CIE IGCSE Mathematics (0580) Geometrical terms Study Notes - New Syllabus
CIE IGCSE Mathematics (0580) Geometrical terms Study Notes
LEARNING OBJECTIVE
- Understanding the Basic Geometrical Terms
Key Concepts:
- Diiferent Shapes and Solids Vocabulary
Basic Geometrical Terms
Basic Geometrical Terms
Point: A precise location or position in space. It has no length, width, or thickness.

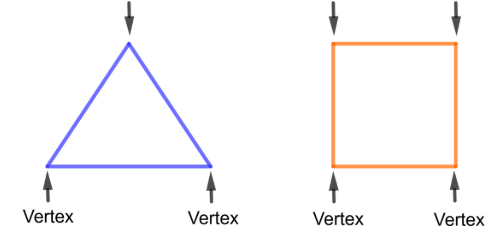
Vertex (plural: vertices): A corner or a point where two or more lines or edges meet.
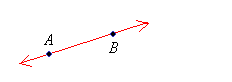
Line: A straight path that extends endlessly in both directions. It has length but no thickness.
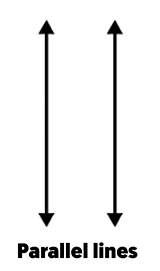
Parallel Lines: Lines in the same plane that never meet, no matter how far extended. They are always the same distance apart.
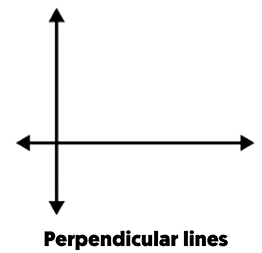
Perpendicular Lines: Lines that intersect at a right angle (90°).
Bearing: A direction or path along a compass measured in degrees from the north, always expressed using three figures (e.g. 045°, 270°).
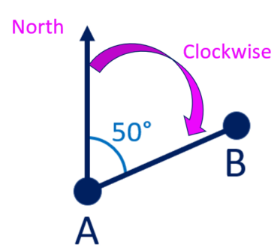
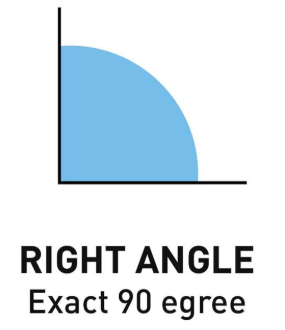
Right Angle: An angle of exactly 90°, often marked with a small square.
Acute Angle: An angle less than 90°.

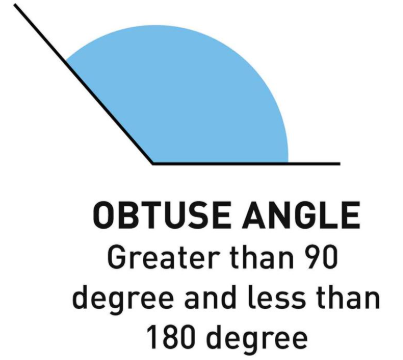
Obtuse Angle: An angle greater than 90° but less than 180°.
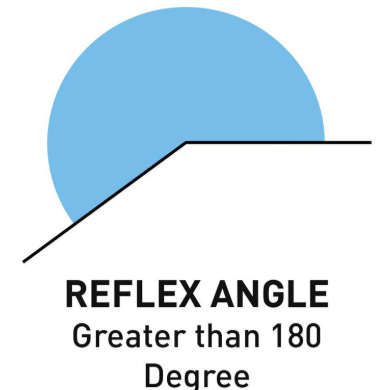
Reflex Angle: An angle greater than 180° but less than 360°.
Interior Angle: An angle formed between two sides inside a polygon.
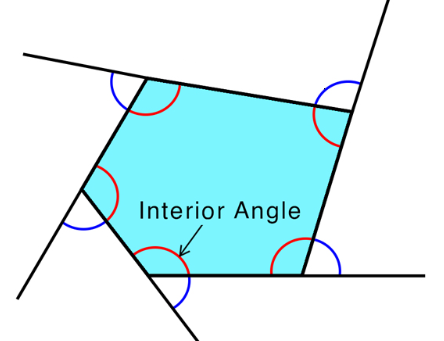
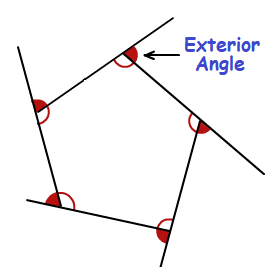
Exterior Angle: The angle formed outside a polygon when one side is extended.
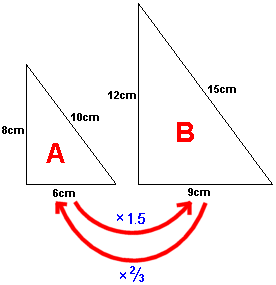
Similar Shapes: Shapes that have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. Their corresponding angles are equal, and corresponding sides are in proportion.
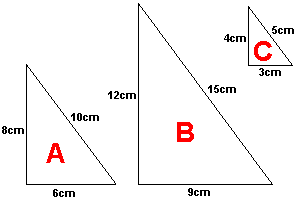
Congruent Shapes: Shapes that are exactly the same in size and shape. Their corresponding sides and angles are equal.

