Question
An oval-shaped stem cell cluster is shown in the micrograph.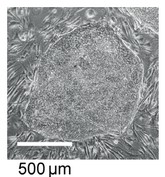
(a) State the main characteristic of stem cells.
(b) Calculate the maximum diameter of the stem cell cluster on the micrograph, showing your working and giving the units.
(c) State one therapeutic role of stem cells.
(d) Discuss how the use of stem cells to treat hereditary diseases could affect the person who received the treatment and their progeny.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a)
undifferentiated/pluripotent/ability to divide/differentiate into any types of cells/differentiate along different pathways;
b)
a. correct formula: 1.1cm = 500 μm, 2.7cm = length, \(\frac{2.7×500}{
1.1}\)= Xμm;
b. correct answer with unit: 1227μm;
c) treatment of Stargardt’s disease/leukemia/diabetes/heart disease/Parkinson’s disease;
d)
a. could improve quality/length of life of the treated person;
b. disease could still be passed on to progeny if defective gene/allele in gametes is not
Question
(a) Describe anaerobic respiration in humans and in yeast.
(b) Methane can be the product of anaerobic respiration in some organisms.
(i) Distinguish between the thermal properties of water and methane.
(ii) Explain the role of methane in climate change.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a)
a. (in both) anaerobic respiration gives a small amount of ATP/2 ATP/energy from glucose;
b. anaerobic respiration occurs when there is no oxygen;
c. anaerobic respiration in yeast produces ethanol and carbon dioxide/alcoholic fermentation;
d. anaerobic respiration in humans (in muscle) produces lactate/lactic acid/lactic acid
fermentation;
e. both undergo glycolysis;
b) i. a. water has higher boiling/melting point;
b. water has a higher specific heat capacity;
c. water has a higher latent heat of vaporization;
d. differences due to water having many H-bonds/polarity between the molecules while methane
has no H-bonds/polarity;
ii.
a. methane is a greenhouse gas
OR
methane causes an increase in temperature of the atmosphere;
b. methane is one of the most powerful greenhouse gases / more powerful than CO2;
