NEET Biology - Unit 8- Health and Disease- Study Notes - New Syllabus
NEET Biology – Unit 8- Health and Disease- Study Notes – New Syllabus
Key Concepts:
- Health and Disease; Pathogens; parasites causing human diseases (Malaria, Filariasis, Ascariasis. Typhoid, Pneumonia, common cold, amoebiasis, ring worm, dengue, chikungunya); Basic concepts of immunology-vaccines; Cancer, HIV and AIDS; Adolescence, drug and alcohol abuse.Tobacco abuse
Health and Disease
🌟 What is Health?
Health is a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being, not merely the absence of disease.
Healthy individuals are productive and resilient.
Factors influencing health:
- Genetic disorders: Inheritable defects passed from parents to children
- Infections: Caused by microorganisms
- Lifestyle: Diet, water quality, exercise, rest, and habits
⚕️ Human Health and Diseases
The human body can repair itself, fight pathogens, and adapt to changing conditions.
Disease: Impairment of normal body functions, often with symptoms.
Symptoms: Body’s reaction to disease; help in diagnosis.
Causes: Genetics, age, nutrition, infections, toxins, lifestyle.
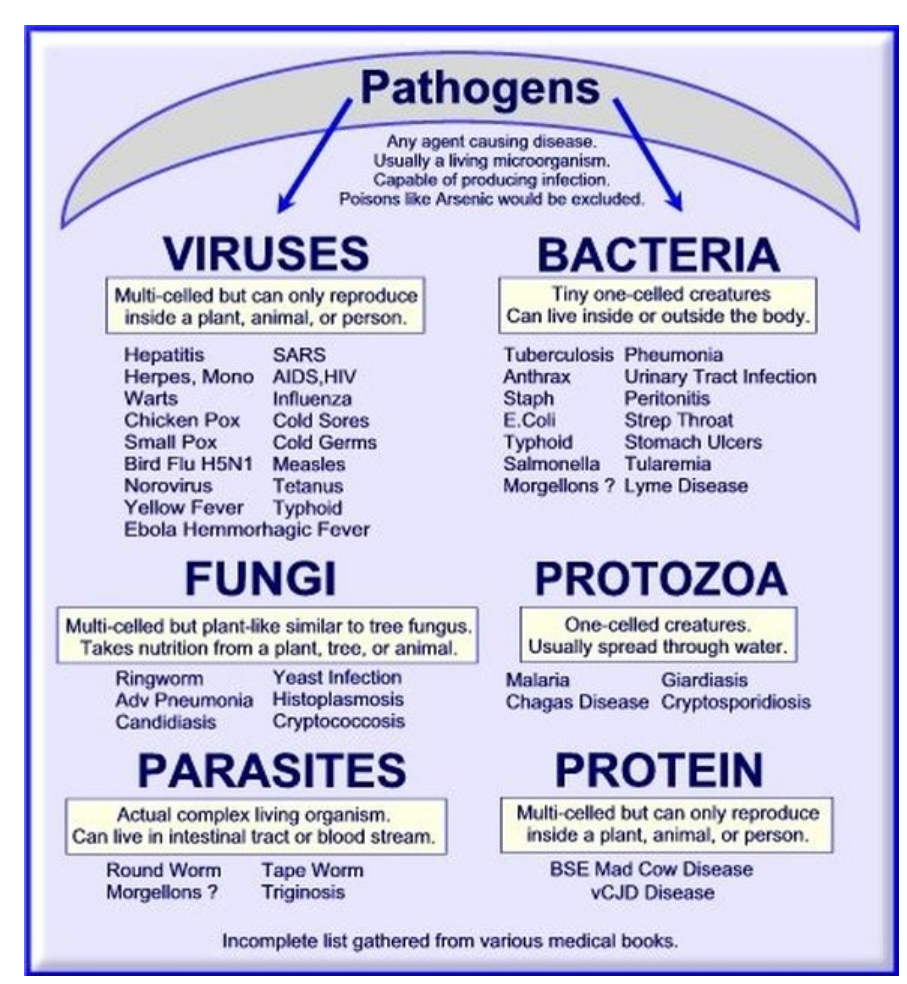
🦠 Pathogens
Pathogens are organisms that cause diseases.
Can be virus, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, or parasites.
Communicable diseases: Spread via air, water, soil, or vectors. Viruses are included even though non-living.
Viruses are included even though non-living.
Bacteria
Unicellular, prokaryotic organisms found in air, water, soil, or human body.
Cause disease by:
- Releasing toxins
- Direct infection
Entry: Cuts, wounds, respiratory or gastrointestinal tracts.
Treatment: Antibiotics (note: drug-resistant strains exist)
Prevention: Hand hygiene, disinfectants, proper food handling
| Disease | Symptoms | Causative Agent |
|---|---|---|
| Syphilis | Mental problems, heart issues, painless chancre, skin rash, blindness | Treponema pallidum |
| Tooth Decay | Pain, rotting teeth | Various bacteria |
| Leprosy | Stuffy nose, skin lesions | Mycobacterium leprae |
| Tetanus | Muscle spasms, jaw stiffness, difficulty swallowing | Clostridium tetani |
| Legionnaire’s | Fever, chills, cough, muscle aches | Legionella pneumophilia |
| Tuberculosis | Fever, cough with blood, weight loss, fatigue | Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
| Plague | Fever, vomiting, blackened tissues | Yersinia pestis |
| Food Poisoning | Diarrhea, vomiting, cramping, fever | Various bacteria |
| Peptic Ulcer | Burning stomach pain | Helicobacter pylori |
Viruses
Non-living particles of DNA or RNA with a protein coat (capsid).
