CIE iGCSE Physics Paper 3 Prediction - 2025
CIE iGCSE Physics Paper 3 Prediction – 2025
Preparing for your IGCSE exam can be daunting, but with the right approach, you can achieve your goals with CIE iGCSE Physics Paper 3 Prediction
Ace your iGCSE exam! Find exam-style questions, detailed notes, and helpful resources to boost your understanding
iGCSE Practice Questions, Past Papers , Flashcards and notes available for iGCSE Students at IITian Academy.
Questions 1
Fig. 1.1 shows the speed–time graph for a car travelling along a flat straight road
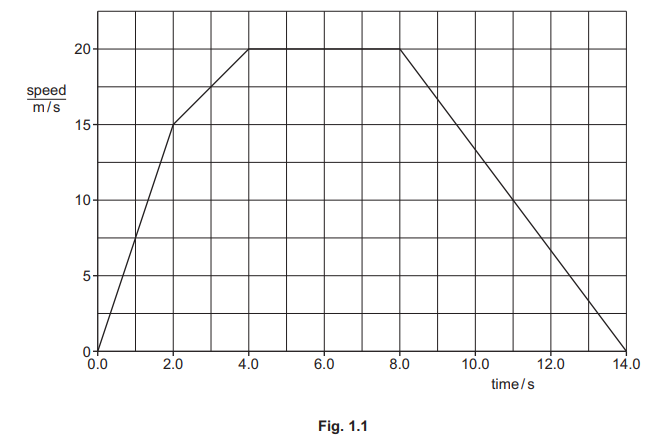
(a) Describe the motion of the car between time = 0 and time = 2.0s.
(b) State the value of the acceleration of the car between time = 4.0s and time = 8.0s.
(c) Calculate the distance travelled by the car between time = 8.0s and time = 14.0s.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a) (constant) acceleration OR accelerating OR increasing speed
(b) zero
(c) 60 (m)
\( \frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 20\)
distance = area under (speed–time) graph OR \( \frac{1}{2} \times b\times h\)
Questions 2
A student wants to find the volume of a piece of metal. The student can use any of the items of equipment shown in Fig. 2.1.
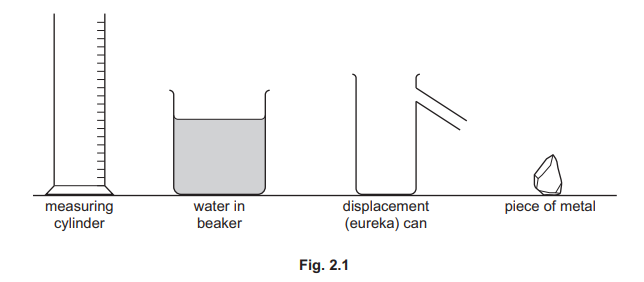
(a) Describe how the student can find the volume of the piece of metal by using equipment from Fig. 2.1.
(b) The volume of a different piece of metal is \(30cm^3\). The mass of this piece of metal is 192g. Calculate the density of the metal. Include the unit.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a) any three from:
measuring cylinder (part) filled with water
volume of water measured or recorded/noted/read
metal submerged / placed in water owtte
new volume read / noted / measured / recorded
volume of metal = difference in volumes
(b) \((\rho =)\) 6
\((\rho =)\) 192 ÷ 30
(density =) mass ÷ volume OR \((\rho =)\) m / V in any form
\(g / cm^3\)
Questions 3
Fig. 5.1 shows a metal container used for storing petrol. There is some petrol gas above the liquid petrol inside the metal container.
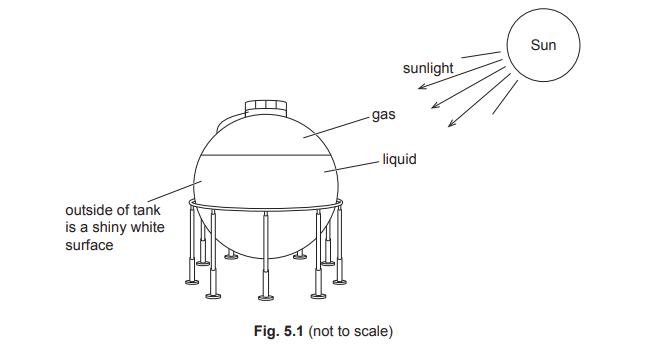
(a) Describe the arrangement and motion of the particles in the liquid petrol stored in the container. Use your ideas from the kinetic particle model of matter.
(b) The temperature of the petrol gas inside the metal container increases. State and explain any change in the pressure of the petrol gas on the metal container.
