CIE IGCSE Mathematics (0580) Coordinates Study Notes - New Syllabus
CIE IGCSE Mathematics (0580) Coordinates Study Notes
LEARNING OBJECTIVE
- Use and interpret Cartesian coordinates in two dimensions.
Key Concepts:
- Cartesian coordinates
Coordinates in Two Dimensions
Coordinates in Two Dimensions
A coordinate is a pair of numbers used to locate a point on a grid. The system used is called the Cartesian coordinate system. Each point is written as an ordered pair \( (x, y) \), where:
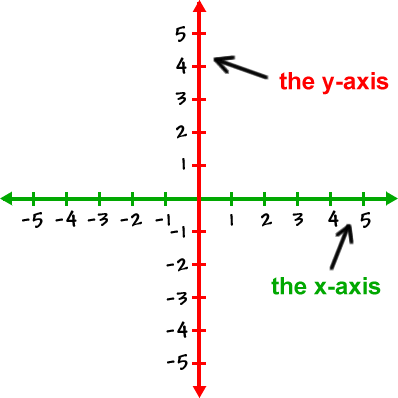
- x is the horizontal position (left or right of the origin).
- y is the vertical position (above or below the origin).
Axes and Quadrants
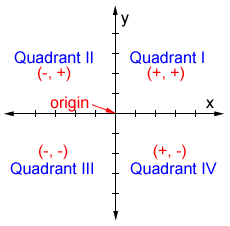
The Cartesian plane is divided into four quadrants by the x-axis (horizontal) and y-axis (vertical):
- Quadrant I: \( x > 0, y > 0 \)
- Quadrant II: \( x < 0, y > 0 \)
- Quadrant III: \( x < 0, y < 0 \)
- Quadrant IV: \( x > 0, y < 0 \)
Plotting and Reading Coordinates
To plot a point like \( (2, 5) \), start at the origin (0, 0), move 2 units to the right along the x-axis, and then 5 units up on the y-axis. Always read coordinates as \( (x, y) \): first left/right, then up/down.
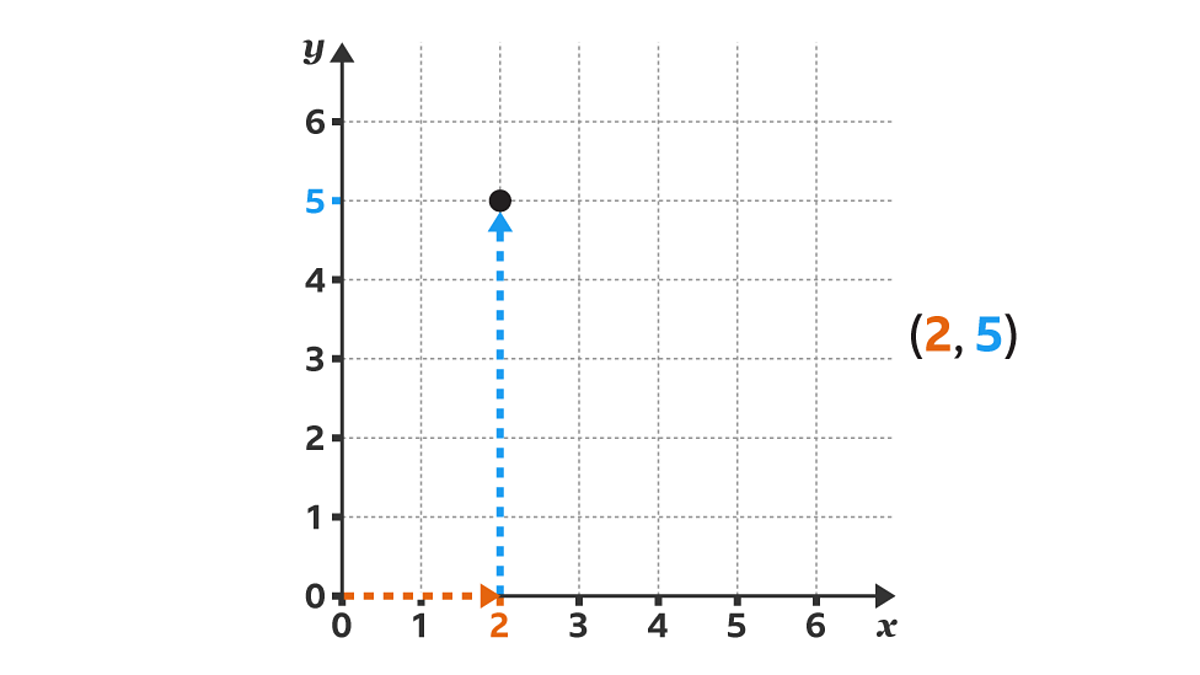
Example:
Plot the point \( (4, -3) \). State the quadrant it lies in.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Start from the origin, move 4 units right and 3 units down.
This point lies in Quadrant IV.
Example :
Plot the points \( A(2, 3) \), \( B(2, -1) \), and \( C(-1, -1) \) on a Cartesian plane. Join them in order to form a triangle.
What type of triangle is formed?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
First, plot the points:
- \( A(2, 3) \) lies 2 units to the right of the origin and 3 units up.
- \( B(2, -1) \) lies 2 units to the right and 1 unit down.
- \( C(-1, -1) \) lies 1 unit to the left and 1 unit down.
Join points A → B → C → A. The triangle has:
- AB is vertical (same x-coordinate)
- BC is horizontal (same y-coordinate)
- AC is diagonal
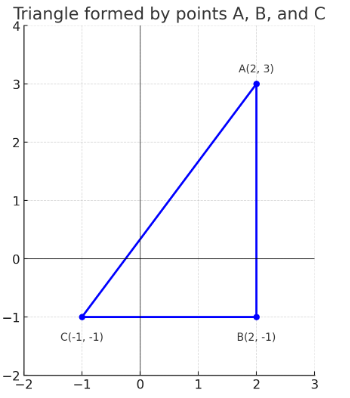
This forms a right-angled triangle at point \( B \).