Cannot metabolize or reproduce outside host cells.
Infection process:
- Virus attaches to specific host cell (lock-and-key fit)
- Inserts genetic material → hijacks host machinery
- Produces viral particles → host cell dies → viruses spread
Prevention: Vaccination
| Disease | Symptoms | Causative Agent |
|---|---|---|
| Smallpox | Fever, pustular rash | Variola major |
| Chickenpox | Itchy rashes, fever | Varicella zoster |
| Polio | Fever, sore throat, sometimes paralysis | Poliovirus |
| Warts | Rough, tumor-like growths | Human Papillomavirus |
| Measles | Fever, cough, conjunctivitis, itchy rash | Morbillivirus |
Vaccine: Weak or dead pathogen particles → stimulate immune response
Fungi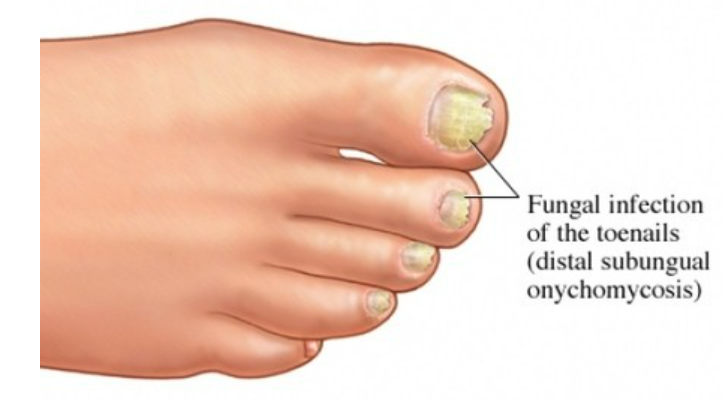
Decomposers, thrive in moist environments.
Infect skin, nails, hair, sometimes lungs.
Examples: Ringworm, athlete’s foot, histoplasmosis, nail fungus, yeast infection.
Treatment: Topical/systemic antifungal medication
Protozoa (Protists)
Unicellular or colonial organisms causing diseases.
Transmission: Vector-borne (mosquito) or contaminated food/water.
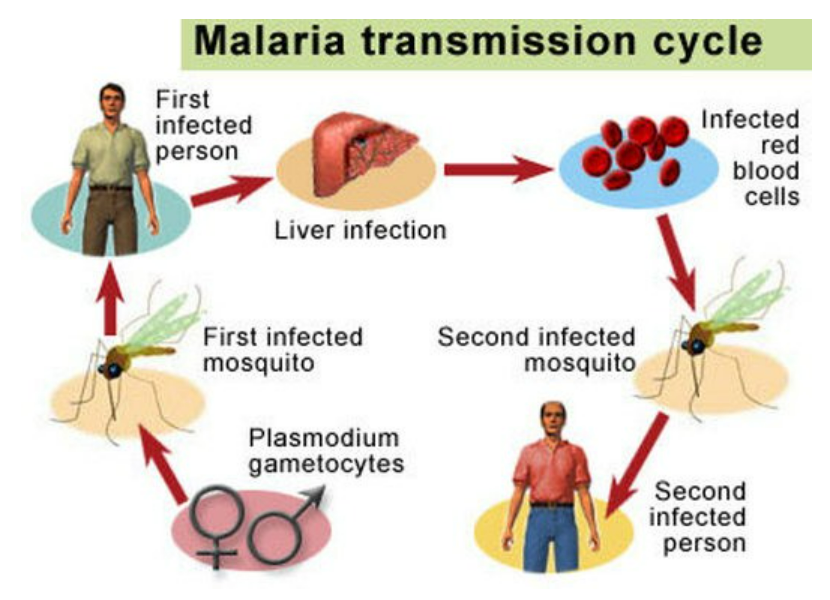
| Disease | Causative Agent | Mode of Transmission |
|---|---|---|
| Malaria | Plasmodium spp. | Mosquito bite |
| Amoebiasis | Entamoeba histolytica | Contaminated food/water |
| African Sleeping Sickness | Trypanosoma | Tsetse fly |
| Chagas Disease | Trypanosoma cruzi | Reduviid bug |
🪱 Parasites
Organisms that live at the expense of a host; usually harm host.
Can be unicellular or multicellular.
Human examples: Mites, lice, roundworms, tapeworms, liver flukes, Wuchereria bancrofti.
Treatment: Specific anti-parasitic drugs/pesticides
☣️ Other Disease-Causing Agents

Toxins: Substances harmful to tissues.
Natural: Bacterial toxins, metabolic by-products (e.g., CO₂)
Man-made: Pesticides, herbicides, arsenic
Toxins may interfere with homeostasis and cause long-term damage
🧬 Genetics and Disease
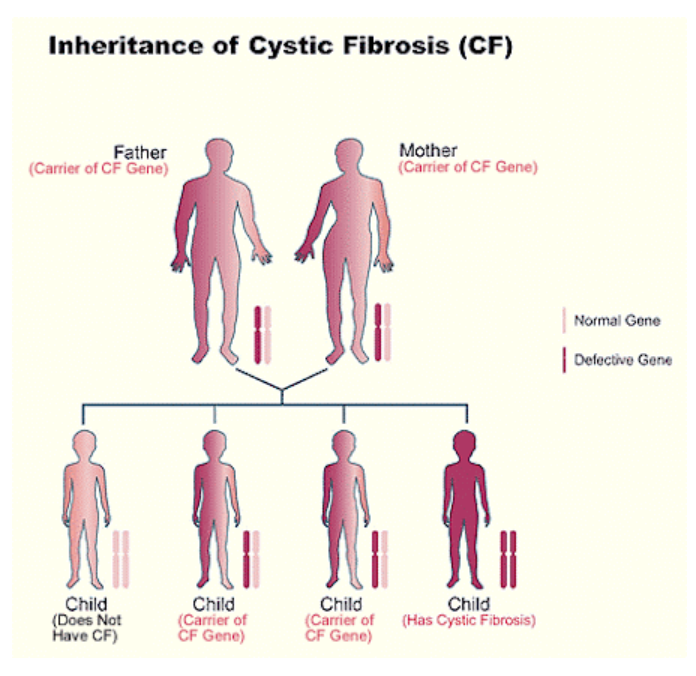
Genes can influence disease susceptibility.
