CIE IGCSE Mathematics (0580) Time Study Notes - New Syllabus
CIE IGCSE Mathematics (0580) Time Study Notes
LEARNING OBJECTIVE
- Time
Key Concepts:
- Time & Clock
- Reading Clocks and Time Zones
Time Calculations and Unit Relationships
Time Calculations and Unit Relationships
Time is measured using various units: seconds (s), minutes (min), hours (h), days, weeks, months, and years. Calculating with time requires knowing the relationships between these units and how to convert between them.
Important Time Conversions:
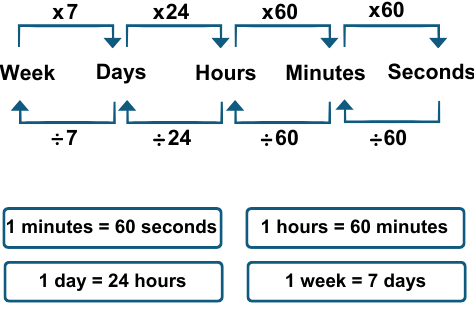
- 1 minute = 60 seconds
- 1 hour = 60 minutes
- 1 day = 24 hours
- 1 week = 7 days
- 1 year = 12 months = 365 days (or 366 in a leap year)
Tips for Calculating with Time:
- When adding or subtracting times, convert all units to the same base first (usually minutes or seconds).
- In word problems, always check what unit the final answer should be in.
- Be aware of how time formats work: 2 hours 30 minutes is not 2.3 hours but 2.5 hours.
Example:
Convert 3 hours 45 minutes into minutes.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
1 hour = 60 minutes
So, \( 3 \times 60 + 45 = 180 + 45 = 225 \) minutes
Answer: 225 minutes
Example:
How many seconds are there in 2.5 hours?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
1 hour = 60 minutes, 1 minute = 60 seconds
\( 2.5 \times 60 = 150 \) minutes
\( 150 \times 60 = 9000 \) seconds
Answer: 9000 seconds
Example:
A person works 8 hours per day for 5 days a week. How many hours does he work in 4 weeks?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Hours per week = \( 8 \times 5 = 40 \)
Total for 4 weeks = \( 40 \times 4 = 160 \) hours
Answer: 160 hours
Understanding 12-Hour and 24-Hour Clock Systems
Understanding 12-Hour and 24-Hour Clock Systems
There are two common ways to tell time: the 12-hour clock and the 24-hour clock.
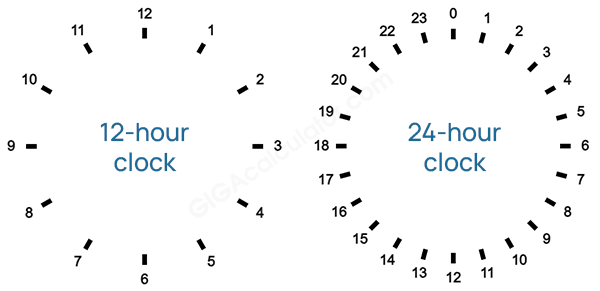
12-Hour Clock
The 12-hour clock splits the day into two halves:
- AM – from midnight (00:00) to just before noon (11:59)
- PM – from noon (12:00) to just before midnight (11:59)
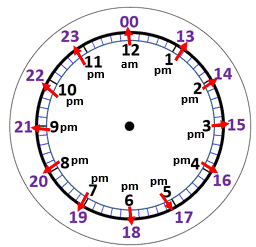
24-Hour Clock
The 24-hour clock runs from 00:00 (midnight) to 23:59. It is commonly used in timetables, airports, and military schedules.
Conversion Rules:
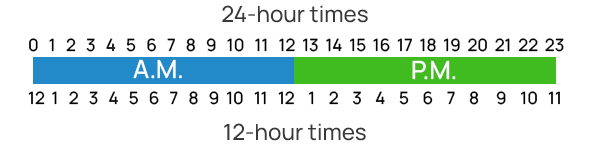
- To convert from 12-hour to 24-hour format:
- Add 12 to the hour for PM times (except 12 PM, which stays 12:00).