(c) Describe how thermal energy travels from the Sun to the petrol inside the metal container.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a) any two from:
• (particles are;) random arrangement / pattern
• close together OR idea slightly further apart than in solid
• move randomly OR move around / about (freely)
• colliding with each other / walls
• have some vibrational energy / motion
(b) pressure increases
any two from: (because)
• particles move faster OR have increased kinetic energy
• more (frequent) collisions (with walls of container)
• harder collisions (with walls of container)
(c) infrared OR radiation (through space and atmosphere)
conduction (through the metal)
Questions 4
(a) State the name of the type of wave in which the direction of vibration is at right angles to the direction of travel.
(b) A teacher uses a ripple tank to demonstrate a wave property. Fig. 6.1 shows the ripple tank viewed from above. The crests of the wave are travelling from left to right.
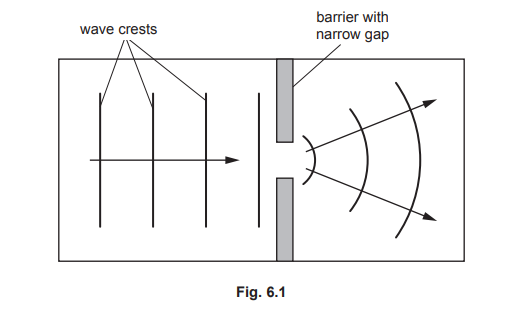
(i) Complete the sentence about the wave property demonstrated in Fig. 6.1.
Choose one word from the list.
diffraction dispersion reflection refraction
The wave property demonstrated in Fig. 6.1 is …………….
(ii) On Fig. 6.1, indicate one wavelength. Label your answer with the letter ‘w’.
(c) In a different ripple tank, the wavelength of the wave is 5.1cm. The speed of the wave is 42cm/ s. Determine the frequency of the wave.
▶️Answer/Explanation
(a) transverse
(b)(i) diffraction
(ii) correct wavelength indicated
(c) 8.2 (Hz)
\(42\div 5.1\)
v =\( f\times \lambda \) OR (frequency =) speed wavelength in any form
Questions 5
(a) Fig. 9.1 shows three devices: a compass, a transformer and an electromagnet. The main parts of the devices are labelled.
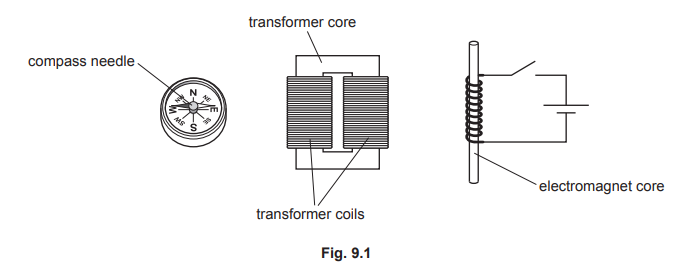
Complete Table 9.1 by adding a suitable metal for each part. Choose from the metals in the list. Each metal can be used once, more than once or not at all.
aluminium copper soft iron silver steel 
(b) The primary coil of a transformer is connected to a mains supply of 220V a.c. The primary coil has 1500 turns and the secondary coil has 650 turns. Calculate the output voltage of the secondary coil.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a)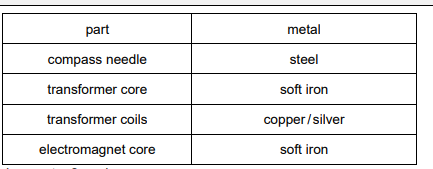
(b) 95 (V)
\((V_s =) 650 / 1500 \times 220\) OR 1500 / 650 = 220 / \(V_s\)
\((V_p / V_s) = (N_p / N_s)\) in any form
Questions 6
Fig. 4.1 shows a flow diagram for the energy transferred in a television.
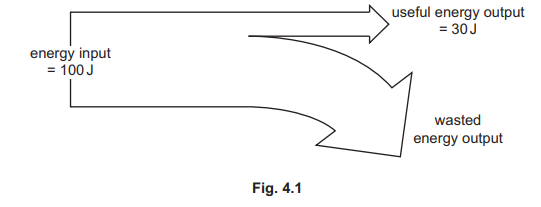
(a) (i) State two ways in which useful energy is transferred from the television.
(ii) Determine the value of the wasted energy output from the television.
(b) Fig. 4.2 represents a hydroelectric power station.