Non-communicable diseases: Cannot spread between individuals.
Examples: Hypertension, diabetes, cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, PKU.
Inheritance + lifestyle determines disease risk
🛡️ Immune Response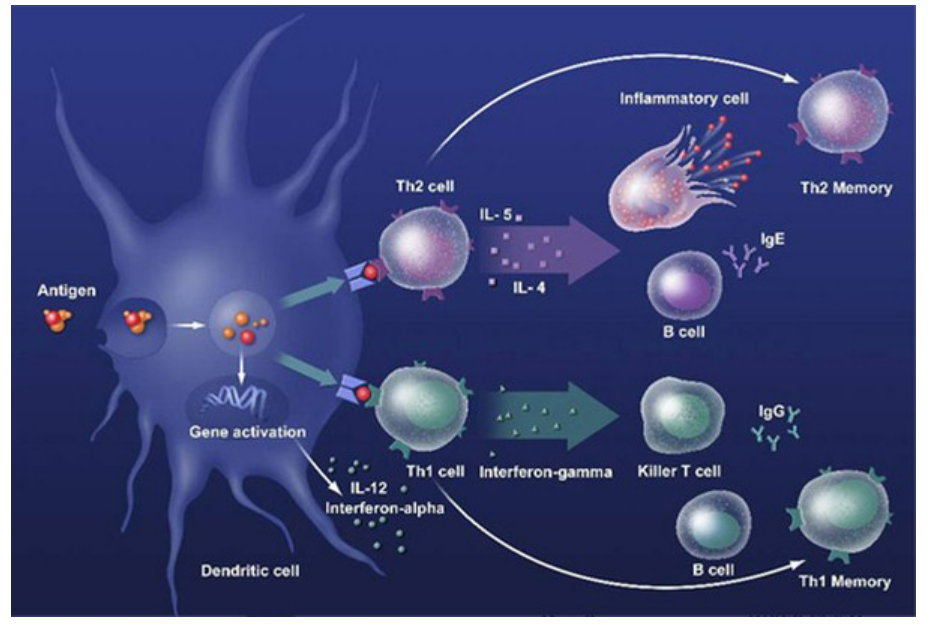
Pathogen enters → via cut, mucous membranes, digestive tract.
Inflammation: Histamine → vasodilation → swelling.
White blood cells attack pathogens.
Antigens detected → immune system activated.
Antibodies produced → neutralize specific antigens.
Immunity:
- Active: Immune system produces antibodies (long-term)
- Passive: Antibodies transferred from mother to child (short-term)
🍏 Nutrition and Health
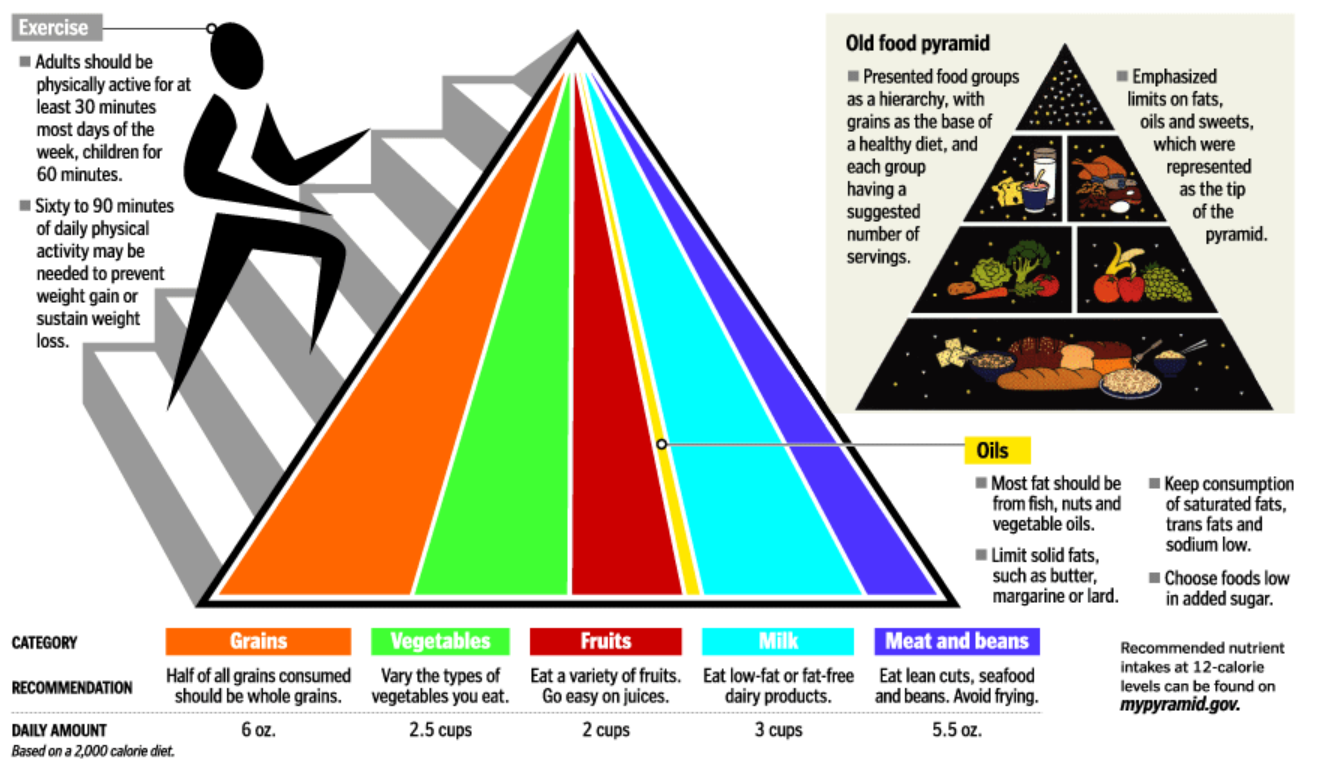
Balanced diet → improves immunity, disease resistance, homeostasis.