Scale Factor: A number that scales or multiplies all dimensions of a shape equally in enlargement or reduction. A scale factor greater than 1 enlarges; between 0 and 1 reduces.
Example:
A teacher draws three angles: 60°, 120°, and 270°. She asks the students to classify them as acute, obtuse, or reflex.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
60°: This is less than 90°, so it’s an acute angle.
120°: This is greater than 90° but less than 180°, so it’s an obtuse angle.
270°: This is greater than 180° but less than 360°, so it’s a reflex angle.
Shapes and Solids Vocabulary
Shapes and Solids Vocabulary
Triangles

- Equilateral Triangle: All three sides and angles are equal. Each angle is 60°.
- Isosceles Triangle: Two sides and two angles are equal.
- Scalene Triangle: All sides and angles are different.
- Right-angled Triangle: Has one angle exactly equal to 90°.
- Acute Triangle: All angles less then 90°.
- Obtuse Triangle: One angle is greater then 90°.
Quadrilaterals
- Square: Four equal sides and four right angles.
- Rectangle: Opposite sides equal, and all angles are right angles.
- Kite: Two pairs of adjacent sides are equal, one line of symmetry.
- Rhombus: All sides equal, opposite angles equal, no right angles unless it is a square.
- Parallelogram: Opposite sides are equal and parallel, opposite angles are equal.
- Trapezium: One pair of opposite sides is parallel.
Polygons
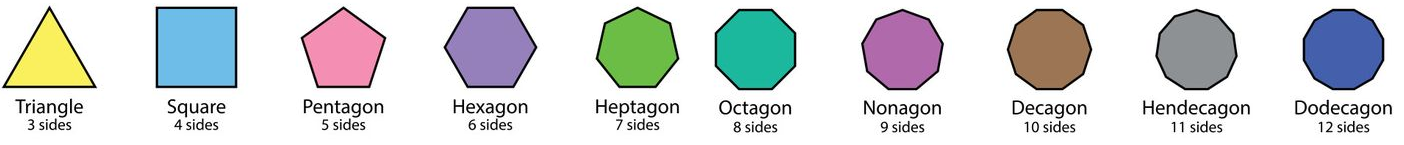
- Regular Polygon: All sides and angles are equal (e.g. regular hexagon).
- Irregular Polygon: Sides and angles are not all equal.
- Pentagon: A polygon with 5 sides.
- Hexagon: A polygon with 6 sides.
- Octagon: A polygon with 8 sides.
- Decagon: A polygon with 10 sides.
Simple Solids
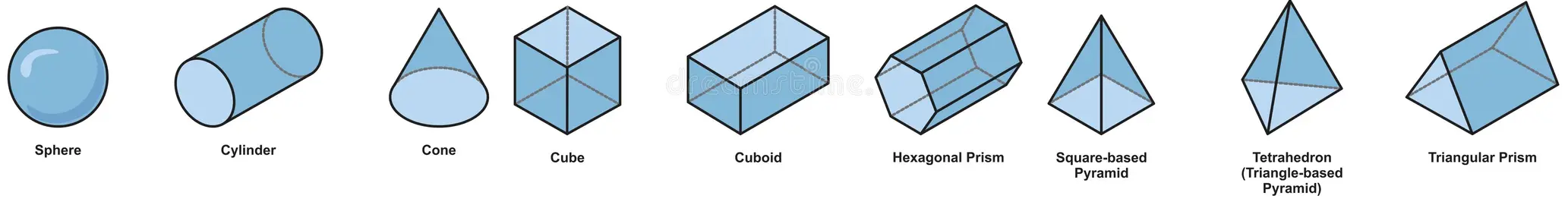
- Cube: A solid with six equal square faces.
- Cuboid: A solid with six rectangular faces.
- Prism: A solid with uniform cross-section (e.g. triangular prism).
- Cylinder: A solid with two parallel circular bases and a curved surface.
- Pyramid: A solid with a polygonal base and triangular faces meeting at a point (the apex).
- Cone: A solid with a circular base and a curved surface tapering to a point (the apex).
- Sphere: A perfectly round solid, every point on the surface is equidistant from the centre.
- Face: A flat surface of a solid shape.
- Surface: The outer layer or boundary of a solid.
- Edge: A line where two faces meet.
Example:
Which of the following solids has flat faces and straight edges only: sphere, cube, or cylinder?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Cube: Has 6 flat square faces and 12 straight edges.
Sphere: Has a smooth curved surface, no edges or flat faces
Cylinder: Has 2 circular flat faces and 1 curved surface, so not all faces are flat
Answer: Cube
Vocabulary of a Circle
Vocabulary of a Circle

- Centre: The fixed point that is equidistant from every point on the circle.
- Radius (plural: radii): A line from the centre of the circle to any point on its boundary. All radii of a circle are equal in length.
- Diameter: A straight line passing through the centre, connecting two points on the circle. It is twice the radius.
- Circumference: The total distance around the edge of the circle (its perimeter).
- Semicircle: Half of a circle, formed by cutting it along its diameter.
- Chord: A line segment whose endpoints both lie on the circle but does not pass through the centre (unless it is the diameter).
- Tangent: A straight line that touches the circle at exactly one point. It is perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact.
- Arc: A part of the circumference of a circle. It is the curved portion between two points on the circle.
- Sector: A “slice” of a circle enclosed by two radii and an arc. It looks like a piece of pie or pizza.
- Segment: A region of the circle bounded by a chord and the arc that lies between the chord’s endpoints (not necessarily a sector).
Example:
In a circle, what is the name of the line that goes from one side to the other, passing through the center?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
This line is called the diameter.
- Radius: From center to edge
- Diameter: Across the circle, through center = 2 × radius
- Chord: Line between two points on the circle (does not have to pass through the center)
Answer: Diameter
