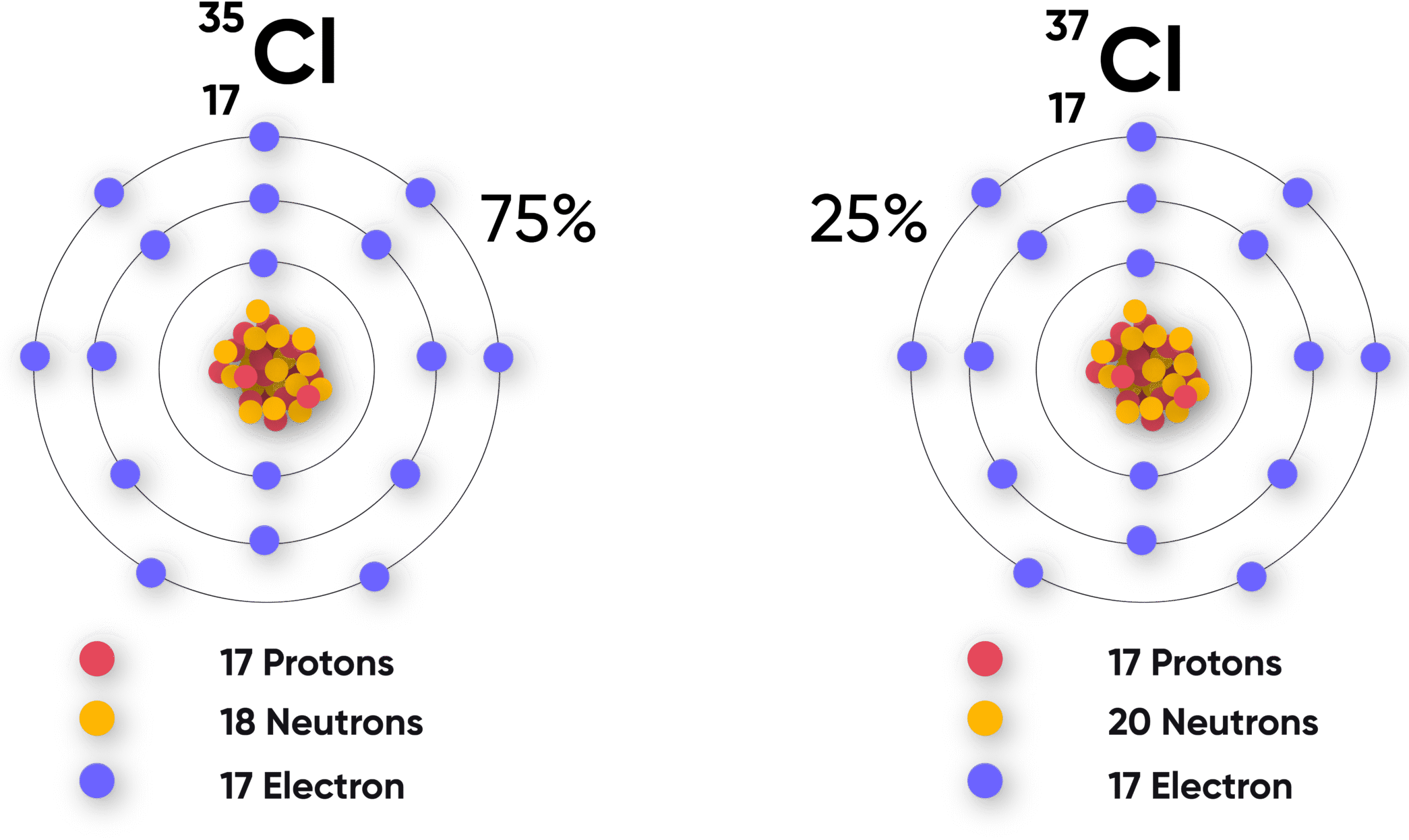
- The same number of protons (same proton/atomic number), but
- Different numbers of neutrons (different mass numbers).
Since the number of protons is the same, isotopes also have the same number of electrons in a neutral atom.
\(\mathrm{Isotopes → Same\ element → Same\ Z\ (protons),\ Different\ A\ (mass)}\)
Reason for Similar Chemical Properties:
- Chemical reactions depend on how electrons are arranged that is, on the electronic configuration.
- Since isotopes of the same element have the same electron arrangement, they react in exactly the same way chemically.
- Differences between isotopes only affect physical properties (like density or rate of diffusion), not chemical behaviour.
Example : Isotopes of Chlorine
- \(\mathrm{^{35}_{17}Cl}\): 17 protons, 18 neutrons, 17 electrons → 2,8,7
- \(\mathrm{^{37}_{17}Cl}\): 17 protons, 20 neutrons, 17 electrons → 2,8,7
- Both isotopes have the same outer shell configuration (7 electrons) → same reactivity.
| Property | Same for Isotopes? | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Properties | Yes | Same number of electrons → same electronic structure |
| Physical Properties | No | Different masses due to different numbers of neutrons |
Example :
Explain why the isotopes \(\mathrm{^{35}_{17}Cl}\) and \(\mathrm{^{37}_{17}Cl}\) have the same chemical properties.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Both isotopes have 17 protons and 17 electrons.
Step 2: Therefore, both have the same electron configuration → 2,8,7.
Step 3: Chemical properties depend on outer shell electrons.
Final Answer: Both isotopes of chlorine have the same electronic configuration (2,8,7), so they have the same chemical properties.