Essential nutrients: Carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, water.
Healthy lifestyle:
- Eat variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, low-fat proteins
- Avoid saturated fats, trans fats, artificial sweeteners
- Stay hydrated, exercise, sleep well
- Avoid smoking, alcohol, drugs
- Reduce stress, adopt safe habits

📝 Quick Recap
Health: Complete physical, mental, social well-being
Disease: Impaired function → symptoms
Pathogens: Bacteria, virus, fungi, protozoa, parasites
Prevention: Hygiene, vaccination, safe food/water
Immune Response: Inflammation → WBC → antibodies → immunity
Nutrition: Essential for immune strength and disease resistance
Pathogens
🌱 What are Pathogens?
Pathogens are microorganisms or other life forms that cause disease.
- A pathogen is a specific organism that causes a specific disease.
- Diseases caused by pathogens are often communicable (infectious).
- Transmission can occur through air, water, soil, or animal intermediates.
- Communicable diseases can spread from one person to another via contact or proximity.
Examples of Pathogens: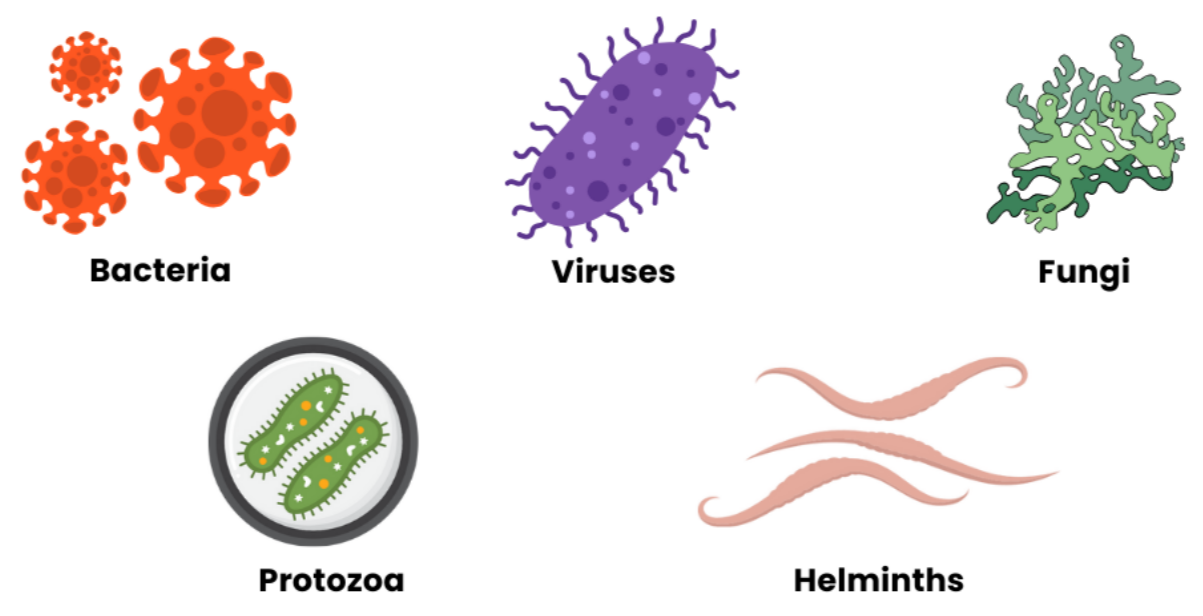
- Viruses – Influenza, HIV, Measles
- Bacteria – Tuberculosis, Cholera, Typhoid
- Protists / Protozoa – Malaria (Plasmodium), Amoebiasis
- Parasites / Helminths – Tapeworms, Roundworms
Note: Viruses are not living microorganisms, but they are considered pathogens because they cause disease.
⚡ Features of Pathogens
- Cause specific diseases in hosts
- Can be transmitted from one host to another
- Multiply within the host to cause infection
- Can be prevented or controlled using vaccines, hygiene, and drugs
🔄 Modes of Transmission of Pathogens
| Mode | Example |
|---|---|
| Airborne | Influenza virus, Tuberculosis bacteria |
| Waterborne | Cholera bacteria, Hepatitis A virus |
| Soil | Tetanus bacteria (Clostridium tetani) |
| Vector-borne | Malaria (mosquito), Dengue (Aedes mosquito) |
| Direct Contact | Common cold, Ringworm (fungal) |
🧾 Quick Recap
Pathogens: Microorganisms or life forms that cause disease
Types: Virus, Bacteria, Protozoa, Parasites/Helminths
Disease Type: Communicable / Infectious
Transmission: Air, water, soil, vectors, direct contact
Viruses: Not living, but still considered pathogens
Parasites and Human Infectious Diseases
🌱 What are Parasites?
