Question
Antiretroviral drugs are used to treat Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) infections. Zidovudine (ZDV) and nevirapine (NVP) are examples of antiretroviral drugs. There are concerns that these drugs may be toxic to body cells in mitosis. In a study using Allium cepa, root tips were exposed to the drugs for 96 hours at a range of concentrations. The control treatment was a drugconcentration of 0 μmol. In the graph, root lengths after the 96-hour treatment period are expressed as a percentage of the length of the control.
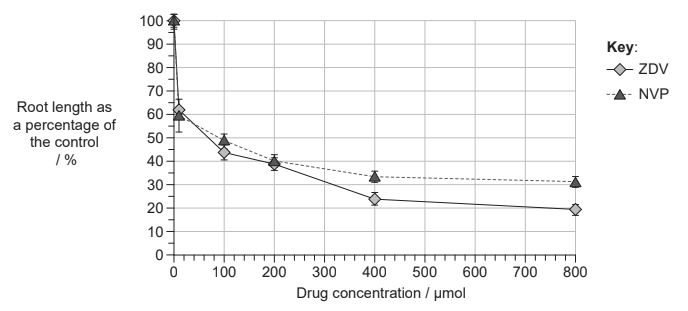
a. (i) Deduce the concentration of ZDV that would cause a 50 % reduction in root growth compared to the control.
(ii) Identify the root length, as a percentage of the control, resulting from a ZDV concentration of 400 μmol.
b. Compare and contrast the effect of ZDV and NVP on the growth of Allium roots.
Both ZDV and NVP are believed to have a damaging effect on the process of mitosis but ZDV in particular is believed to block the formation of the spindle.
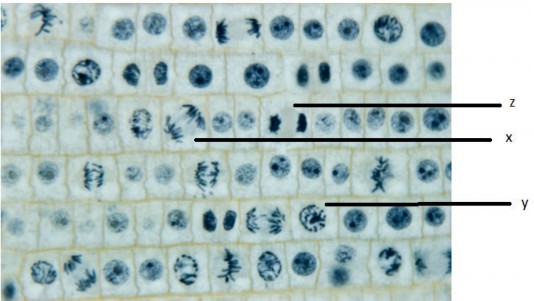
c. Based on this information, suggest with a reason which of the labelled cell types will become more common in Allium root tips treated with ZDV.
d. Allium root tips continue to show some growth even at high concentrations of NVP. Suggest a possible reason for the growth seen in root tips with 800 μmol NVP.
Mitosis plays an important role in tissue regeneration and can be an important factor in recovery from surgery. The hormone leptin has been shown to promote mitosis in certain circumstances. The bar chart shows the mitotic indices of liver tissue exposed to leptin and control tissue during 72 hours after surgery.
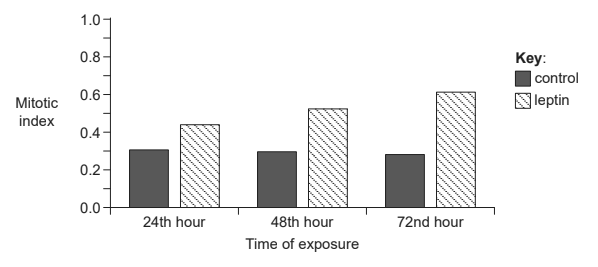
e. Deduce the change in mitotic index after 72 hours compared to the control.
f. Based on the data, evaluate the evidence for leptin promoting regeneration of liver tissue.
g. Outline the role of leptin in appetite control.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a i) 75 μmol Deduce Allow answers in the range of 70 μmol-80 μmol
a ii) 24 % Identify Allow answers in the range 23%-25%
b) Similarities:
a. reduce root length (compared to the control)
b. (ZDV and NVP) have greatest change (in growth) at lowest concentrations (of ZDV and NVP)
c. same effect at 200 μmol
d. above/at about 400 μmol effect levels off
Differences:
e. the change/differences become significant after 200 μmol
f. ZDV has a (slightly) larger effect / NVP has a (slightly) smaller effect / WTTE OR above 400 μmol effect of ZDV remains higher / NVP remains lower Compare and contrast Answer must contain one similarity and one difference Credit may be given for numeric differences when accurately stated
c)
a. Y (will become more common)
b. spindle not formed yet OR cells x and z have spindles
c. cells in Y cannot progress (into Z/into metaphase) Suggest
d)
a. still some mitosis
b. individual cells grow/elongate (expand by absorbing water)
c. NVP is not 100% effective / does not enter all of the cells / not all cells have come in contact with NVP
d. roots have reached maximum saturation of NVP and are no longer functionally affected
e. some cells are resistant to the drug Suggest Accept reasonable suggestions. If in doubt contact your team leader.
e 0.3 / 100% increase / doubling Deduce Do not penalize errors in significant figures. For example, 0.34 would be acceptable
f)
a. mitotic index in treatment greater than in control/leptin appears to promote mitosis
b. mitotic index increases with time suggests ongoing regeneration/growth OR positive correlation between exposure to leptin and increased mitotic index
c. but experiment limited to 72 hours/regeneration/recovery may take longer than 72 hours
d. no error bars shown/no information on significance/sample size Evaluate Acknowledge WTTE
g)
a. acts on receptors in the hypothalamus/appetite centre
Question
(a) Outline how cuts in the skin are sealed to prevent blood loss.
(b) Outline how two parents could have a child with any of the four ABO blood groups.
(c) Explain how ventilation and lung structure contribute to passive gas exchange.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a)
a. platelets respond to/detect skin/blood vessel damage Accept answers presented as a flow chart.
b. platelets release clotting factors
c. clotting factors trigger a chain/cascade of reactions
d. «leading to» formation of thrombin
e. thrombin causes fibrinogen conversion into fibrin
f. blood clot seals the wound due to fibrin network of fibres
b)
a. «first set of» gametes/parental genotype IA, i
b. «other set of» gametes/parental genotype IB, i
c. «genotypes of offspring are respectively» IAI B, IBi, IAi, ii All four correct required.
d. «phenotypes of offspring are respectively» AB, B, A, O
c)
a. air carried through trachea AND bronchi/bronchioles AND alveoli
b. alveoli increase the surface area/thin walled for gas exchange
c. gas exchange carried out through type I pneumocytes
d. type II pneumocytes secrete surfactant to reduce surface tension
e. moist surface/surfactant allows gases to diffuse in solution
f. ventilation/moving blood maintains concentration gradients of oxygen and carbon dioxide
g. between air in alveoli and blood in «adjacent» capillaries OR oxygen diffuses from alveoli to capillaries and carbon dioxide from capillaries to alveoli
h. external intercostal muscles/diaphragm contract during inspiration
i. lowering air pressure «in lungs»/increasing thorax volume
j. relaxation of external intercostal muscles/diaphragm enable «passive» expiration
k. internal intercostal «and abdominal muscles» contract «to force» expiration
l. expiration due to increasing air pressure «in lungs»/decreasing thorax volume
