CIE IGCSE Mathematics (0580) Magnitude of a vector Study Notes - New Syllabus
CIE IGCSE Mathematics (0580) Magnitude of a vector Study Notes
LEARNING OBJECTIVE
- Magnitude of a Vector
Key Concepts:
- Magnitude of a Vector
Magnitude of a Vector
Magnitude of a Vector
The magnitude (or length) of a vector is denoted using modulus signs like absolute value bars.
Notation:
- \( | \vec{a} | \) is the magnitude (length) of vector \( \vec{a} \)
- \( | \vec{AB} | \) is the magnitude of the vector from point A to point B
Formula for magnitude:
For vector \( \vec{v} = \begin{pmatrix} x \\ y \end{pmatrix} \),
\( \left| \begin{pmatrix} x \\ y \end{pmatrix} \right| = \sqrt{x^2 + y^2} \)
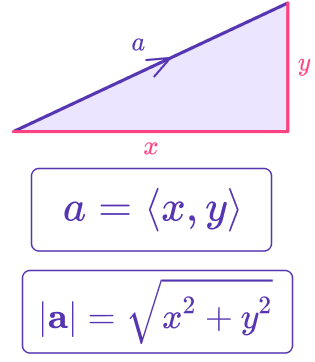
This comes from the Pythagorean Theorem where the vector forms the hypotenuse of a right triangle with legs \( x \) and \( y \).
Example :
Find the magnitude of \( \vec{a} = \begin{pmatrix} 3 \\ 4 \end{pmatrix} \)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
\( | \vec{a} | = \left| \begin{pmatrix} 3 \\ 4 \end{pmatrix} \right| = \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} = \sqrt{9 + 16} = \sqrt{25} = \boxed{5} \)
Example :
Given \( A = (2, 1) \) and \( B = (-4, 5) \), find \( |\vec{AB}| \)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
First, find vector \( \vec{AB} = \begin{pmatrix} -4 – 2 \\ 5 – 1 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} -6 \\ 4 \end{pmatrix} \)
Then, \( | \vec{AB} | = \sqrt{(-6)^2 + 4^2} = \sqrt{36 + 16} = \sqrt{52} = \boxed{2\sqrt{13}} \)