Parasites are organisms that live on or inside another host organism, deriving nutrition at the host’s expense.
- Parasites often act as pathogens, causing disease in humans.
- They can be unicellular (protozoa) or multicellular (helminths/worms).
- Some viruses, bacteria, and fungi also act as pathogens, though not technically parasites.
🦠 Major Human Infectious Diseases
| Disease | Pathogen / Parasite | Type | Mode of Transmission | Key Symptoms | Prevention / Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malaria | Plasmodium spp. (Protozoa) | Vector-borne | Bite of female Anopheles mosquito | Fever, chills, sweating, anemia | Mosquito control, nets, antimalarial drugs |
| Filariasis | Wuchereria bancrofti (Helminth) | Vector-borne | Bite of infected mosquito | Swelling of limbs (elephantiasis), fever | Mosquito control, diethylcarbamazine (DEC) |
| Ascariasis | Ascaris lumbricoides (Helminth) | Soil-transmitted | Ingesting eggs from contaminated food/water | Abdominal pain, malnutrition, intestinal blockage | Proper hygiene, sanitation, deworming |
| Typhoid | Salmonella typhi (Bacteria) | Water/food-borne | Contaminated water/food | Fever, headache, abdominal pain, diarrhea | Safe water, vaccination, hygiene |
| Pneumonia | Streptococcus pneumoniae (Bacteria), viruses/fungi | Airborne | Droplets from cough/sneeze | Cough, fever, chest pain, difficulty breathing | Vaccination, hygiene, antibiotics |
| Common Cold | Rhinovirus, Coronavirus | Airborne | Droplets from cough/sneeze | Sneezing, runny nose, mild fever | Hand hygiene, avoid contact with infected person |
| Amoebiasis | Entamoeba histolytica (Protozoa) | Water/food-borne | Contaminated water/food | Diarrhea, abdomi nal pain, dysentery | Safe drinking water, sanitation, hygiene |
| Ringworm | Trichophyton, Microsporum (Fungi) | Contact-borne | Direct skin contact or contaminated surfaces | Itchy, circular skin rashes | Avoid sharing clothes, keep skin dry, antifungal creams |
| Dengue | Dengue virus | Vector-borne | Bite of infected Aedes mosquito | Fever, joint pain, rash, bleeding | Mosquito control, nets, repellents |
| Chikungunya | Chikungunya virus | Vector-borne | Bite of infected Aedes mosquito | Fever, severe joint pain, rash | Mosquito control, nets, repellents |
🔄 Key Points
- Parasites can be protozoa (unicellular) or helminths (worms).
- Vector-borne diseases are transmitted by mosquitoes (Malaria, Dengue, Chikungunya, Filariasis).
- Water/food-borne diseases are caused by ingestion of contaminated water/food (Typhoid, Amoebiasis, Ascariasis).
- Airborne diseases spread through cough, sneeze, or droplets (Pneumonia, Common Cold).
- Fungal infections like Ringworm spread via direct contact or contaminated surfaces.
🧾 Quick Recap
Parasites: Live at the expense of host → cause disease
Vector-borne: Malaria, Dengue, Chikungunya, Filariasis
Water/food-borne: Typhoid, Amoebiasis, Ascariasis
Airborne: Pneumonia, Common Cold
Contact/fungal: Ringworm
Prevention: Hygiene, vaccination, mosquito control, clean water
Basic Concepts of Immunology
🌟 What is Immunology?
Immunology is the study of the immune system, which protects the body from pathogens, toxins, and abnormal cells.
The immune system maintains homeostasis by defending against infections.
Key components:
- White blood cells (leukocytes)
- Antibodies
- Antigens
- Immune organs (bone marrow, thymus, spleen, lymph nodes)
Immunity
Immunity is the ability of an organism to resist infection by pathogens.
Types of Immunity:
| Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Innate / Natural Immunity | Present from birth, non-specific | Skin, mucus, phagocytosis by macrophages |
| Adaptive / Acquired Immunity | Developed after exposure, specific | Antibodies against measles virus |
Adaptive Immunity Subtypes: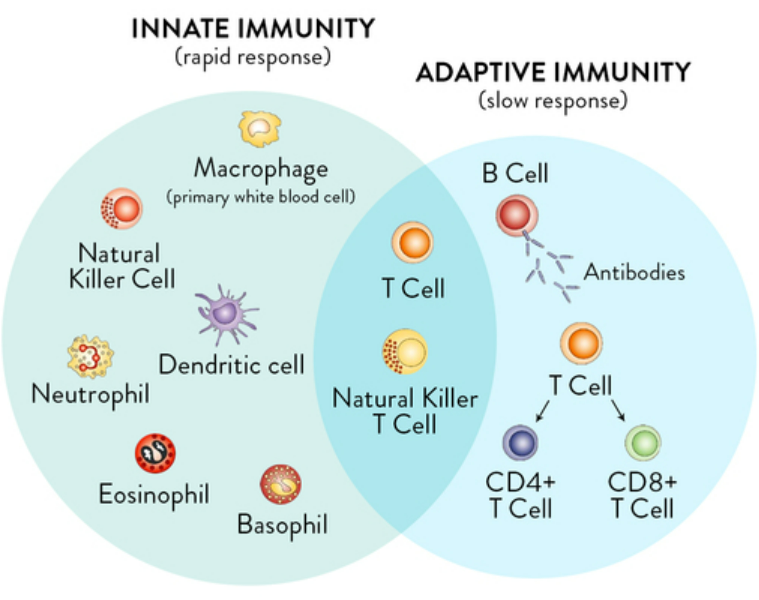
Humoral Immunity
- Mediated by B lymphocytes
- Produces antibodies (immunoglobulins) in response to antigens
- Example: Immunity against bacteria like Streptococcus
Cell-Mediated Immunity
- Mediated by T lymphocytes
- Destroys virus-infected or abnormal cells
- Example: Killing of TB-infected cells
🧬 Antigens and Antibodies
Antigen: Foreign substance that triggers an immune response (protein, polysaccharide, toxin).
