Question
The density of a material in SI unit is 128 kg m-3. In certain units in which the unit of length is 25 cm and the unit of mass is 50 g, the numerical value of density of the material is:
(a) 40 (b) 16 (c) 640 (d) 410
Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a) 40
(a) Density of material in SI unit, = \(\frac{128kg}{m^3}\)
Question
A metal sample carrying a current along X-axis with density J is subjected to a magnetic field Bz (along z-axis). The electric field EY developed along Y-axis is directly proportional to Jx as well as Bz. The constant of proportionality has SI unit
\((a)\;\frac{m^2}{A}\;(b)\;\frac{m^3}{As}\;(c)\;\frac{m^2}{As}\;(d)\;\frac{As}{m^3}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans
(b)
(b) According to question
\(E_{y} \alpha J_{x}B_{Z}\)
\(\therefore \) Constant of proportionality
\(K=\frac{E_{y}}{B_{z}J_{x}}=\frac{C}{J_{x}}=\frac{m^3}{As}\)
Question
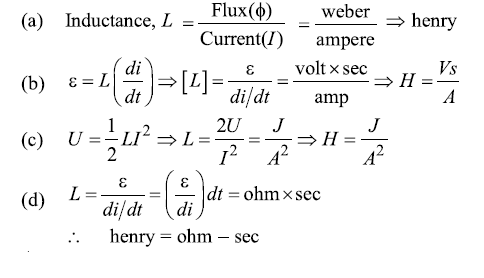
The SI unit of inductance, the henry can be written as
\((a)\;\frac{weber}{ampere}\;(b)\;\frac{volt-sec}{amp}\;(c)\;\frac{joule}{(amperer)^2}\;(d)\;ohm-second\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a, b, c, d)
Question
Column I Column II
(A) \(_{GM_eM_s}\) , \(_{G-}\) (p) (volt) (coulomb)(metre)
universal gravitational
constant,
\(_{M_e}\) – mass of the eart ,
\(_{M_s}\) – mass of the Su
(B) \(_{\frac{3RT}{M}}\) , R-universal (q) (kilogram) (metre)3(second)-2
gas constant,
T– absolute temperature,
M – molar mass
(C) \(\frac{F^2}{q^2B^2}\) , F– Force , (r) (metre)2 (second)-2
q-charge,
B-magnetic field
(D) \(\frac{GM_e}{R_e}\) , G– universal , (s) (farad) (volt)2 (kg)-1
Me – mass of the earth,
Re – radius of the earth
Answer/Explanation
Answer
A → p, q
Using F= \(\frac{GM_eM_s}{r^2}\) ⇒ GMeMs = Fr2 = Nm2 = kg\(\frac{m}{s^2}\) x m2
=kg m3s-2
Also (volt) (coulomb) (metre) = (joule) (metre)
(\(\because \) volt= Joule/coulomb)
= (N– m) (m) = Nm2 = kg m3s-2
B → r, s
Using \(\displaystyle v\)rms = \(\sqrt{\frac{3RT}{M}}\) ⇒ \(v_{rms}^{2}\) = \(\frac{3RT}{M}\)
Unit of \(\frac{3RT}{M}\) is \(m^{2}\) \(s^{-2}\)
Also (farad) (volt)2 (kg)-1 = (joule) kg-1 \((\because u = \frac{1}{2} cv^2)\)
= N-m kg-1 = kg ms-2 m kg-1 = m2s-2
C → r, s
Using \(\displaystyle F = qvB \) ⇒ \(v^2= \frac{F^2}{q^2B^2}\)
∴ Unit of v2 is m2s-2 which is further equal to FV2 kg-1.
D → r, s
Reason : Escape velocity \(v_{e} = \sqrt{\frac{2GM}{R}}\) ⇒ \(v_{e}^{2} = \frac{2GM}{R}\)
∴ Unit of \(\frac{GM}{R}\) is m2 s-2
Question
Column I Column II
(A) Capacitance (i) ohm-second
(B) Inductance (ii) coulomb2-joule-1
(C) Magnetic Induction (iii) coulomb (volt)-1
(iv) newton (amp-metre)-1
(v) volt-second(ampere)-1
Answer/Explanation
Answer
Capacitance \(C=\frac{q}{v}=\frac{q}{\omega}\) coulomb-volt-1, coulomb2-joule-1.
Inductance \(\frac{L}{R}=t\) and \(R=\frac{v}{I}\) ohm-sec, volt-second (ampere)-1
Magnetic Induction \(F=lIB\Rightarrow B=\frac{F}{lI}\) newton (ampere-metre)
Question
Give the MKS units for each of the following quantities.
(A) Young’s modulus
(B) Magnetic Induction
(C) Power of a lens
Answer/Explanation
Answer
(i) The M.K.S. unit of Young’s modulus \(\left ( Y=\frac{F}{A}/\frac{\triangle l}{l_0} \right )\) is Nm-2.
(ii) The M.K.S. unit of magnetic induction \(\left ( B=\frac{\phi }{A} \right )\) is tesla or wb/m2.
(iii) The M.K.S. unit of power of lens \(P=\frac{1}{f\textup{(in metre)}}\) is dioptre or m-1
