NEET Biology - Unit 1- Salient features and classification of animals- Study Notes - New Syllabus
NEET Biology – Unit 1- Salient features and classification of animals- Study Notes – New Syllabus
Key Concepts:
- Salient features and classification of animals-nonchordate up to phyla level and chordate up to classes level (three to five salient features and at least two examples).
Animal Kingdom: Salient Features & Classification
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic, heterotrophic organisms that show a wide diversity in body plan, symmetry, habitat, and mode of reproduction.
🌱 General Salient Features of Animals
- Heterotrophic: Depend on other organisms for food.
- Eukaryotic and multicellular: Cells lack cell walls.
- Locomotion: Most animals are motile at some stage of life.
- Reproduction: Sexual (common) and asexual (some groups).
- Tissue Organisation: Cells organised into tissues, organs, and organ systems.
🐚 1) Non-Chordates (up to Phyla level)
Salient Features:
- Absence of notochord at any stage of life.
- Mostly invertebrates, no backbone.
- Body symmetry: Asymmetrical, radial, or bilateral depending on the phylum.
- Coelom: Can be acoelomate, pseudocoelomate, or coelomate.
- Digestive system, circulatory system, excretory structures vary with phylum complexity.
Major Phyla of Non-Chordates:
| Phylum | Salient Features | Examples | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
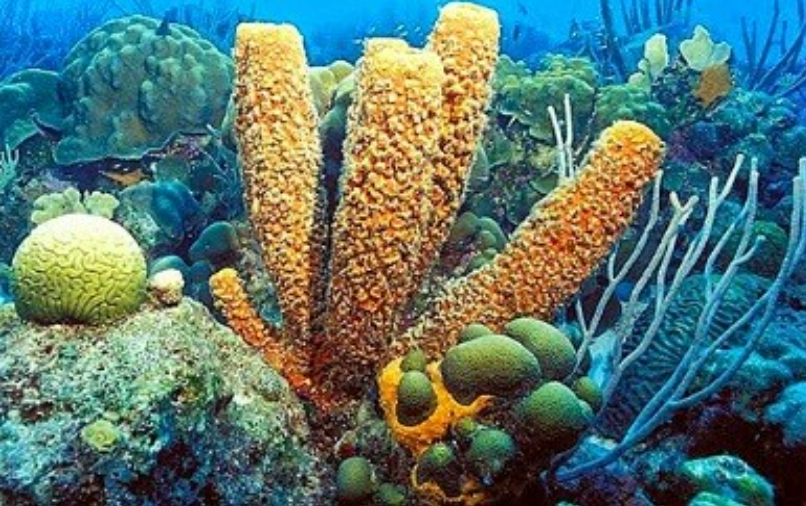
| Porifera | Asymmetrical, body with pores & canals, no true tissues, aquatic, filter feeders | Spongilla, Sycon |
|
| Coelenterata / Cnidaria | Radial symmetry, diploblastic, tentacles with cnidocytes, aquatic | Hydra, Obelia, Aurelia, Physalia |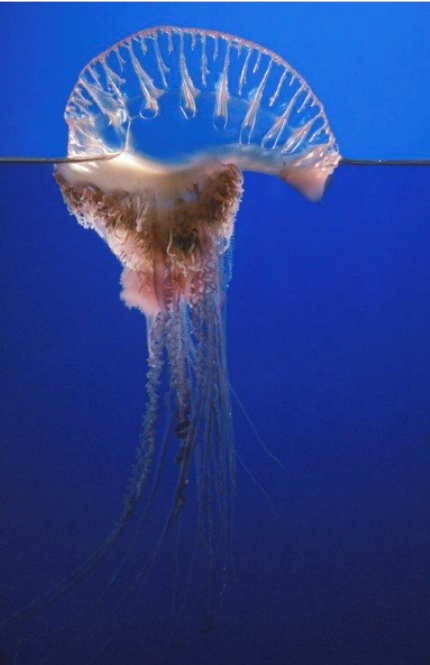  |
| Platyhelminthes | Bilateral symmetry, acoelomate, dorsoventrally flattened, parasitic/free-living | Taenia, Planaria |  |
| Annelida | Bilateral, coelomate, segmented body, closed circulatory system | Earthworm, Leech, Hirudinaria |  |
| Arthropoda | Segmented body, exoskeleton of chitin, jointed appendages | Cockroach, Scorpion, Crab |  |
| Mollusca | Soft, unsegmented body, usually with shell, coelomate | Pila, Octopus, Lamellidens, Loligo | 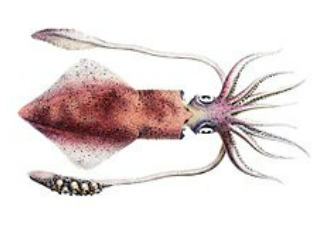 |
| Echinodermata | Radial symmetry in adults, water vascular system, spiny skin | Starfish, Sea Urchin, Cucumaria |  |
🦴 2) Chordates (up to Classes level)
Salient Features:
- Presence of notochord at some stage.
- Dorsal hollow nerve cord present.
- Pharyngeal gill slits at some stage of life.
- Post-anal tail present at least during embryonic development.
- Closed circulatory system (except some lower chordates).
Major Classes of Chordates:
| Class | Salient Features | Examples | Images |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pisces | Aquatic vertebrates with gills, scales, fins, cold-blooded, mostly oviparous | Labeo, Catla |  |
| Amphibia | Moist skin, lungs present, tetrapod, metamorphosis from larva to adult | Frog, Salamander |  |
| Reptilia | Dry scaly skin, lungs, amniotic eggs, ectothermic | Cobra, Crocodile |  |
| Aves | Feathers, forelimbs modified as wings, warm-blooded, amniotic eggs | Crow, Pigeon |  |
| Mammalia | Hair/fur, mammary glands, warm-blooded, internal fertilization | Human, Dog, Bat | 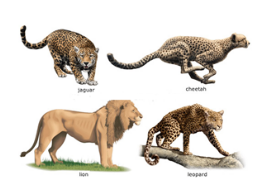 |
📌 Quick Recap
Non-chordates: No notochord, diverse body plans & symmetry, examples Porifera to Echinodermata.
Chordates: Notochord present, dorsal nerve cord, post-anal tail, examples Agnatha to Mammalia.
Classification based on symmetry, coelom type, skeleton type, habitat, and reproduction.