Antibody: Protein produced by B-cells that specifically binds to antigen.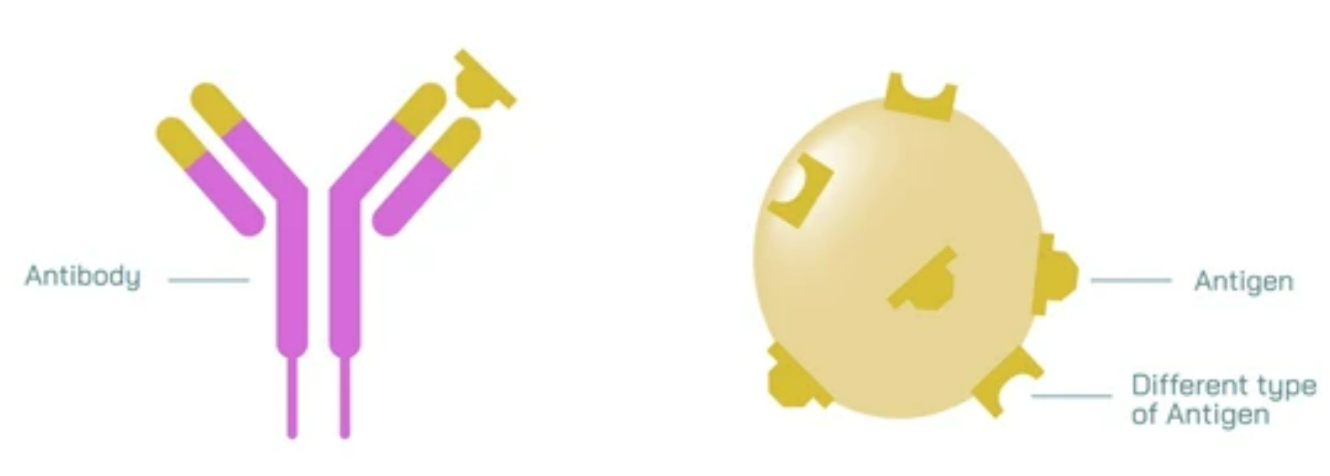
Types of antibodies: IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE, IgD
Mechanism:
- Pathogen enters → antigen recognized
- B-cells activated → plasma cells → antibodies
- Antibodies neutralize pathogen, opsonization, complement activation
- Memory B-cells formed → faster response on next exposure
🦠 Vaccines
A vaccine is a preparation of weakened, killed, or parts of pathogens that stimulates the immune system without causing disease.
Types of Vaccines:
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Live attenuated | Weakened form of pathogen | Measles, MMR, Oral Polio |
| Inactivated / Killed | Dead pathogen | IPV, Rabies |
| Subunit / Recombinant | Only antigenic parts used | Hepatitis B, HPV |
| Toxoid | Inactivated toxin | Tetanus, Diphtheria |
| mRNA vaccines | mRNA coding for pathogen protein | COVID-19 (Pfizer, Moderna) |
| DNA vaccines | Plasmid DNA coding antigen | Experimental vaccines |
💉 Principles of Vaccination
- Introduce antigen without causing disease
- Stimulate primary immune response → antibody production
- Formation of memory cells → long-term immunity
- Boosters strengthen immune response
Examples of Vaccination Programs:
- BCG: Tuberculosis
- Polio vaccine: OPV/IPV
- MMR: Measles, Mumps, Rubella
- DPT: Diphtheria, Pertussis, Tetanus
- Hepatitis B
🔹 Passive and Active Immunity
| Type | How it occurs | Duration | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active Immunity | Exposure to antigen (natural infection or vaccine) | Long-term | Measles infection, vaccination |
| Passive Immunity | Transfer of antibodies | Short-term | Maternal IgG (placenta), IgA (breast milk) |
📝 Quick Recap
Immunology: Study of defense against pathogens
Immunity: Innate (non-specific) and Adaptive (specific)
Adaptive: Humoral (B-cells, antibodies) and Cell-mediated (T-cells)
Antigen triggers response; Antibody neutralizes pathogen
Vaccines: Weakened, killed, or part of pathogen
Passive immunity: Immediate, short-term
Active immunity: Long-term after infection or vaccination
Cancer, HIV and AIDS
🔹 Cancer
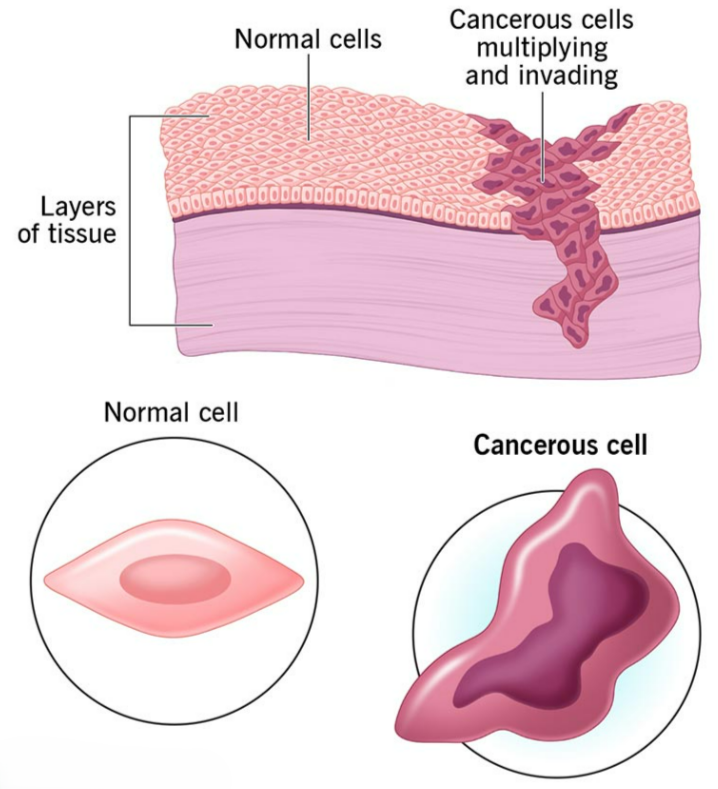
Cancer is the uncontrolled division of abnormal cells in the body, which can invade nearby tissues or spread to distant parts (metastasis).