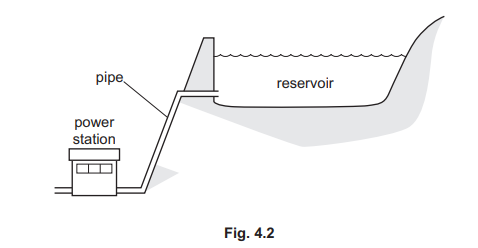
(i) Describe how a hydroelectric power station generates electrical power.
(ii) Apart from cost, state one advantage and one disadvantage of generating electrical power using a hydroelectric power station compared to a coal-fired power station.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a)(i) light
sound
(ii) (100– 30 =) 70 (J)
(b)(i) any three from:
water (behind dam) has gravitational OR potential energy
water flows down / moves in / goes through pipe OR through (HEP) station OR through turbine
water turns / moves / rotates / spins turbine
(turbine) turns / moves / rotates / spins generator
(ii) any one advantage from:
renewable form of energy
no greenhouse gases OR no \(CO_2\)
no atmospheric / air pollution
short start-up time owtte
any one disadvantage from:
(large area of) land flooded
relocation of population
damage to (land / valley) habitats OR migration of fish (upriver) interrupted owtte
vulnerable to drought
idea of limited suitable sites
reduced water supply downstream owtte
Questions 7
Fig. 7.1 represents an object placed close to a thin converging lens. The scale for the grid is shown.
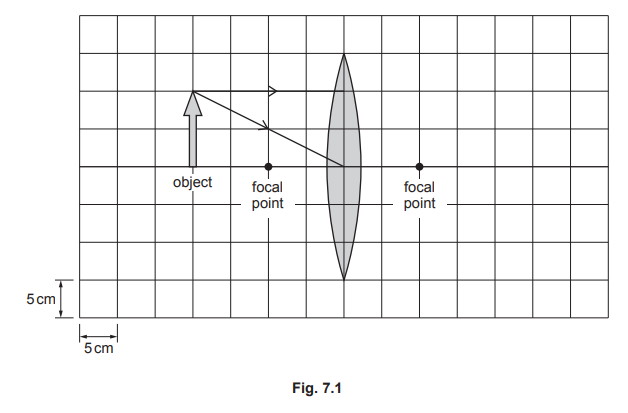
(a) (i) Determine the focal length of the converging lens. Use the information in Fig. 7.1.
focal length = ……………………………………………. cm
(ii) On Fig. 7.1, determine the position of the image formed by the lens, by continuing the path of each ray beyond the lens. Use an arrow to indicate the position of the image.
(b) Fig. 7.2 shows the regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.

(i) In Fig. 7.2, one region is unlabelled. State the name of the unlabelled region.
(ii) Describe one use of ultraviolet light.
(iii) Describe one harmful effect on people due to excessive exposure to ultraviolet light.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a)(i) 10 (cm)
\((focal length =) 2 \times 5\)
(ii) ray continued in straight line through centre of lens
ray parallel to axis continued to pass through focal point
(top of) image position indicated as where rays cross
(b)(i) X-rays
(ii) security marker OR detecting fake bank notes OR sterilising food / water
(iii) damage to (surface) cells / skin / eyes OR (leading to) cancer / eye conditions
Questions 8
(a) Fig. 9.1 shows an electricity cable that has a fault.
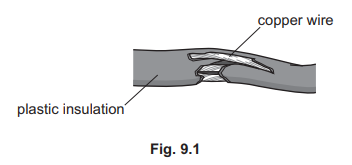
The cable is used for supplying electricity at a high voltage. State the fault and describe the hazard shown in Fig. 9.1.
(b) Fig. 9.2 shows a piece of cable used in a mains circuit. 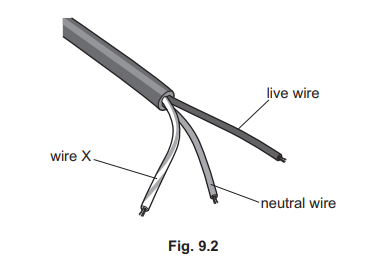
(i) State the name of wire X in Fig. 9.2.
(ii) An electrical appliance is connected in the mains circuit. One of the wires in the cable is connected to the switch for the appliance. State and explain which wire is connected to the switch.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a) fault: insulation damaged owtte
hazard: electrocution OR electric shock
(b)(i) earth (wire)
(ii) (switch is connected in) live (wire)
(so appliance is) disconnected from main / supply OR disconnected from high voltage (when switch is open / off)
Question 9
Fig. 11.1 shows lamps in series. Fig. 11.2 shows lamps in parallel.
