Question
(a) Distinguish between the structure of the chromosomes of prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
(b) Outline the causes of sickle cell anemia.
(c) The karyogram shown is for the African marsh rat (Dasymys incomtus). In this species, sex is determined by X and Y chromosomes. Females are XX and males are XY.
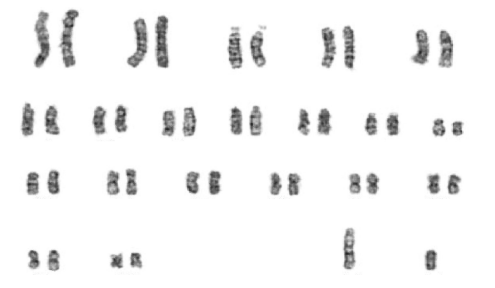
i. Identify, with a reason, the sex of this individual.
ii. State the haploid number for this nucleus.
(d) Thomas Hunt Morgan established that genes for body colour and wing size in Drosophila are autosomally linked. The allele for grey body ($b^+$) is dominant over that for black body (b) and the allele for normal wing size ($vg^+$) is dominant over that for vestigial wing (vg).
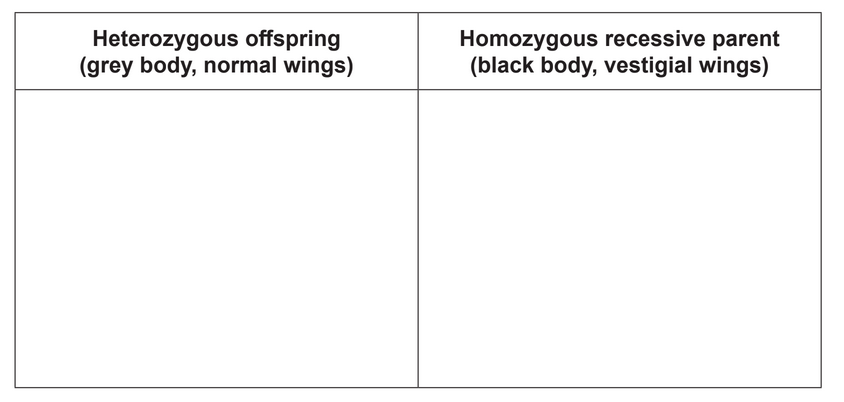
(i). A fly that is homozygous dominant for both body colour and wing size mates with a fly that is recessive for both characteristics. In the table, draw the arrangement of alleles for the offspring of this mating and for the homozygous recessive parent.
(ii). The offspring, which were all heterozygous for grey body and normal wings, were crossed with flies that were homozygous recessive for both genes. The table shows the percentages of offspring produced.
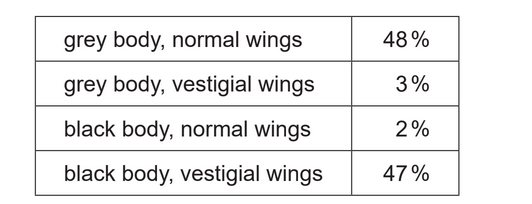
Explain these results, based on the knowledge that the genes for body colour and wing size are autosomally linked.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a)
a. prokaryotes have circular DNA/chromosome but eukaryote chromosomes linear/OWTTE
OR
eukaryotes have telomeres/centromeres whereas prokaryotes do not
b. some prokaryotes have plasmids whereas eukaryotes do not
c. eukaryotes have multiple chromosomes whereas prokaryotes «typically» have only one
d. histones/nucleosomes/proteins associated with DNA in eukaryotes but not in prokaryotes/naked DNA in prokaryotes
OR
eukaryote DNA can coil/supercoil/condense «due to histones» but not prokaryote DNA
b)
a. genetic disease/caused by a gene
OR
inherited «from parents»
OR
caused by mutation «of a gene»
b. base substitution OR
GAG → GTG
c. hemoglobin gene mutated / different allele/form/version of hemoglobin gene
OR
HbA → HbS
d. leads to change in amino acid sequence «in hemoglobin»
OR
glutamic acid → valine
e. only homozygotes have full disease/sickled cells / heterozygote has milder form
OR
hemoglobin crystallizes at low oxygen concentration
f. «selected for/spreads in population» as it gives resistance to malaria
c (i) male because «X and» Y chromosome present OR male because sex chromosomes/last two chromosomes/pair 21 are unpaired/different «from each other»/not homologous
c (ii) 21
d (i)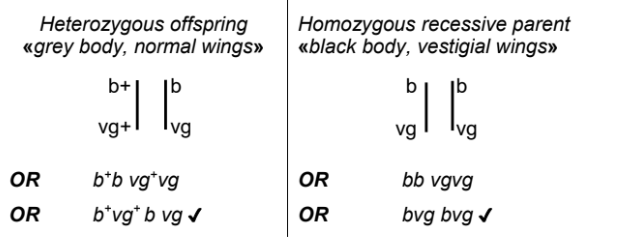
d (ii)
a. not a 1:1:1:1 ratio «because of linkage»
OR
not independent assortment
OR
grey normal and black vestigial types/parental combinations/double dominant and double recessive were commoner than 25 %/commoner than expected
b. «linked genes» so were on the same chromosome
c. grey body vestigial wing and black body normal wing are recombinants
OR
2 % plus 3 % of the offspring are recombinants
d. recombinants due to crossing over/exchange of genes between «non-sister» chromatids
OR
2 % and 3 % of offspring were due to crossing over
OR
genes inherited together unless separated by crossing over
e. crossing over between the two loci/between the two genes on the chromosomes
Question
The electron micrographs show a typical prokaryote and a mitochondrion.
Prokaryote Mitochondrion
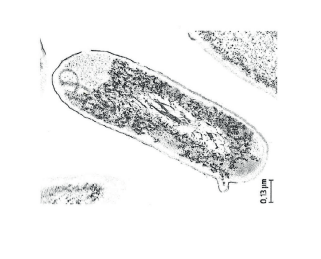
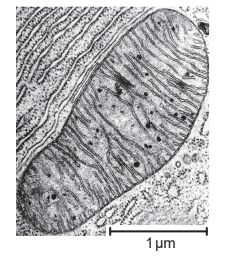
a. Compare and contrast the structure of a typical prokaryotic cell with that of a mitochondrion.
b. Explain how mitochondria could have been formed from free living prokaryotes.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a)
differences
a. prokaryote has cell wall but mitochondrion does not
b. mitochondrion has double membrane whereas prokaryote has single membrane
OR
«Gram negative» bacteria have cell wall between two membranes whereas mitochondria has intermembrane space between two membranes
c. mitochondrion has cristae/invaginations of inner membrane but prokaryote does not
OR
prokaryote «may have» flagella/pili/«slime» capsule which mitochondria do not have
similarities
d. 70S ribosomes in both
e. DNA in both / loop of DNA in both / naked DNA in both
f. shape similar/both rod shaped/OWTTE
OR s
ize of both is similar/both about 3 μm long
g. both are membrane-bound/OWTTE
b)
a. endocytosis/engulfing of prokaryote by a larger/another/anaerobic prokaryote/cell.
b. double membrane of the mitochondrion is the result of endocytosis
OR
inner membrane of mitochondrion from engulfed cell and outer from food vacuole
c. «engulfed prokaryotic cell» was aerobic/respired aerobically/consumed oxygen
OR
«engulfed prokaryotic cell» provided energy/ATP
d. «engulfed prokaryotic cell» not destroyed/not digested
OR
«endo»symbiotic/mutualistic relationship developed