- AM times stay the same (but 12 AM becomes 00:00).
- To convert from 24-hour to 12-hour format:
- For times from 13:00 to 23:59, subtract 12 and add PM.
- 00:00 becomes 12:00 AM, and times from 01:00 to 11:59 are AM.
Example:
Convert 3:15 PM to 24-hour time.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
\( 3:15 + 12 = 15:15 \)
Answer: 15:15
Example:
Convert 07:40 (24-hour clock) to 12-hour time.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
07:40 is before 12:00 → AM
Answer: 7:40 AM
Example:
A flight is scheduled to depart at 00:45. What is this time in 12-hour format?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
00:45 = 12:45 AM
Answer: 12:45 AM
Reading Clocks and Time Zones
Reading Clocks and Time Zones
Being able to read and interpret time on both analog and digital clocks, as well as timetables (e.g. transport schedules, school/TV timetables), is an important real-life skill.
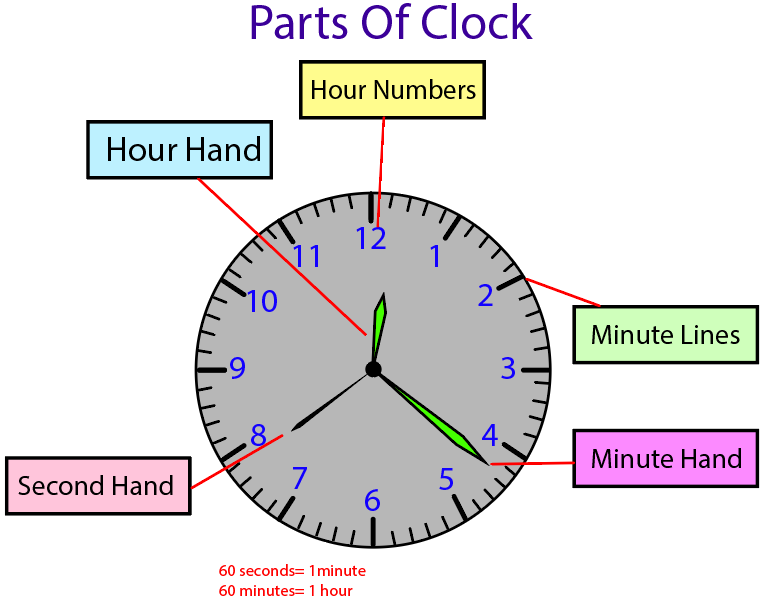
Key Ideas:
- Use either 12-hour (with AM/PM) or 24-hour format.
- Always check headings and time format on timetables.
- Add or subtract time to find durations or arrival/departure times.
Time Zones and Local Time
The Earth is divided into different time zones. The standard reference is GMT (Greenwich Mean Time), and all other zones are written as an offset, e.g. GMT+5:30 (India), GMT-4 (New York).
When a plane leaves one time zone and arrives in another, you must apply time difference to calculate local arrival/departure times.
Example:
A train departs from Delhi at 18:20 and arrives in Jaipur at 22:35. How long does the journey take?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
From 18:20 to 22:35 → Subtract:
Hours: 22 – 18 = 4
Minutes: 35 – 20 = 15
Answer: 4 hours 15 minutes
Example:
A flight leaves London (GMT) at 14:00 and takes 8 hours to reach Singapore (GMT+8). What is the local arrival time in Singapore?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
14:00 GMT + 8 hours (flight) = 22:00 GMT
Now adjust for time zone: 22:00 GMT + 8 hours = 06:00 (next day) Singapore time
Answer: 06:00 next day
Example:
New York (GMT-4) is 9 hours behind India (GMT+5:30). If it is 10:00 AM in New York, what is the local time in India?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Time difference = +9.5 hours
\( 10:00 + 9.5 \text{ hours} = 19:30 \)
Answer: 7:30 PM IST
