CIE iGCSE Biology-7.2 Digestive system- Study Notes- New Syllabus
CIE iGCSE Biology-7.2 Digestive system- Study Notes – New syllabus
CIE iGCSE Biology-7.2 Digestive system- Study Notes -CIE iGCSE Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
Core
- Identify in diagrams and images the main organs of the digestive system, limited to:
(a) alimentary canal: mouth, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine (duodenum and ileum), and large intestine (colon, rectum, anus)
(b) associated organs: salivary glands, pancreas, liver and gall bladder - Describe the functions of the organs of the digestive system listed in 7.2.1, in relation to:
(a) ingestion – the taking of substances, e.g. food and drink, into the body
(b) digestion – the breakdown of food
(c) absorption – the movement of nutrients from the intestines into the blood
(d) assimilation – uptake and use of nutrients by cells
(e) egestion – the removal of undigested food from the body as faeces
Identifying and Understanding the Main Organs of the Digestive System
The human digestive system is a group of specialized organs that work together to break down food, absorb nutrients, and remove waste.
A. The Alimentary Canal (Digestive Tract)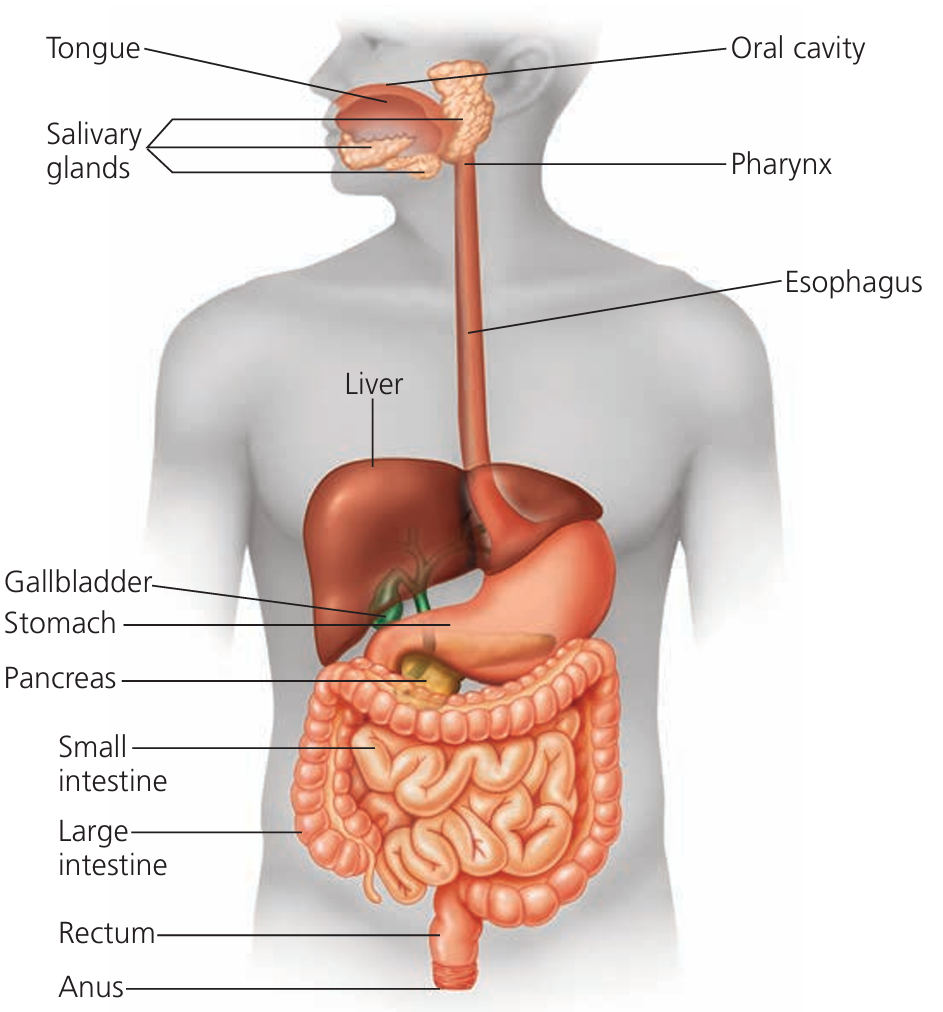
A continuous muscular tube through which food travels:
1. Mouth – Ingestion and mechanical digestion
- Teeth chew food (mastication)
- Saliva (with amylase) begins starch breakdown
- Tongue mixes food into bolus for swallowing
2. Esophagus – Muscular tube
- Moves food from mouth to stomach by peristalsis
- No digestion here
3. Stomach – J-shaped muscular organ
- Secretes gastric juice (HCl + pepsin)
- Begins protein digestion
- Mixes food into chyme
4. Small Intestine
- Duodenum: Digests food using enzymes & bile
- Ileum: Absorbs nutrients via villi
5. Large Intestine
- Colon: Absorbs water and salts
- Rectum: Stores feces
- Anus: Egestion (waste removal)
B. Associated Organs (Aid in Digestion)
1. Salivary Glands
- Produce saliva with amylase
- Moistens and begins starch digestion
2. Pancreas
- Releases enzymes into duodenum:
- Amylase, lipase, trypsin
3. Liver
- Produces bile for fat emulsification
- Stores glucose (as glycogen)
- Detoxifies blood
4. Gall Bladder
- Stores and concentrates bile
- Releases bile into duodenum when needed
🧾 Summary Table of Digestive Organs
| Organ | Type | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Mouth | Alimentary Canal | Chewing, salivary amylase starts starch digestion |
| Esophagus | Alimentary Canal | Transports food via peristalsis |
| Stomach | Alimentary Canal | Acid and enzymes digest protein; churns food |