Causes of Cancer:
- Genetic mutations – changes in DNA (proto-oncogenes → oncogenes)
- Carcinogens – chemical, physical, or biological agents
- Chemical: Tobacco, pesticides
- Physical: X-rays, UV radiation
- Biological: Oncogenic viruses (HPV, EBV)
- Lifestyle factors – poor diet, alcohol, smoking, obesity
Characteristics of Cancer Cells:
| Feature | Normal Cell | Cancer Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Division | Controlled | Uncontrolled |
| Growth | Limited | Unlimited |
| Contact Inhibition | Present | Absent |
| Differentiation | Normal | Often undifferentiated |
| Apoptosis | Occurs | Avoided |
Types of Cancer:
| Type | Tissue of Origin | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Carcinoma | Epithelial cells | Lung, breast cancer |
| Sarcoma | Connective tissue | Bone, muscle |
| Leukemia | Blood cells | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| Lymphoma | Lymphatic system | Hodgkin’s lymphoma |
| Melanoma | Pigment cells | Skin melanoma |
Treatments:
- Surgery: Removal of tumor
- Radiation therapy: Kill cancer cells using high-energy rays
- Chemotherapy: Drugs to destroy rapidly dividing cells
- Immunotherapy: Boost body’s immune system to fight cancer
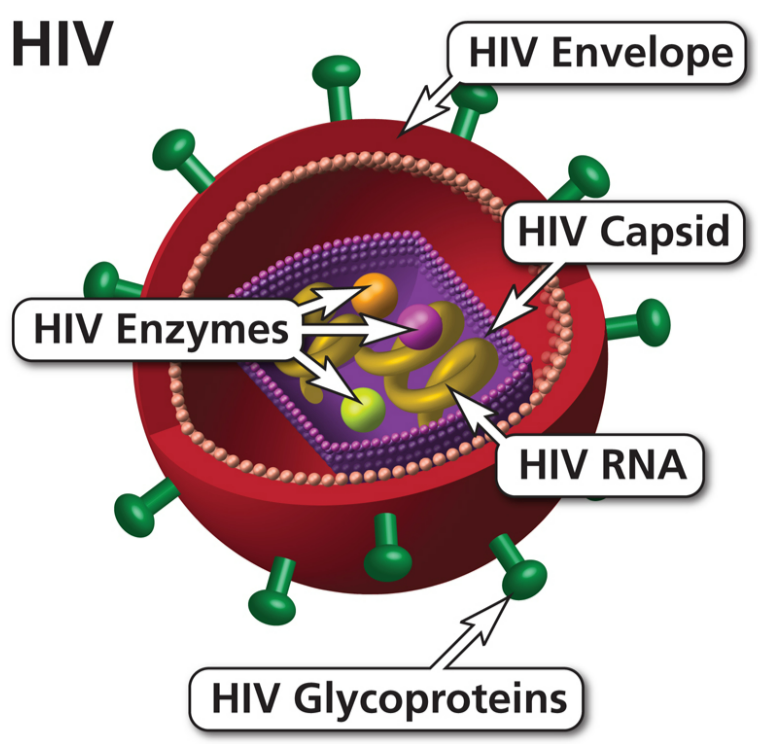
🔹 HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)
HIV is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system, specifically CD4+ T-lymphocytes, weakening the body’s ability to fight infections.
Structure of HIV:
- Enveloped RNA virus

- Contains reverse transcriptase enzyme
- Has surface glycoproteins gp120 and gp41 for attachment to host cells
Transmission:
- Unprotected sexual contact
- Sharing of infected needles
- From mother to child (pregnancy, childbirth, breastfeeding)
- Blood transfusion with infected blood
Life Cycle of HIV:
- Virus binds to CD4 receptor on T-helper cells
- Fusion and entry into host cell
- Reverse transcription of RNA → DNA
- Integration of viral DNA into host genome
- Production of new viral particles
- Budding and release to infect more cells
🔹 AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome)
AIDS is the advanced stage of HIV infection, characterized by severe immune suppression and susceptibility to opportunistic infections.
