CIE IGCSE Mathematics (0580) Functions Study Notes - New Syllabus
CIE IGCSE Mathematics (0580) Functions Study Notes
LEARNING OBJECTIVE
- Understanding Functions, Domain and Range
Key Concepts:
- Functions, Domain and Range
- Inverse Functions
- Composite Functions
Functions, Domain and Range
Functions, Domain and Range
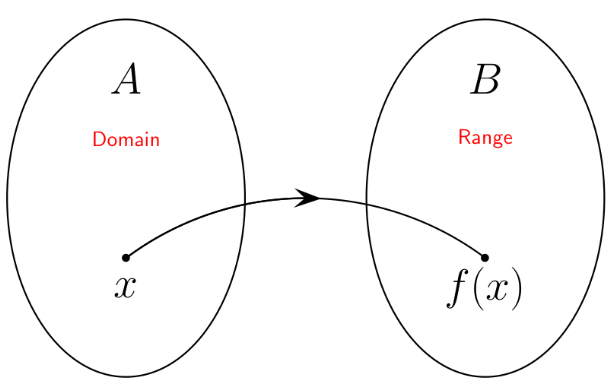
A function is a rule that assigns exactly one output value to each input value. In mathematics, this relationship is often written as:
$ f(x) = \text{some expression in } x $
The letter \( f \) is the name of the function, and \( x \) is the input variable. The output is denoted by \( f(x) \). This is called function notation.
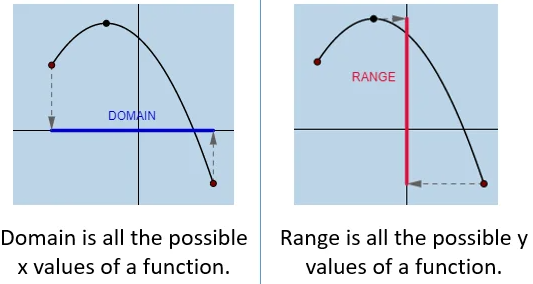
Domain
The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values (x-values) for which the function is defined.
- Example: The function \( f(x) = \frac{1}{x – 2} \) is undefined when \( x = 2 \), so the domain is all real numbers except 2.
Range
The range of a function is the set of all possible output values (f(x)) the function can take based on the domain.
- Example: For \( f(x) = x^2 \), where \( x \in \mathbb{R} \), the output is always \( \geq 0 \), so the range is \( f(x) \geq 0 \).
Function Notation
If \( f(x) = 2x + 1 \), then to evaluate the function at \( x = 4 \), substitute:
$ f(4) = 2(4) + 1 = 9 $
Example:
Let \( f(x) = 3x^2 – 5 \). Find:
- \( f(2) \)
- \( f(-1) \)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
\( f(2) = 3(2)^2 – 5 = 3(4) – 5 = 12 – 5 = 7 \)
\( f(-1) = 3(-1)^2 – 5 = 3(1) – 5 = 3 – 5 = -2 \)
Answers: \( f(2) = 7 \), \( f(-1) = -2 \)
Example:
Given \( f(x) = \frac{4}{x + 3} \), state the domain and evaluate \( f(-2) \).
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Domain: Denominator cannot be 0 → \( x \neq -3 \)
So domain is all real numbers except \( x = -3 \)
\( f(-2) = \frac{4}{-2 + 3} = \frac{4}{1} = 4 \)
Inverse Functions
Inverse Functions
An inverse function reverses the effect of a function. If a function takes an input \( x \) and gives an output \( y \), the inverse function takes \( y \) and gives back the original input \( x \).
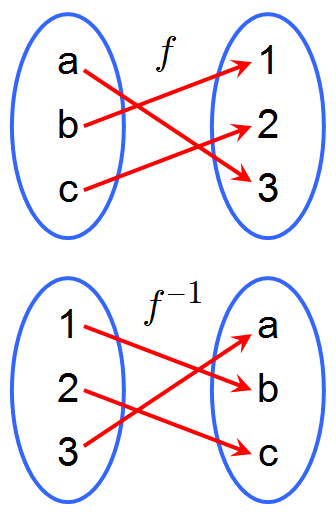
If \( f(x) \) is a function, its inverse is written as \( f^{-1}(x) \). The key idea is:
$ f(f^{-1}(x)) = x \quad \text{and} \quad f^{-1}(f(x)) = x $
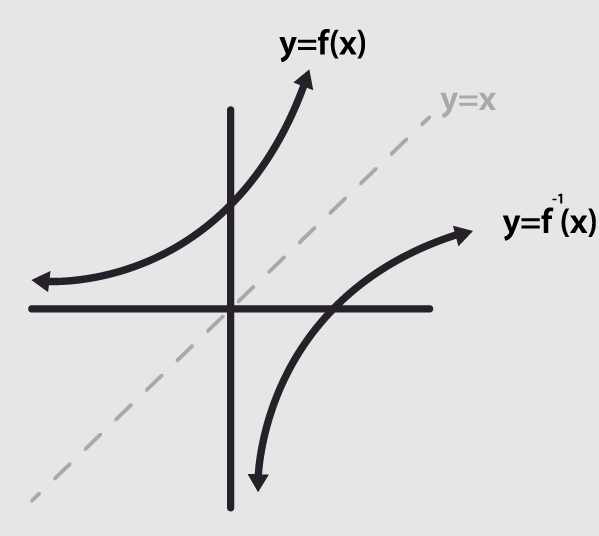
Steps to find the inverse of a function:
- Start with the equation \( y = f(x) \).
