CIE IGCSE Mathematics (0580) Vectors in two dimensions Study Notes - New Syllabus
CIE IGCSE Mathematics (0580) Vectors in two dimensions Study Notes
LEARNING OBJECTIVE
- Vectors in two dimensions
Key Concepts:
Describing a Translation Using a Vector
Adding and Subtracting Vectors
Multiplying a Vector by a Scalar
Describing a Translation Using a Vector
Describing a Translation Using a Vector
A translation is a type of transformation that moves a shape from one position to another without rotating, resizing, or changing its orientation.
A translation is described using a vector, which shows how far and in what direction each point moves.
Vector Notation:
A translation of
\( \begin{pmatrix} x \\ y \end{pmatrix} \)
means:
- Move x units right (if positive) or left (if negative)
- Move y units up (if positive) or down (if negative)
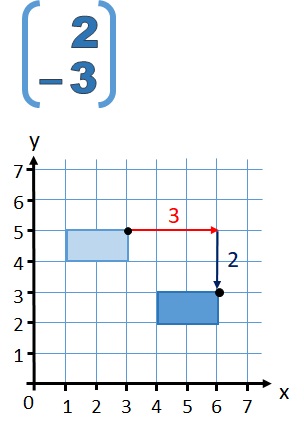
You may also see translations written as \( \vec{AB} \) or simply vector \( \vec{a} \) if points A and B define the movement.
Example:
A point moves by the vector \( \begin{pmatrix} 4 \\ -2 \end{pmatrix} \). Describe the movement.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The point moves:
- 4 units to the right (positive x)
- 2 units down (negative y)
This is a translation described by the vector \( \begin{pmatrix} 4 \\ -2 \end{pmatrix} \).
Example:
Point A is at (3, 5) and is translated to point B at (8, 2). Write the translation vector \( \vec{AB} \).
▶️ Answer/Explanation
To find vector \( \vec{AB} \), subtract coordinates:
\( \vec{AB} = \begin{pmatrix} 8 – 3 \\ 2 – 5 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 5 \\ -3 \end{pmatrix} \)
So the translation moves 5 units right and 3 units down.
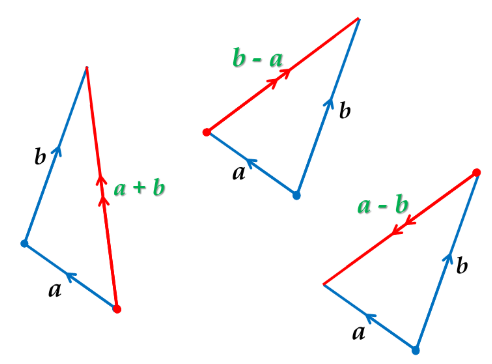
Adding and Subtracting Vectors
Adding and Subtracting Vectors
Vectors can be added or subtracted by combining their components.
Addition:
To add two vectors:
\( \begin{pmatrix} a \\ b \end{pmatrix} + \begin{pmatrix} c \\ d \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} a + c \\ b + d \end{pmatrix} \)
Subtraction:
To subtract two vectors:
\( \begin{pmatrix} a \\ b \end{pmatrix} – \begin{pmatrix} c \\ d \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} a – c \\ b – d \end{pmatrix} \)
Example:
Add: \( \begin{pmatrix} 3 \\ 4 \end{pmatrix} + \begin{pmatrix} 2 \\ -1 \end{pmatrix} \)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Add the top and bottom components separately:
\( \begin{pmatrix} 3 + 2 \\ 4 + (-1) \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 5 \\ 3 \end{pmatrix} \)
Example:
Subtract: \( \begin{pmatrix} 6 \\ -2 \end{pmatrix} – \begin{pmatrix} 4 \\ 3 \end{pmatrix} \)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Subtract the corresponding components:
\( \begin{pmatrix} 6 – 4 \\ -2 – 3 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 2 \\ -5 \end{pmatrix} \)
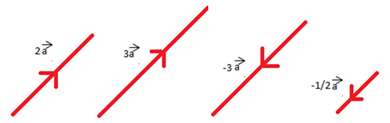
Multiplying a Vector by a Scalar
Multiplying a Vector by a Scalar
To multiply a vector by a scalar means to scale the vector’s magnitude without changing its direction (unless the scalar is negative, which reverses the direction).
Rule:
If \( k \) is a scalar and \( \vec{v} = \begin{pmatrix} a \\ b \end{pmatrix} \), then:
\( k \cdot \vec{v} = k \cdot \begin{pmatrix} a \\ b \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} ka \\ kb \end{pmatrix} \)
- If \( k > 0 \), the vector keeps the same direction.
- If \( k < 0 \), the vector reverses direction.
- If \( |k| > 1 \), the vector gets longer. If \( 0 < |k| < 1 \), the vector becomes shorter.
Example:
Find \( 3 \cdot \begin{pmatrix} 2 \\ -1 \end{pmatrix} \)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Multiply each component by 3:
\( \begin{pmatrix} 3 \cdot 2 \\ 3 \cdot (-1) \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 6 \\ -3 \end{pmatrix} \)
Example:
Find \( -2 \cdot \begin{pmatrix} 4 \\ 5 \end{pmatrix} \)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Multiply each component by -2:
\( \begin{pmatrix} -2 \cdot 4 \\ -2 \cdot 5 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} -8 \\ -10 \end{pmatrix} \)
The vector has the same length as \( \begin{pmatrix} 4 \\ 5 \end{pmatrix} \) scaled by 2, but its direction is reversed.
