Question
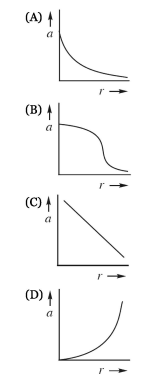
As shown above, the +Q charge is fixed in position, and the +q charge is brought close to +Q and then released from rest. Which graph best shows the acceleration of the +q charge as a function of its distance r from +Q ?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
The acceleration of an object with charge +q and mass m is given by \(a = \frac{F_{E}}{m}=\frac{1}{4\pi\varepsilon _{0}}\left ( \frac{q_{1}q_{2}}{mr^{2}} \right )\) Graph (A) shows an inverse square law.
Question
You are tasked with creating a real image using a concave mirror as your imaging system. Which of the following criteria is true about both the image and the object?
(A) A real image can be created only if the object is farther away from the lens than the radius of curvature of the lens.
(B) A real image can be created only with the object located between the center of the lens and the focal length of the lens.
(C) A real image can be created with the object located anywhere farther from the lens than the focal point.
(D) A real image cannot be created using only a concave lens.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
A concave mirror can only make a real image when the object is placed beyond the focus.
Question
A thermodynamic process is conducted wherein an ideal gas is taken from State A to B to C to D to A. State A is at a pressure P and a volume 5V. State B is at pressure 4P and volume V. State C is at pressure 4P and volume 4V. State D is at pressure 2P and volume 10V. Which step in the process requires the largest change in internal energy of the system?
(A) State A to State B
(B) State B to State C
( C) State C to State D
(D) State D to State A
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The internal energy is proportional to the temperature of the system, and the Ideal Gas Law explains that the product of pressure and volume is also proportional to the temperature. State A is at 5PV, State B is at 4PV, State C is at 16PV, and State D is at 20PV. The change from State D to State A requires the largest change in energy.
Question
The converging lens above has a focal length of 25 cm. The object is located at a distance of 65 cm from the lens. Where should a screen be placed so that the observer will see a focused image on the screen?
(A) 65 cm to the right side of the lens
(B) 40.6 cm to the right side of the lens
( C) At the focus of the lens
(D) The image in such an arrangement will be virtual and cannot be seen on a screen.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
The screen must be placed at the image location in order for the image to appear in focus on the screen. We use the equation \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{s_{0}}+\frac{1}{s_{i}}\)
\(\frac{1}{s_{i}}=\frac{1}{25 cm}-\frac{1}{65 cm}\rightarrow s_{i}=40.6 cm\)
Question
An ideal gas is confined to a leak-proof box. What type of processes could occur to cause the gas to absorb heat, but have no net work done on the gas? Select two answers.
(A) Isothermal expansion to the original volume, then isobaric compression to the original volume
(B) A doubling of pressure at constant volume
(C) A doubling of pressure at constant volume, then doubling the volume at constant pressure, then halving the pressure at constant volume, and finally halving the volume at constant pressure to return to the initial state
(D) A doubling of pressure at constant volume, then finally halving the pressure at constant volume, then doubling the volume at constant pressure, then finally halving the volume at constant pressure to return to the initial state
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B, D
Work is done on a gas when volume changes at constant pressure, or it can be found from the area under a pressure-volume curve. Choice (B) involves no change in volume. The first two steps in (D) involve no volume change. The last two steps involve the same amount of work first being done by the gas, then the same amount being done on the gas.