The lamps are all identical 6.0 V lamps. In each circuit there are three ammeters \(A_1\), \(A_2\) and \(A_3\).
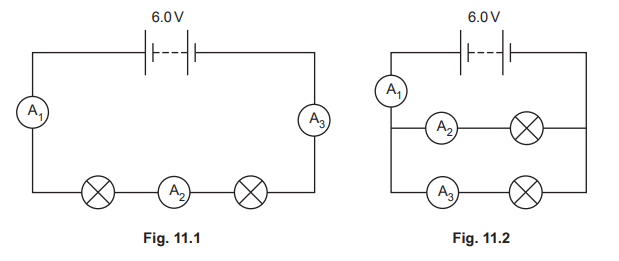
(a) (i) Compare the readings on ammeters \(A_1\), \(A_2\) and \(A_3\) in Fig. 11.1.
(ii) Compare the readings on ammeters \(A_1\), \(A_2\) and \(A_3\) in Fig. 11.2.
(iii) State two advantages of connecting the 6.0 V lamps in parallel with the 6.0 V battery,
compared with connecting the lamps in series with the battery.
1.
2.
(b) Each lamp has a resistance of 12 Ω.
(i) Determine the combined resistance of the two lamps connected in series.
resistance = ……………………………………………. Ω
(ii) Compare the resistance of one lamp with the combined resistance of the two lamps in
parallel.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a)
(i) the ammeters all have the same reading
(ii) the reading on \(A_1\) is the biffest
(iii) lamps have normal brightness *in parallel) or brighter (than lamps in series)
If one lamp fails the other lamp is still lit
(b)
(i) 24 (Ω)
(ii) (resistance of one lamp/12 (Ω)) is more (than the combined resistance (or lamps in parallel)
Questions 10
(a) The nuclide notation for an atom of protactinium‑234 is:

(i) State the number of protons in an atom of protactinium‑234. ………………………………..
(ii) State the number of nucleons in an atom of protactinium‑234. ………………………………
(b) Three forms of the element protactinium are: protactinium‑234, protactinium‑230 and protactinium‑233. State the name given to these different forms of the same element.
(c) A teacher demonstrates radioactive decay by using a sample of protactinium‑234m.
(i) The sample emits beta (β)‑particles. State the nature of a beta (β)‑particle.
(ii) The teacher obtains data for a decay curve. Fig. 10.1 shows the decay curve for the sample of protactinium‑234m
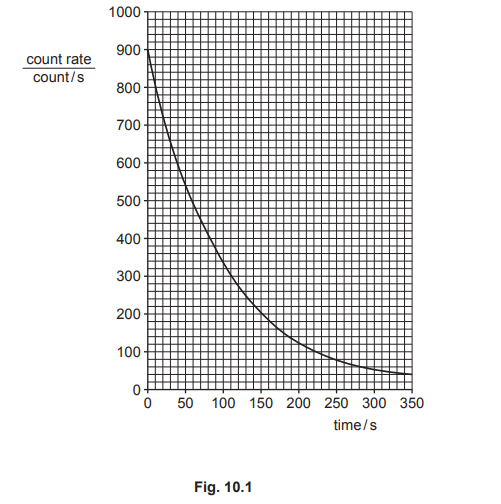
Calculate the half‑life of protactinium‑234m using the information in Fig. 10.1. Clearly show your working on the graph or in the space provided.
(iii) Suggest a reason why the half‑life of protactinium‑234m makes it suitable for this demonstration in a lesson.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a)(i) 91
(ii) 234
(b) isotopes
(c)(i) electron
(c)(ii) range 65–75 (s)
range 55–85 (s)
2 associated values (e.g. 900 and 450 or 800 and 400 etc) seen / indicated
small half-life / time in a lesson to collect enough data for a decay curve owtte
Question 11
Which data is needed to calculate the average orbital speed of a satellite around a planet?
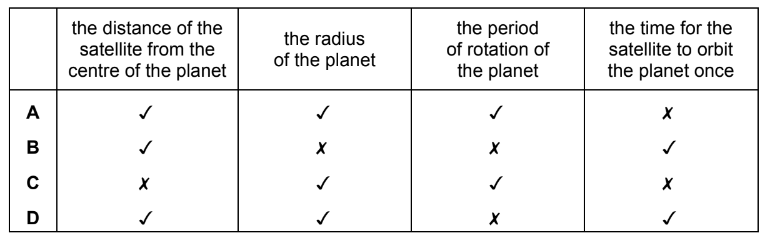
key
\(\checkmark=\) needed
\(x=\) not needed
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
