IIT JEE Main Maths -Unit 8 -Integral as an antiderivative- Exam Style Questions- New Syllabus
Question
Let \( f : \mathbb{R} \to \mathbb{R} \) be a twice differentiable function such that \( f(x+y) = f(x)f(y) \) for all \( x, y \in \mathbb{R} \). If \( f'(0) = 4a \) and \( f”(x) – 3a f'(x) – f(x) = 0 \), \( a > 0 \), then the area of the region \( R = \{(x,y) \mid 0 \le y \le f(ax),\ 0 \le x \le 2\} \) is:
(1) \( e^2 – 1 \)
(2) \( e^4 + 1 \)
(3) \( e^4 – 1 \)
(4) \( e^2 + 1 \)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Since \( f(x+y) = f(x)f(y) \), we have \( f(x) = e^{\lambda x} \). Given \( f'(0) = \lambda = 4a \), so \( f(x) = e^{4ax} \).
From \( f”(x) – 3a f'(x) – f(x) = 0 \), we get \( \lambda^2 – 3a\lambda – 1 = 0 \).
Substituting \( \lambda = 4a \), we have \( 16a^2 – 12a^2 – 1 = 0 \Rightarrow 4a^2 = 1 \Rightarrow a = \frac{1}{2} \).
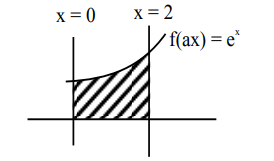
Then \( f(ax) = e^{x} \).
The required area is: $ \text{Area} = \int_{0}^{2} e^{x} \, dx = e^2 – 1 $
Hence, the correct answer is (1) \( e^2 – 1 \).