Symptoms:
- Persistent fever and fatigue
- Weight loss
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Diarrhea
- Opportunistic infections (e.g., tuberculosis, pneumonia, candidiasis)
Opportunistic Infections:
| Infection | Causative Agent | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Tuberculosis | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Lung infection |
| Pneumocystis pneumonia | Pneumocystis jirovecii | Severe respiratory disease |
| Kaposi’s sarcoma | Human herpesvirus 8 | Skin tumor |
| Candidiasis | Candida albicans | Oral/throat infection |
Treatment:
- Antiretroviral Therapy (ART): Combination of drugs to suppress HIV replication
- No complete cure, but ART increases life expectancy and reduces transmission
Prevention:
- Safe sexual practices (condoms)
- Screening of blood before transfusion
- Avoid sharing needles
- Mother-to-child transmission prevention (ART during pregnancy)
📝 Quick Recap
Cancer: Uncontrolled cell growth → tumor formation, metastasis
Causes: Genetic mutations, carcinogens, lifestyle
HIV: Retrovirus attacking CD4+ T-cells → immunodeficiency
AIDS: Advanced HIV → opportunistic infections, immune failure
Prevention: Safe practices, vaccines (HPV for cervical cancer), ART for HIV
Adolescence, Drug and Alcohol Abuse, Tobacco Abuse
🔹 Adolescence
What is Adolescence?
A transitional period between childhood and adulthood.
Begins around 10–12 years and continues till 18–19 years.
Characterized by rapid physical, emotional, hormonal, and social changes.
Key Features:
- Puberty begins because of increased hormonal secretion.
- Development of secondary sexual characters.
- Emotional sensitivity, mood swings, curiosity, self-identity formation.
- Cognitive development: logical thinking, decision making, social understanding.
Problems Faced During Adolescence:
- Peer pressure and risk-taking behavior.
- Stress about academics, body image, relationships.
- Curiosity about drugs, alcohol, and sexual activities.
- Hormone-driven emotional changes.
Why Adolescents are Vulnerable:
- Strong desire to be accepted by peers.
- Lack of experience in decision-making.
- Easily influenced by media and surroundings.
- Feeling of independence and experimentation.
🔹 Drug Abuse
What is Drug Abuse?
Use of psychoactive substances for non-medical purposes that alter brain function and harm physical/mental health.
Common Drugs Misused:
- Cannabinoids – from Cannabis sativa (ganja, charas).
- Cocaine – obtained from Erythroxylum coca.
- Opioids – morphine, heroin, brown sugar.
- Hallucinogens – LSD.
- Depressants – barbiturates, benzodiazepines.
Why Adolescents Use Drugs:
- Peer pressure
- Curiosity
- Stress relief
- Escape from emotional problems
- Easy availability
- Media influence
Effects of Drug Abuse:
- Poor academic performance
- Aggression, mood swings, anxiety
- Damage to liver, kidneys, heart, brain
- Loss of appetite, weight loss
- Dependence and addiction
- Increased risk of accidents, violence
- Withdrawal symptoms when stopped
Dependence and Addiction:
- Dependence: Body requires the drug to feel “normal”.
- Addiction: Compulsive drug-seeking behavior despite harmful effects.
Prevention Strategies:
- Awareness at school and community level
- Strong family support and communication
- Healthy peer groups
- Early identification of stress, anxiety, depression
- Professional counseling
🔹 Alcohol Abuse
What is Alcohol Abuse?
Excessive or regular consumption of alcohol that affects health and behavior.
Why Adolescents Start Alcohol:
- Peer influence
- Family environment (parental drinking)
- Curiosity
- Media glamorization
Effects of Alcohol on Health:
- Loss of coordination and judgement
- Liver damage (fatty liver, cirrhosis)
- Gastric ulcers
- Impaired memory and brain function
- Risk of accidents
- Withdrawal symptoms (sweating, tremors, anxiety)
Long-term Consequences:
- Addiction (Alcoholism)
- Organ failure
- Social and family problems
- Increased risk of violence
🔹 Tobacco Abuse
What is Tobacco Abuse?
Using tobacco in smoking or chewing forms.
Contains nicotine, a highly addictive substance.
Types of Tobacco Use:
- Cigarettes
- Cigars
- Bidis
- Chewing tobacco
- Gutkha, pan masala
Harmful Substances Present:
- Nicotine (addictive)
- Tar (carcinogenic)
- Carbon monoxide
- Benzene
- Formaldehyde
- Nitrosamines
Effects of Tobacco on Health:
- Decreased lung function
- Chronic bronchitis, emphysema
- Lung cancer
- Oral cancer, throat cancer
- Heart disease (blocks arteries)
- Reduced stamina and immunity
- Pregnancy complications in women
Passive Smoking:
Inhalation of smoke by a non-smoker.
Causes asthma, respiratory infections, heart issues.
Why Adolescents Use Tobacco:
- Peer pressure
- Stress
- Misconception that it “relieves tension”
- Easy access
Prevention and Control:
- Education on harmful effects
- Avoiding smokers and high-risk places
- Strong anti-tobacco campaigns
- Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT)
- Counseling and support groups
🧾 Summary Table
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Adolescence | Rapid physical, emotional, hormonal changes |
| Drug Abuse | Cocaine, opioids, cannabinoids, LSD; causes dependence and health damage |
| Alcohol Abuse | Impairs judgement, damages liver and brain |
| Tobacco Abuse | Nicotine addiction; lung cancer, heart disease |
| Prevention | Awareness, family support, counseling |
📘 Quick Recap
Adolescence is the phase of growth + hormonal + emotional changes.
Drug abuse involves psychoactive substances causing dependence and addiction.
Alcohol affects liver, brain, coordination, leading to long-term health issues.
Tobacco contains nicotine and carcinogens, causing cancer and heart diseases.
Prevention requires awareness, strong family bonding, counseling, and healthy lifestyle choices.