- Swap \( x \) and \( y \).
- Make \( y \) the subject again (solve for \( y \)).
- Replace \( y \) with \( f^{-1}(x) \).
Example:
Find the inverse of the function \( f(x) = 2x + 5 \)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Write \( y = 2x + 5 \)
Step 2: Swap x and y → \( x = 2y + 5 \)
Step 3: Solve for y:
\( x – 5 = 2y \Rightarrow y = \frac{x – 5}{2} \)
Step 4: Replace y with \( f^{-1}(x) \):
\( f^{-1}(x) = \frac{x – 5}{2} \)
Example:
Find the inverse of \( f(x) = \frac{x – 1}{3} \)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Write \( y = \frac{x – 1}{3} \)
Step 2: Swap x and y → \( x = \frac{y – 1}{3} \)
Step 3: Solve for y:
\( 3x = y – 1 \Rightarrow y = 3x + 1 \)
Step 4: Replace y with \( f^{-1}(x) \):
\( f^{-1}(x) = 3x + 1 \)
Composite Functions
Composite Functions
A composite function is formed when one function is applied after another. If you have two functions \( f(x) \) and \( g(x) \), then the composite function \( gf(x) \) means:
$ (gf)(x) = g(f(x)) $
This means: first apply the function \( f \), then apply \( g \) to the result of \( f(x) \).
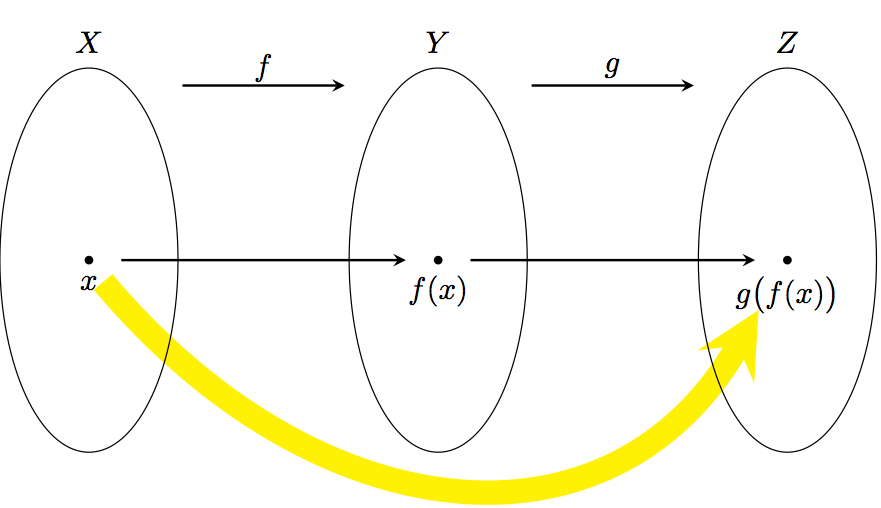
Steps to form a composite function:
- Start with the inside function \( f(x) \).
- Substitute \( f(x) \) into the outer function \( g(x) \).
- Simplify the resulting expression.
Example:
If \( f(x) = 2x + 3 \) and \( g(x) = x^2 \), find \( gf(x) \).
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Find \( f(x) = 2x + 3 \)
Step 2: Substitute into \( g(x) = x^2 \):
\( gf(x) = g(f(x)) = (2x + 3)^2 \)
Step 3: Expand the square:
\( (2x + 3)^2 = 4x^2 + 12x + 9 \)
Answer: \( gf(x) = 4x^2 + 12x + 9 \)
Example:
If \( f(x) = \dfrac{3}{x + 2} \) and \( g(x) = (3x + 5)^2 \), find \( fg(x) \).
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Find the expression for \( g(x) \):
$ g(x) = (3x + 5)^2 $
Step 2: Use this as input for \( f(x) \). That is, replace x in \( f(x) \) with \( g(x) \):
$ fg(x) = f(g(x)) = \dfrac{3}{(3x + 5)^2 + 2} $
Step 3: Final simplified expression:
$ fg(x) = \dfrac{3}{(3x + 5)^2 + 2} $
