Question
Which of the following graphs correctly shows the relationship between magnitude of gravitational force and distance between two masses?
(A) 
(B) 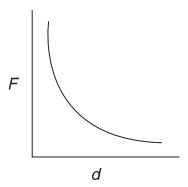
(C) 
(D) 
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:(B)
The gravitational force between two masses has a \(1/R^{2}\) relationship (where R is the distance from center to center).
Graph B shows the correct inverse relationship.
Question
Standing wave nodes in a string occur every 20 cm. If the velocity of the incident waves is equal to 5 m/s and the length of the string is 80 cm, what is the frequency of the waves equal to?
(A) 25 Hz
(B) 6.25 Hz
(C) 12.5 Hz
(D) 3.125 Hz
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:(C)
Since node to node is half a wavelength:
\( \lambda=\) 0.4 m
\( f=v/\lambda=\) 5/0.4 = 12.5 Hz
Question
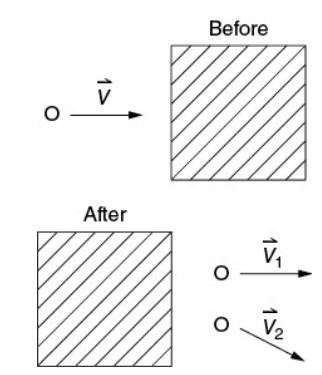
In an experiment, a marble rolls to the right at speed v, as shown in the top diagram. The marble rolls under a canopy, where it is heard to collide with marbles that were not initially moving. Such a collision is known to be elastic. After the collision, two equal-mass marbles are observed leaving the canopy with velocity vectors \(\vec{v_{1}} and \vec{v_{2}}\) directed as shown. Which of the following statements justifies why the experimenter believes that a third marble was involved in the collision under the canopy?
(A) Before collision, the only marble momentum was directed to the right. After the collision, the combined momentum of the two visible marbles is still to the right. Another marble must have a leftward momentum component to conserve momentum.
(B) Before collision, the only marble momentum was directed to the right. After the collision, the combined momentum of the two visible marbles has a downward component; another marble must have an upward momentum component to conserve momentum.
(C) Before collision, the only marble kinetic energy was directed to the right. After the collision, the combined kinetic energy of the two visible marbles is still to the right. Another marble must have a leftward kinetic energy component to conserve kinetic energy.
(D) Before collision, the only marble kinetic energy was directed to the right. After the collision, the combined kinetic energy of the two visible marbles has a downward component; another marble must have an upward kinetic energy component to conserve kinetic energy.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Choices C and D are wrong because kinetic energy doesn’t have a direction. Choice A is wrong because momentum conservation does not require a leftward momentum component—since the initial momentum was all to the right, the final momentum should be to the right. It’s the vertical momentum that’s the problem. Since the vertical momentum was zero to start with, any vertical momentum after collision must cancel out.
Question
The radius of Mars is about half that of Earth; the mass of Mars is about one-tenth that of Earth. Which of the following is closest to the gravitational field at the surface of Mars?
(A) 10 N/kg
(B) 4 N/kg
(C) 2 N/kg
(D) 0.5 N/kg
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
The gravitational field at the surface of a planet is \(g=G\frac{M}{r^{2}}\). The numerator for Mars is 1/10 that of Earth, reducing the gravitational field by 1/10. The denominator for Mars is \((1/2)^{2}=1/4\) that of Earth, increasing the gravitational field by a factor of 4 (because a smaller denominator means a bigger fraction). The overall gravitational field is multiplied by 4/10. On Earth, the gravitational field is 10 N/kg, so on Mars, g = 4 N/kg.