| Duodenum | Alimentary Canal | Digestion of all nutrients with enzymes and bile |
| Ileum | Alimentary Canal | Absorbs nutrients via villi |
| Colon | Alimentary Canal | Absorbs water from waste |
| Rectum | Alimentary Canal | Stores feces |
| Anus | Alimentary Canal | Egestion (removal of waste) |
| Salivary Glands | Associated Organ | Produce saliva with amylase |
| Pancreas | Associated Organ | Enzymes for digestion (amylase, lipase, trypsin) |
| Liver | Associated Organ | Produces bile; stores glucose |
| Gall Bladder | Associated Organ | Stores bile |
Functions of Digestive Organs in Relation to Ingestion, Digestion, Absorption, Assimilation, and Egestion
(a) INGESTION – Taking Food into the Body
Definition: Ingestion is the process of eating – taking in substances (food and drink) through the mouth.
Organs Involved:
- Mouth – Chews food into smaller pieces (mechanical digestion)
- Teeth – Cut and grind food
- Tongue – Rolls food into a bolus and pushes it back for swallowing
- Salivary Glands – Release saliva with amylase to begin starch digestion
(b) DIGESTION – Breaking Down Food into Small Molecules
Definition: Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble molecules into small, soluble ones.
Two Types: Mechanical (chewing, churning) and Chemical (enzymes)
Organs Involved:
- Mouth: Amylase begins breaking starch → maltose
- Stomach: HCl + Pepsin break proteins → peptides
- Duodenum: Bile emulsifies fats, pancreatic enzymes digest food
(c) ABSORPTION – Movement of Nutrients into the Blood
Definition: Absorption is when digested food molecules pass into the blood or lymph.
Main Organ: Ileum
- Villi and microvilli increase surface area
- Capillaries absorb glucose and amino acids
- Lacteals absorb fatty acids and glycerol
(d) ASSIMILATION – Using Absorbed Nutrients in Cells
Definition: Assimilation is the uptake and use of nutrients for energy, growth, and repair.
- Liver: Stores glucose, processes amino acids
- Body Cells: Use glucose in respiration, amino acids to build proteins
(e) EGESTION – Removal of Undigested Material
Definition: Egestion is the elimination of undigested food as feces.
- Colon: Absorbs water from waste
- Rectum: Stores feces
- Anus: Expels feces during defecation
🧾 Summary Table
| Process | Meaning | Organs Involved |
|---|---|---|
| Ingestion | Taking in food and drink | Mouth, Teeth, Tongue, Salivary Glands |
| Digestion | Breaking food into small molecules | Mouth, Stomach, Duodenum, Pancreas, Liver |
| Absorption | Nutrients into blood/lymph | Ileum, Villi, Capillaries |
| Assimilation | Using nutrients in cells | Liver, Body Cells |
| Egestion | Eliminating undigested food | Colon, Rectum, Anus |
